Timeline, Prehistory 8 000 – 7 500 BC. First settlements in South
advertisement

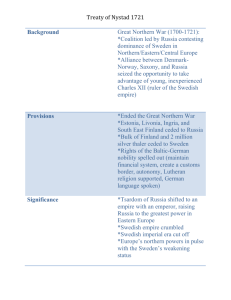
Timeline, Prehistory 8 000 – 7 500 BC. First settlements in South-west / South-east Finland. At this point the edge of the ice (Ice age) was at the Salpausselkä ridge (where there is now f.ex. the city Lahti) 7 500 – 1 500 BC Stone age 6 800 BC Fishing nets (found in the Antrea marshland, Karelia) 5 170 – 1 130 BC Moose head of soapstone/steatite (found from Huittinen, length 15 cm) 5 790 BC Wooden moose head (found from Lehtojärvi Lake in Rovaniemi, length 37 cm) 4 200 – 2 800 BC Develpoment of ceramics 4 000 BC Fenno Ugrian protolanguage 3 000 BC – 500 AD Rock paintings 2 500 BC Population growth, most likely due to Indo-european immigration 2 000 BC The Sami language and the Finnish protolanguage diverge 1 500 – 150 BC Bronze age. Use of bronze spreading to South and West Finland 1 000 BC Immigration of German tribes 500 BC – 1 050 AD Iron age. Use of iron spreads to South and West Finland BC ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- AD 800-1 000 Era of the Vikings 1 050 – 1 150 / 1 300 Era of the Crusades PRE-HISTORIC ROCK ART Concentrated in area fron the city of Lappeenranta to the the Kymijoki river and the lake Saimaa area F.ex. Astuvansalmi in Ristiina, Vitträsk in Kirkkonummi, Värikallio in Suomussalmi, Hossa in Kuusamo Situated on high up rising stone walls. Composed in North-east – South-west direction. Pictures 9 – 80 cm high. Red colour fron iron oxide Subjects: elk, human figures (70%), boat, birds, human hand, geometric forms Pictures do not represent a specific time, place or event, but rather evoke the eternal presence of the spirit world. Related to hunting magic and fertility cult. Photographs, http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ibBvsYm-YyU Shamanism Šaman (Siberian languages) - šramanā (ancient India, veda-language) Finnish and Sami pre-Christian religion (as well as that of the other Finno Ugric peoples) have a clear shamanistic character Hunter-gatherers believe in spiritual realms above and below the world of daily life Altered states of consciousness. The visual, aural and somatic experiences in those states give rise to perceptions of an alternative reality People with special powers and skills, the shamans, are believed to have access to this alternative reality Shamans are believed to contact spirits and supernatural entities, heal the sick, control the movement and lives of animals, change the weather. This is believed to be facilitated by supernatural entities f.ex. animal-helpers and spirits (bear, elk, birds, snake etc.) Timeline, Medieval era 800-1000 Era of the Vikings 1000 Catholic and orthodox monks are circulating in Häme-area 11 th Century first traces of Christianity in pictures on coins and jewelry 1000 – 1100 Immigration of the Swedih speaking population 1030 Olof, the king of Norway, makes a trip to South Finland 1040 In South Finland deceased are being buried in a Christian manner 1042 Vladimir, the Duke of Novgorod makes a crusade to Häme 1050 – 1150 / 1300 Era of the Crusades 1120 The Swedes and the Russians divide Finland. The border divides Häme area in two parts, west belonging to Sweden east to Russia 1154 Arabic geographer al-Idrisi publishes a map in Palermo Sicily, he mentions Turku and Häme and uses word “Tbst” ...”wealthy and richly populated area with cattle-farmers” 1155 First crusade to Finland by King Erik and Bishop Henrik, era of the Swedish rule begins 1156 Farmer named ‘Lalli’ kills Bishop Henrik with an axe on the ice of Köyliöjärvi lake 1180 Karelians and Estonians sail to Sigtuna which is the ancient capitol of Sweden and kill the Archbishop of Sweden 1194 Famine year in Finland 1228 Pope allows bishop of Häme to take over all old non-Christian places of worship, sacrificial spots and sacred groves 1250 Construction of the Hämeenlinna castle begins 1280 Severe famine year in Finland 1290s Turku gets city rights, it has been the biggest city on Finland from early 13th Century when a monastery dedicated to Saint Birgitta was founded there 1293 City of Viipuri is founded 14th Century First roads in the Finnish mainland: Great Coastal Road between the cities of Turku and Viipuri, Bull Road of Häme between the cities of Turku and Hämeenlinna 1300 First divine service in the new Dome of Turku 1323 Pähkinäsaari peace divides Finland between catholic Sweden and orthodox Russia, traces of history can still be seen between Western Finland and Eastern so called Old Finland 1346 Porvoo gets city rights …Did you know?…In 1365 there were four cities in Finland: Turku, Porvoo, Viipuri and Ulvila. Most part of salesmen in these cities were of Germa origin… …Did you know? By the beginning of the 15th Century there were 22 stone churches on the Finish mainland, plus Turku Dome and Hattula church: 13 in South-west Finland, 4 in Uusimaa, 4 in Satakunta and 1 in Häme. On Ahvenanmaa islands there were 8 churches built of stone 1442 Rauma gets city rights 1450 A thirty-year period of cold weather and starvation in Finland begins 1520s King Gustaf Vasa begins the protestant reformation, era of Catholic Church ends in Sweden and Finland PRE-URBAN ERA 800-the 12th Century Trade centres, Viking trade routes, Birk-harbours (Birka, Sweden, destroyed in 957). Gotland, Sigtuna and Uppsala. Ancient citadels, f.ex. Hämeenlinna Varikkoniemi MEDIEVAL ERA, 1155-1524 First crusade to Finland. Bishop Henrik, 1155 Roman catholic church and religion Hansa, trade union between the cities around the Baltic sea * Sarcophagus of Bishop Henrik, 1415-1420, Nousiainen church, black limestone and brass, made in Flanders Stone churches (built of natural stone (grey stone or red granite) and brick) - By the 15th Century there were 23 stone churches in the mainland of Finland. - Only Turku dome was comparable with the cathedrals in central European cities. - On the Ahvenanmaa (Åland) islands there were 8 stone churches a) Ahvenanmaa, f.ex. Jomala church, Finnström church, Lemland church b) Uusimaa and Häme , f.ex. Porvoo church, Lohja church, Inkoo church, Hattula church of the Holy cross, 1370-1420 c) Turku dome, 1276-1546 (inaugurated 1300) Wall paintings - Al secco –technique earth and mineral pigments on plaster * Maaria church (Turku), c. 1450, wall and ceiling paintings in “primitive” style * Hattula, Church of the Holy Cross, 1510-1522 * Espoo church, early 16th Century, scenes of the devil doing his deeds * Inkoo church, 1510-1522, Dance macabre Retables and painted wooden statues * The Altar of the Pyhä Barbara in Kalanti Church, Master Francke, Hamburg 1415, The National museum - Madonna from the church of Korppoo, 1200-1225, height 70 cm, walnut - Madonna from the church of Nousiainen, early 14th Century, made by a from Gotland Sweden - Madonna from the church of Hattula, 1320-1350, height 85 cm, painted birch, made by a Finnish master (“master from Lieto”) Castles - Turku castle, 1280-1588/1706 - Häme castle (Hämeenlinna), late 13th Century – 16th Century - Olavinlinna castle (Savonlinna), 1475 – the 18th Century Timeline, from the protestant reformation until the era of Sweden a Great Power 1548 New testament of the Bible is published in Finnish language, translation by Mikael Agricola 1550 The city of Helsinki is founded by Gustaf Vasa, the king of Sweden 1590 ‘Nuijasota’ a revolt of farmers 1594-1632 King Gustaf II Adolf rules Sweden and the country becomes one of Europe’s superpowers …Did you know? By the end of the 16th Century there were 2800 inhabitants in Turku, 1700 in Viipuri, 800 in Pori, 650 in Rauma and 560 in Helsinki 1600-1603 Severe famine years in Finland, due to exceptionally cold climate 17 th century is being called ‘the minor ice age’ in Europe 1618 The 30 years war begins in Europe, Finland fights in South-Eastern Europe under the flag of Sweden 1633 Severe famine year in Finland 1640 Academy of Turku, first university in Finland, is founded by general governor of Finland Per Brahe 1640-1650 City of Helsinki is transferred to its present location from the Vanhakaupungin lahti bay area 1658 Peace of Roskilde, the area reigned by Sweden is at its largest 1664 Severe famine year in Finland 1671 Severe famine year in Finland 1688 Severe famine year in Finland 1695-1697 During the last severe famine years in 17th Century Finland, every third citizen dies in starvation. Year 1696 is a severe famine year throughout Europe …Did you know? There were 11 cities in Finland in 1614 and 30 cities by the end of 1660s VASA-ERA, 1524-1617 Reformation 1524, Finland and Sweden turn into lutheran protestant countries Stockholm ans the Hansa cities compete over power in trade in the Baltic Sea region Fortifications f.ex. in Viipuri, Hämeenlinna, Savonlinna, Turku THE RENAISSANCE ERA OF DUKE JUHANA Turku castle 1556-1563 SWEDEN AS SUPER POWER, 1617-1700 Strong king and central power 30-year’s war 1618-1648 Painter’s guilds, 1620-luku: Jochim Neiman (1600-1672), Diedrich Möllerum (1642-1702), Elias Brenner (1647-1716) Manor houses - Kuitia, Fleming, 1480S - Sjundby, Hornit (Hästesko), 1560S - Louhisaari, Fleming, 1655 - Pernaja Sarvilaks, Creutz, 1670Grave monuments and chapels - Monuments were made by order in the workshops of North German and Baltic cities - Torsten Stålhandske and Kristiina Horn, Turku dome, 1654 * Åke Tott and Kristina Brahe, grave monument, Turku dome, 1678 Votive paintings - Votive painting of the Speitz family, Sääksmäki church, 1619, 90x105 Timeline, 18th century, from the Swedish era to the era as an Autonomous Grand Duchy of Russia 1700-1721 Great Northern War, 50 000 men from Finland are ordered to serve in the Swedish army (total population of Finland after the famine years in 1690’s is approx. 350 000 – 40 000 inhabitants) 1704-1709 A period of famine years in Finland 1713-1721 Period of Great Hatred, a time of great horror and controversies during which Russians occupy whole Finland. During the first year ruling upper class and priests escape to Sweden with their belongings, farmers hide in Finnish forests. Those caught by Russians (20 000 people) are taken to Russia to build St Petersburg or to slavery, most of them never return 1721 Peace of Uusikaupunki, border between Finland and Russia is drawn almost to its present line as eastern regions of Finland (Viipuri, Sortavala, Käkisalmi) stay as part of Russia. Those who escaped to Sweden during ‘Great Hatred’ are returning to Finland 1735 Swedish Art Academy is founded in Stockholm…from the late 18th Century first Finnish architects and painters start studying in this Royal Academy of Sweden 1742-1743 Period of Little Hatred, a time of controversies but not at all as bad as during the previous one (‘Great Hatred’) 1743 Peace of Turku, more Finnish regions is joined into Russia. New border between Finland and Russia goes along Kymijoki. Cities like Savonlinna, Lappeenranta and Hamina are now parts of Russia 1762 Severe famine year in Finland 1770 Henrik Gabriel Porthan founds the Aurora Society in order to educate and spread knowledge of cultural history 1772 Gustaf III takes rule over Sweden 1788 Sweden in a war with Russia 1796-1797 Henrik Gabriel Porthan gives first lectures in Finland about antique archaeology and art history 1801 Severe famine year in Finland 1802 Painter Alexander Lauréus is sent to Art Academy in Stockholm after a fund raising campaign …Did You know? There were 1 million inhabitants in Finland in 1811 and 1,8 million inhabitants by the end of 1860s. In Helsinki there were 8000 inhabitants in 1820s and by the end of 19th Century there were 50 000 inhabitants 1806-1809 War of Finland, at the end Finland is joined into Russia 29.3.1809 Emperor of Russia, Alexander I declares in the city of Porvoo that Finland gets special rights and large autonomy as The Autonomous Grand Duchy of Russia 1809 Gustav Wilhelm Finnberg is sent to Art Academy in Stockholm after a fund raising campaign 18TH CENTURY Viapori - Sveaborg - Suomenlinna Fortress, 1748-1791 - Augustin Ehrensvärd (1748-1772) - Built on six islands in front of Helsinki harbor Manor houses - Fagervik, 1762-1773, Christoffer Friedrich Schröder - Mustio, 1783-1791, Erik Palmstedt - Viipuri Monrepos manor and park Merchant’s city houses * Lebell merchant’s house, 1762, Kristiinankaupunki Hand-painted wallpapers * Jakkarila manor, 1764, painter Johan Bromander, The National museum - Hand-painted wallpapers in the Mustio (Svartå) manor Wooden churces and wallpaintings - F.ex. Margareta Capsia (1682-1759), Mikael Toppelius (1738-1821), Emanuel Granberg (1754-noin 1787) - Haukipudas church, 1774-1777 - Kiiminki church, 1779, painter Mikael Toppelius * Paltaniemi church , 1778-1781, painter Emanuel Granberg Public buildings - Vaasa court house, Carl Fredrik Adelcrantz - Hämeenlinna church, Louis Jean Desprez, 1795-1798 - The Academy of Turku, Carl Christoffer Gjörwell and Charles Bassi - Halikon Joensuun kartano, Carl Christoffer Gjörwell and Charles Bassi Portrait & decorative painting with still-lifes and landscapes Isak Wacklin (1720-1758) * Portrait of Dorothea Maria Losch, 1755, 71,5x56,5, Ateneum Nils Schillmark (1745-1804) * Portrait of Mrs Heckford, 1757, 76,5x63,5, Ateneum * Strawberry girl (Ulrika Charlotta Armfelt), 1782, Ateneum * Still-life with a glass and caraffe, a silver goblet, a pewter candlestick and chalk pipes, 1795-1797, 64x111,5, Ateneum * Heinola, Jyränkö stream, 1787, 58x105, Ateneum Gustav Wilhelm Finnberg (1784-1833) * Portrait of Anton af Tengström, 1826, 84x66,5, Ateneum