Maths Long Term Plan Year 6
advertisement
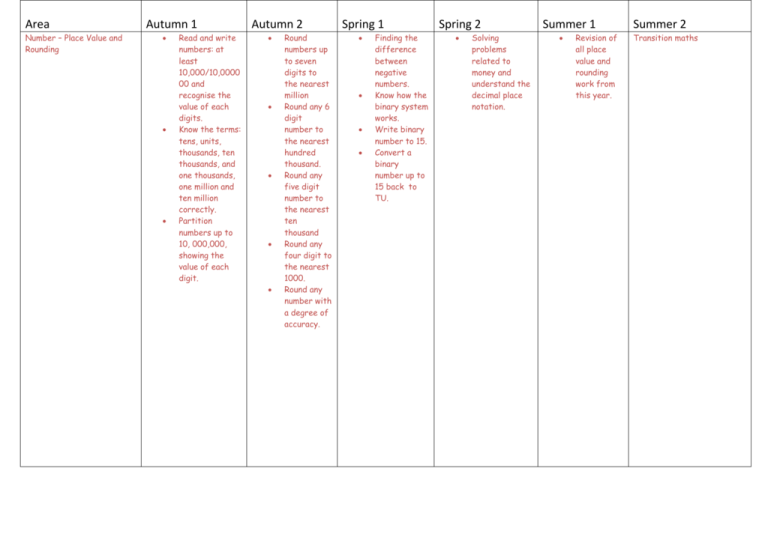
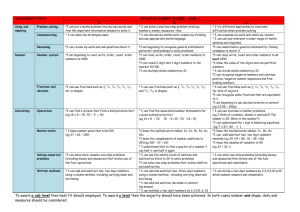
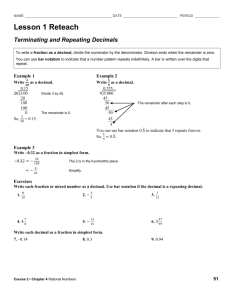
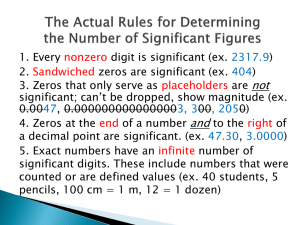
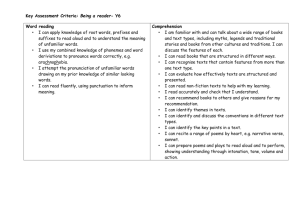
Area Number – Place Value and Rounding Autumn 1 Read and write numbers: at least 10,000/10,0000 00 and recognise the value of each digits. Know the terms: tens, units, thousands, ten thousands, and one thousands, one million and ten million correctly. Partition numbers up to 10, 000,000, showing the value of each digit. Autumn 2 Round numbers up to seven digits to the nearest million Round any 6 digit number to the nearest hundred thousand. Round any five digit number to the nearest ten thousand Round any four digit to the nearest 1000. Round any number with a degree of accuracy. Spring 1 Finding the difference between negative numbers. Know how the binary system works. Write binary number to 15. Convert a binary number up to 15 back to TU. Spring 2 Solving problems related to money and understand the decimal place notation. Summer 1 Revision of all place value and rounding work from this year. Summer 2 Transition maths Number – Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division Revise standard addition method Estimate the answer to any given addition involving 2 2 digit numbers to the nearest 10, 3 digit numbers to the nearest 10 and 100. Carry out combined operations involving the four operations correctly. Revise the subtraction method up to 4 digits by 4 digits and decimals. Solve word problems involving large numbers. Perform mental calculations Revise multiplicatio n of HTU and ThHTU Multiply 4 digit numbers by 2 digit number using our standard written method. Estimate answers of multiplicatio n. Divide numbers up to 4 digits by 2 digits with remainder. Divide numbers and round up to whole numbers. Use estimation to check answers. Divide whole numbers and express Add together 2 negative numbers Know what happens when you subtract one negative number from another negative. Use estimation to check answers. Solve word problems involving large numbers. Perform mental calculations Perform mental calculations which require at least two operations, e.g. addition and multiplication Perform mental calculation which require at lea st two different operations. Use estimation to check answers. Solve word problems involving large numbers. Perform mental calculations with large numbers Perform mental calculations which require at least two operations, e.g. addition and multiplication Use estimation to check answers. Solve word problem involving large number. Revision of all operation work. Perform mental calculations with large numbers Perform mental calculations which require at least two operations, e.g. addition and multiplicatio n Solve word problems with addition, subtraction, multiplicatio n and Transition maths. Perform mental calculations which require at least two operations, e.g. addition and multiplication Solve word problems with addition, subtraction, multiplication and division with numbers up to 10,000,000. the remainder as a fraction and decimal. Use estimation to check answers Know the term BODMAS Solve word problem involving large number. Perform mental calculations division with numbers up to 10,000,000. Fractions Finding fractions of shapes, numbers and quantities. Add and subtract fractions with the same denominator. Know that 1/10 =01. Know that ¼ = 0.25 Know that ¾ = 0.75 Find equivalent fractions. Work out common denominator s. Turn mixed number into an improper fraction. Know all decimal equivalent fractions for fractional values where the denominator is 3,4,56,8 or 10. Work out a common denominator for a pair of fractions with different denominators. Add fraction with different denominators. Subtract fraction with different denominators. Multiply a whole number and a fraction. Turn mixed fractions into improper fractions. Give the answer to a multiplication of a fraction in its simplest form. Divide a proper fraction by a whole number. Revision of all fraction work. Transition maths Decimals Know the value of each digit as a fraction up to 3 decimal places. Adding and subtracting decimals to 2 decimal places. Know the value of each digit as a fraction up to 3 decimal places. Adding and subtracting decimals to 2 decimal places. Percentages Recognise 50% as a half Recognise 25% as a quarter. Recognise 75% as ¾. Recognise 10% as a tenth of the original value. Know that to find 1 % you divide by 100. Know that to find 10 % you divide by 10. Find 25%, 50%, 75% solve problem. Solve problems with simple percentages . Multiply and divide decimal fractions by 2 decimal places Know when multiplying a decimal by 10 it moves one place to the right, by 100 2 places, by 1000 3 places. Know that when dividing a decimal by 10 it moves it moves one place to the left, by 100 2 places to the left etc. Find 10%, 20%, 30% etc.. – solve problems. Know all the decimal equivalent fraction for fractional values where the denominator is 3,4,5,6,8, or 10. Consolidation of all decimal work Know the value of each digit as a fraction up to 3 decimal places. Revision of all decimal work. Transition maths Find a percentage of any given value. Know that to find 1 % you divide by 100. Know that to find 10 % you divide by 10. Find 25%, 50%, 75% - solve problem. Solve problems with simple percentages. Revision of all percentage work. Transition work Ratio and proportion Understand the term ratio. Recognise the symbol associated with ratio. Know what is meant by 1:2 Algebra To write known rules algebraically. Work out equations involving missing amounts. Continue a number sequence involving positive and negative number. To continue a linear number sequence involving positive and negative numbers Use division to work out fractional values, decimal values and percentages of ratio. Use ratio in defining certain shapes. Know how to reduce the ratio into its lowest form. Write rules algebraically for known relationships like p + 4s. Complete linear sequence involving decimals. Work out calculations when given the value of 2 letters. Complete linear sequence involving fraction. Revision of ratio and proportion. Transition work. Revision of algebra Transition maths Properties of shape/ Position and direction and angles Classify all names and properties of 2d/3d shapes. Describe the properties of a cube, cuboid, sphere, prism, and pyramid. Point out parallel in 3d shapes Identify lines of symmetry in 3d shapes. Describe a right angle and parallel/perpen dicular. Describe a square and oblong in terms of their properties. Know the properties of rectangles such as parallelogram. Trapezium and rhombus. Know what the net of a cube looks like Create the net of a cube Know what the net of an oblong is like Know what the net of a prism is like. Create a prism using knowledge of what the net looks like. Know what the net for a square based pyramid is like and create one. Classify triangle in terms of properties, knowing about their angles. Know that Know that a quadrilateral has 360 degrees, work out angles of quadrilaterals Translate shapes. Given 2 angles of a triangle to know what the third is. Given 3 angles of a quadrilateral and to know what the forth is. Reflect given shapes. Illustrate and name the parts of a circle, including radius, diameter and circumference. Find coordinates; identify the points in each part of the quadrant. Create shapes follow pairs of numbers one the grid. Construct shapes into different quadrants. Know missing angles for parallelogram, rhombus, and trapezium from working out the angles opposite. Revision of shapes. Transition maths. Know that the line across the centre of a circle is known as the diameter. Know that the distance from the centre to the arc of the circle is the radius. Know that distance around the outside of a circle is the circumference. the total of a triangle is 180 degrees. Recognise that 90 degrees is a corner angle and can recognise that 40 degrees is half and can estimate an angle greater or smaller than 45 degrees. Draw a triangle given size and angle sizes. Use a protractor to measure angles. Measures Work out areas and perimeters of regular/irr egular shapes. Draw a number of squares with the same perimeter. Add and subtract positive and negative integers for measures such as temperatu re and money. Convert large number of mass capacity and length. Convert large number of mass capacity and length. Recognise when it is necessary to use the formulae for area and volume of shapes. Calculate areas of cubes and cuboids. Convert large number of mass capacity and length. Use decimal notation to 3 d.p. to solve calculatio ns with measures. Revision of all measures work Transition maths Data Draw read and interpret line graphs to solve problems. Numeracy Long Term Plan Year 6 Mrs L Shaw Understand and interpret mean, mode, median and range. Use language associated with probability such as certain etc. Work on probability problems using the terms learnt. Revision Transition maths core/modified set