Crop and Pest Management AGRI 3001 – Entomology Module
advertisement

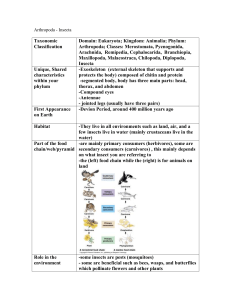
Pests and Crop Protection CFAN 3001 – Entomology Module Lecture: MW 8:30 – 9:20; Lab: F 8:30 – 10:25 Lecture: 132 Plant Growth; Lab: Hodson Hall 485 Web page, www.ipmworld.umn.edu Dr. Bill Hutchison, 219 Hodson Hall: 612-624-1299, hutch002@umn.edu Amy Morey (TA, Lab Section, 485 Hodson Hall), morey041@umn.edu Science - The art of deriving sufficient conclusions from insufficient data. (Study of the Universe) Biology – Study of Life Zoology – Study of Animals Entomology – Study of Insects Entomology: a pest-based discipline Insects are the most prevalent taxa in our environment Attract human attention when they occur in LARGE numbers What causes change in abundance, dispersion, and diversity? (Insect Ecology) Identification • Pest Management – first step is to know what insect(s) are present • What stage is easiest to control • How many are too many • What tactics can be used – Prevention – Therapeutic (insecticide) – Impact of control on the agroecosystem Classification • Systematics - study of the classification of related organisms based on ancestral characters (Phylogenetics) • Taxonomy is the science of naming organisms Species Name • All organisms have a Latin “binomial”. The Genus and species • Examples: Leptinotarsa decimlineata Say Latin Names • Latin names are descriptive • Used worldwide Leptinotarsa decimlineata Say • Key to the scientific literature Classification Hierarchy • • • • • • Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species • Kings play chess on Friday’s generally speaking WHAT MAKES AN ANIMAL AN INSECT? Principle Features of Phylum Arthropoda and Class Insecta 1. SEGMENTED BODY - with three principal body regions a. Head (fusion of 5 or 6 six segments into a functional unit – Tagmosis) b. Thorax (locomotor tagma) c. Abdomen (digestive and reproductive organs) 2. Exoskeleton comprised of CHITIN 3.TRACHEAL system for gas exchange 4. One pair of ANTENNAE Class Insecta • Order classification primarily based on – structure of: • wings • mouthparts • metamorphosis Major events in Insect Evolution 1.Development of wings – in Carboniferous (Pterygota: Paleoptera) 2.Wing Flexion – (Pterygota: Neoptera) 3.Metamorphosis a. Simple – (Exopterygota) 1) Orthopteroid Orders 2) Hemipteroid Orders (sucking mouthparts) b. Complex – Holometabolous (Endopterygota) 1) Bees, wasps, ants 2) Beetles 3) Flies 4) Butterflies/moths See lab manual for details Insect Diversity Why are insects so abundant? Small size - takes little food to mature to reproductive age Ability to fly - escape enemies, adverse environmental conditions Unique body - waxy layer, strong exoskeleton, jointed legs High reproductive capacity - e.g. CPB female can lay 3000 eggs Metamorphosis - adults and young use different resources Facts you should know about insects World-wide entomologists have described about 1 million species, systematists estimate between 2 and 10 million There are about 100,000 species described in the U.S. 15,000 - 20,000 insect species in Minnesota Q: How many (%) are pests? < 1% are injurious - ca. 3,000 species worldwide 600 pest insects in the United States Insect Abundance and Diversity 1. Insects live in every habitable place on earth except ocean floor 2. Chief consumers of plants on the planet 3. Major predators of plant eaters 4. Key role in decay of organic matter 5. Key role as food for other organisms a) In some human cultures insects comprise 10% of the diet 6. Nearly 1 million described species a) From from 2 to 10 million yet to be described. b) Outnumber humans by nearly 200 million to 1 How Do Insects Cause Damage? Injury to crops DIRECT or INDIRECT injury Injury to Humans and animals Blood feeding - disease transmission Internal & External Parasites Annoyance Injecting toxic substances Destroy stored products and possessions Pest - A living organism that occurs in such numbers and places so that it is inconvenient to human health, economics, comfort, or aesthetics. Beneficial - An insect which favorably affects humans with the result of its actions or products. Insect Losses in Agriculture Preharvest 13.0% Postharvest 3.5% TOTAL 16.5% Annual loss in the U.S. about $7 billion annually to insects IPM - Integrated Pest Management IPM - an ecologically based pest control strategy that maintains pest species below the economic injury level by use of the most appropriate and environmentally sound methods available. Pest Control The application of technology, in the context of biological knowledge, to achieve satisfactory reduction of pest numbers or effects. Control Strategies 1. Natural 2. Biological 3. Cultural 4. Legislative and Regulatory 5. Mechanical and Physical 6. Genetic 7. Chemical What is a Land-Grant Institution? 1. Established by an act of Congress in 1862, known as the Morrill Act. a. “Donating Public Lands to the several States and Territories which may provide Colleges for the Benefit of Agriculture and Mechanic Arts. …..an amount of public land …. equal to thirty thousand acres for each senator and representative in Congress.” b. Land sales funded establishment of the University of Minnesota. c. Mandate was to: “…teach agriculture, military tactics, and the mechanical arts as well as classical studies”. 2. Hatch Act – 1887, Established the Agricultural Experiment Stations 3. Extension Service – Smith-Lever Act, 1914, “In order to aid in diffusing among the people of the United States useful and practical information on subjects relating to agriculture…..”