Urinary Catheter Removal Protocol (draft)
advertisement

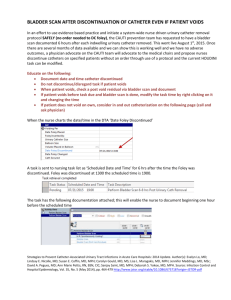
Urinary Catheter Removal Protocol Notice: the "Foley Catheter" order MUST have " Urinary Catheter Removal Protocol option chosen as YES to follow the guidelines below (# 1& 2) 1. D/C urinary catheter within one day following insertion unless patient meets one of the following criteria: Need for accurate I and O in critically ill patients or patient undergoing aggressive diuresis Relief of urinary tract obstruction/urinary retention or patient has a suprapubic catheter Patients in whom catheter has been inserted for a urologic or pelvic surgery Management of urinary incontinence in patients with stage 3 or 4 pressure ulcers or wounds Promote comfort in terminally ill patients or patients who have significant pain when moved Patient with an epidural Post-op patient per physician order Foley placed by urologist due to technical difficulty 2. If patient meets one of the above criteria, assess daily to determine if urinary catheter is still necessary. Post Urinary Catheter Removal Care Document time of removal and amount of urine in bag on I&O Encourage po fluid intake (unless contraindicated) Scheduled toileting q 2-3 hours to provide opportunity to urinate—OOB or BSC if possible Goal is not to exceed bladder volume >500 ml If patient spontaneously voids within 4 hours ≥ 250 ml, continue to measure urinary output X 24 hours. If no void or voids < 250 ml within 4 hours: Perform bladder scan every 4 hours until spontaneous voiding resumes. If bladder volume ≥ 350 ml, perform straight cath. If bladder volume <350, rescan in 2 hours if patient has not voided; cath if volume >350 ml. If straight cath is required X 2, call MD for further orders Call MD if urinary output < 250 ml over 8 hours If bladder volume < 250 ml and pt voiding continue to monitor I & O Consider alternatives to indwelling catheterization such as condom catheters. Consider patient’s medications for side effects such as urinary retention. Infection Prevention and Epidemiology October, 2010