Insects - Newfield Central Schools
advertisement

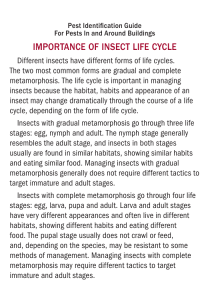
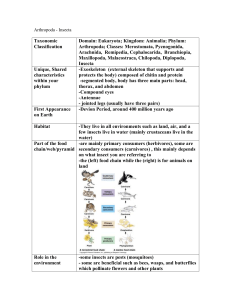
Insect Domain Vocabulary habitats, n. The natural homes or environments of plants and animals Example: Desert habitats are home to plants and animals that can survive without regular rainfall. Variation(s): habitat host, n. A plant or animal on which, or in which, another organism lives Example: The milkweed plant is a host for the Monarch butterfly. Variation(s): hosts insects, n. Small animals with six legs and three main body parts Example: Mackenzie likes all kinds of insects, especially butterflies. Variation(s): insect social, adj. Living together in organized communities Example: The social honeybees worked all through the night to take care of the queen bee. Variation(s): none solitary, adj. Living alone or in pairs Example: The solitary fly circled the food-covered table alone before landing on my ham sandwich. abdomen, n. The end part of an insect’s body; the body segment that contains the digestive and reproductive structures Example: The abdomen is the largest body part of most insects. Variation(s): abdomens antennae, n. Sensory appendages, or feelers, on the heads of insects Example: The mosquito’s feathery antennae provide it with a highly developed sense of smell. Variation(s): antenna exoskeletons, n. The stiff body coverings of insects, providing support and protection; skeletons on the outside of the body Example: The thick exoskeletons on beetles protect them from being squashed by larger animals. Variation(s): exoskeleton microscopic, adj. Refers to something that is too small to be seen without the aid of a microscope; very small Example: Tiny microscopic bugs live in the pond behind my house, but they are too small for me to see with my eyes alone. Variation(s): none thorax, n. The middle part of an insect’s body between the head and the abdomen; the body segment that contains the heart and the leg attachments Example: Joshua’s favorite dragonflies have a bright green thorax. larva, n. The immature stage of an insect’s complete metamorphosis, between egg and pupa; insect larva do not resemble the adult insect Example: A butterfly egg turns into a larva known as a caterpillar. Variation(s): larvae metamorphosis, n. The process of change, taking place in two or more distinct stages, in the life of an insect Example: Tadpoles develop into frogs during a process of change known as metamorphosis. Variation(s): metamorphoses molt, v. To shed old feathers, hair, skin, or shells, making way for new growth Example: As it grows, a snake will molt, leaving behind the skin it sheds. Variation(s): molts, molted, molting nymph, n. The immature stage of an insect that does not undergo a complete metamorphosis, between egg and adult; the nymph resembles the adult insect Example: The nymph stage of a cicada can last for years before the cicada emerges as a fullydeveloped, winged adult. Variation(s): nymphs progression, n. A continuous and connected series of actions or events Example: The progression of the phases of the moon from new moon to full moon and back to new moon again follows a predictable pattern. Variation(s): progressions pupa, n. The inactive, immature stage of an insect, between larva and adult Example: The moth larva spun its cocoon, a safe place to stay during its transformative pupa stage. colonies, n. Communities of animals living close together, often sharing a physically connected structure like a beehive Example: Scientists are concerned over the disappearance of some bee colonies. Variation(s): colony cooperate, v. To work together for the good of everyone or everything involved Example: Students cooperate with their teachers and their classmates so that everyone can learn. Variation(s): cooperates, cooperated, cooperating drones, n. Male bees in social bee colonies whose job is to fertilize the queen Example: The queen bee left her hive to mate with the drones before returning to the hive to lay her eggs. Variation(s): drone pollen, n. A fine, powdery substance produced within flowers, its transport from flower to flower being necessary for new flower seeds to grow Example: Many fruit trees depend upon the honeybee to transport pollen to the tree so it will produce fruit. Variation(s): none societies, n. Groups of people or animals living together in organized communities Example: Social ants live in societies called colonies. aggressive, adj. Forceful or ready to attack Example: The mother bear became aggressive, wanting to protect her cubs. Variation(s): none chambers, n. Empty, enclosed spaces; rooms Example: Bees develop in separate chambers in a hive. Variation(s): chamber destructive, adj. Causing a large amount of damage or harm Example: The destructive puppy chewed through the new sofa. Variation(s): none emit, v. To send out or give off Example: Fire alarms emit a very loud noise so people will hear them easily. Variation(s): emits, emitted, emitting nurseries, n. Places to breed and care for young animals and plants Example: Worker ants feed baby ants in separate chambers, or nurseries. bioluminescence, n. Light given off by some plants and animals, such as fireflies, caused by a biochemical reaction Example: The night sky was filled with the bioluminescence of dancing fireflies. Variation(s): none forelegs, n. The front legs of a four-legged animal Example: Since kangaroos hop, they use their forelegs more for balancing than they do for walking. Variation(s): foreleg lanterns, n. Lights that have a covering, usually made of glass Example: The campers all carried lanterns as they went from tent to tent. Variation(s): lantern transparent, adj. A clear material that allows objects behind it to be seen Example: The bird bumped into the transparent window, thinking that it was flying onto the porch. Variation(s): none tymbals, n. Thin skins that help produce sounds in some insects Example: Vibrating tymbals are responsible for the cicadas’ piercing sounds on a summer’s night. adapt, v. Change in order to adjust to new conditions Example: Children must adapt to new classrooms every year. Variation(s): adapts, adapted, adapting armor, n. Protective layer or shell of some plants and animals Example: A turtle’s protective shell provides heavy armor against its predators. Variation(s): none beetles, n. Insects known for their tough outer coverings, including hardened forewings Example: Beetles have the ability to adapt to nearly every environment on Earth, both land and water. Variation(s): beetle elytra, n. Hardened front wings of beetles that cover and protect the back wings ExampIe: The beetle’s elytra are not used for flight, but provide excellent protection for its delicate back wings. Variation(s): elytron mimicry, n. The close resemblance of one plant or animal to another, often serving a protective purpose Example: A wasp beetle’s mimicry, which makes it look like a stinging wasp, keeps its predators away. entomologist, n. One who studies insects Example: The entomologist traveled to rainforests worldwide to compare the kinds of insects living in each one. Variation(s): entomologists extinction, n. The dying out of a species until it no longer exists Example: Some scientists believe that the extinction of the dinosaurs occurred many millions of years ago. Variation(s): none foe, n. Enemy or opponent Example: The Athenians and Spartans of ancient Greece fought together against their foe, the Persian Empire. Variation(s): foes pesticides, n. Substances used to destroy insects that threaten the life or health of plants and animals Example: Some people prefer to eat organic plants because they are not sprayed with chemical pesticides. Variation(s): pesticide pollinators, n. Insects that carry pollen from one plant to another, a necessary act for new plant growth Example: Bees and butterflies are both important pollinators, collecting pollen from one plant and depositing it on another.