The Reproductive System: Male Anatomy
advertisement

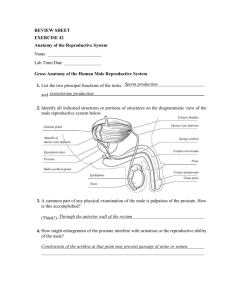
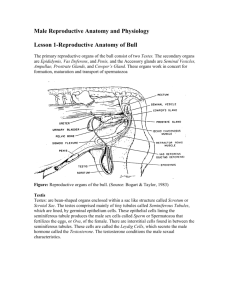
The Reproductive System: Male Anatomy ____________ — primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete ____________ Sperm—male gametes Ova (eggs)—female gametes Male Reproductive System Overview Testes Duct system ____________ Ductus (vas) deferens Urethra Accessory organs Seminal vesicles ____________ Bulbourethral glands External genitalia Penis ____________ 16.1.2 When provided with a model or diagram, identify the organs of the male reproductive system and discuss the general function of each. Testes Olive-sized Coverings of the testes ____________ ____________ —capsule that surrounds each testis, fibrous connective tissue Septa—extensions of the capsule that extend into the testis and divide it into lobules Each lobule contains ____________ ____________ seminiferous tubules Tightly coiled structures Function as ____________ -forming factories Empty sperm into the rete testis (first part of the duct system) Sperm travels through the ____________ to the epididymis Interstitial cells in the seminiferous tubules produce androgens such as ____________ 16.1.5 - Trace the pathway followed by a sperm from the testis to the body exterior. Duct System 16.1.6 - Define erection, ejaculation, and circumcision. Epididymis Ductus (vas) deferens Urethra Epididymis _____________ -shaped, tightly coiled tube Found on the superior part of the testis and along the posterior lateral side 1 Functions to _____________ and ___________ sperm cells (at least 20 days) Expels sperm with the contraction of muscles in the epididymis walls to the _____________ About______ long Ductus Deferens (Vas Deferens) Carries sperm from the epididymis to the _____________ duct Passes through the inguinal canal and over the bladder Moves sperm by _____________ (wave like motion of smooth muscles) _____________ cord—ductus deferens, blood vessels, and nerves in a connective tissue sheath Ends in the ejaculatory duct which unites with the urethra Expanded end is called the _____________ Ejaculation — _____________ muscle in the walls of the ductus deferens create peristaltic waves to squeeze sperm forward Vasectomy cutting of the ductus deferens at the level of the testes to prevent _____________ of sperm Sperm is still produced, but they eventually deteriorate and are _________________ . Urethra Extends from the base of the _____________ bladder to the tip of the penis Carries both urine and sperm ___________ enters from the ejaculatory duct Regions of the urethra Prostatic urethra—surrounded by prostate _____________ urethra—from prostatic urethra to penis Spongy (penile) urethra—runs the length of the _____________ Accessory Organs Seminal vesicles _____________ Bulbourethral glands Seminal Vesicles Located at the _____________ of the bladder Produces a thick, yellowish secretion (_____% of semen) _____________ (sugar) Vitamin C Prostaglandins Other substances that _____________ and activate sperm Prostate Size and shape of a chestnut Encircles the upper part of the _____________ Secretes a _____________ fluid Helps to activate sperm Enters the urethra through several _________ Reputation as a health destroyer Hyertrophy (________________) – affects nearly every elderly male. Difficulty urinating, bladder infections, kidney damage, cancer Bulbourethral Glands Pea-sized gland inferior to the prostate Produces a thick, clear _____________ Cleanses the urethra of _____________ 2 Serves as a lubricant during sexual intercourse 16.1.4 Discuss the composition of semen and name the glands that produce it. Semen Mixture of _____________ and accessory gland secretions Advantages of accessory gland secretions Fructose provides ____________ for sperm cells Alkalinity of semen helps _____________ the acidic environment of vagina Semen inhibits bacterial multiplication Elements of semen enhance sperm motility 2-5mL of semen propelled during ejaculation Contains _____________ million sperm per mL Male infertility Commonly caused by a problem with semen. Sperm count, motility and morphology, semen volume, pH, fructose content 16.1.6 - Define erection, ejaculation, and circumcision. External Genitalia Scrotum Penis Scrotum Divided sac of skin outside the abdomen Maintains testes at 3°C (about ______ºF) lower than normal body temperature to protect sperm viability When it is cold out side the skin will become highly _____________ and pull the testes closer to the body to be able to maintain temperature. Penis Delivers _____________ into the female reproductive tract Regions of the penis Shaft _________ penis (enlarged tip) Prepuce (foreskin) Folded cuff of skin around proximal end Often removed by _____________ External Genitalia Internally there are three areas of _____________ erectile tissue around the urethra Erections occur when this erectile tissue fills with _____________ during sexual excitement 3