The Chemistry of Respiration and Photosynthesis
advertisement

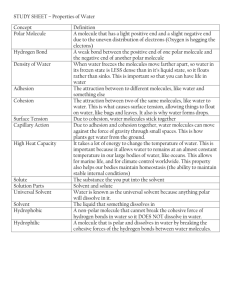
The Chemistry of Respiration and Photosynthesis Introduction: The chemistry of RESPIRATION and PHOTOSYNTHESIS are probably two of the most important concepts in biology. In order to understand many of the processes that take place in living organisms, each student will need to have a complete understanding of the details of these processes. At the end of this laboratory activity, you will be expected to write the equations for combustion, respiration, and photosynthesis. You should be able to list differences and similarities between the equations. Pre-Lab Questions: As you recall from The Chemistry of Combustion, the equation for combustion is: O2 + Fuel H2O + CO2 + Energy (heat and light) Let’s compare this with the cellular respiration process. Organisms, such as animals, require O2 and food. The main food molecule for cells is GLUCOSE. Organism also produce (breath out) CO2 and H2O. You can test this yourself. What happens when you breathe on a cold window? Similar to combustion, organisms also release energy. We, as animals, do not produce light energy, but what other forms of energy do we produce? 1. Write an equation for the process of cellular respiration using the reactants and products described above. 2. Compare the respiration equation you wrote to the combustion equation. How are they similar? How are they different? 3. The process of photosynthesis also has certain reactants and products. The things a plant needs to grow (water, light, CO2) are the reactants of photosynthesis. The products of photosynthesis are the things a plant produces. Plants produce O2 and the basic food molecule of cells (glucose) for both themselves and animals to use. Using this information, write an equation photosynthesis. 4. For photosynthesis to occur, plants need to absorb sunlight. Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll that absorbs the sunlight for a plant. In writing an CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 equation for photosynthesis, chlorophyll will be placed above the reaction arrow. Why do plants need chlorophyll? 5. The interdependences between cellular respiration and photosynthesis can be diagrammed here What do you notice when you compare the reactants of respiration with the products of photosynthesis? C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O 6. What do you notice when you compare the products of respiration with the reactants of photosynthesis? 7. When you compare the respiration equation to the photosynthesis equation, one thing to notice is that one is just the _____________ of the other. Procedure: To further understand how animals can obtain and use the energy stored in the food they eat, and how plants can trap light energy and impart that light energy into food, it will be necessary to study a little basic chemistry. The specific food substances from which animals get their energy is glucose. Glucose has the chemical formula C6H12O6. The best way to learn about a glucose molecule is to build one. BUT DO NOT START TO BUILD ONE UNTIL ACTUALLY INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. Every group will receive a bag of m&ms, white board, and white board marker from the teacher. The different colored m&ms will represent the different atoms that make up glucose (carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen). Each bag should have the color code and number of each m&m color written on it. Check to make sure the information is correct. Carbon should have 6 m&ms, hydrogen should have 12 m&ms, and oxygen should have 18 m&ms. 1. Write down the color and number of m&ms for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. 2. The chemical formula for glucose is C6H12O6. Glucose also has a structural formula. This is what you will be building with your m&ms. Write down the chemical formula for glucose. 3. You will also need to know the structural formula for CO2, H2O, and O2. They are as follows: CO2 H2O O2 Notice that each atom is held together by a COVALENT BOND (the lines drawn between atoms). A covalent bond represents the sharing of electrons between atoms. A single covalent bond shares 2 electrons. How many electrons are shared in a double bond? Different elements have different numbers of covalent bonds they can form: CARBON: 4 bonds OXYGEN: 2 bonds HYDROGEN: 1 bond 4. You will now make glucose. Place your correct colored m&m atoms on half of your whiteboard. Using your marker, draw the covalent bonds holding the atoms together. Start by creating the basic “ring” of 5 C atoms and 1 O atom, as shown below: Add the remaining atoms and draw the covalent bonds between them. Remember to always draw the correct number of covalent bonds. When you are finished, show this glucose molecule to the teacher. Have the teacher initial your paper. SAVE THIS MOLECULE. 5. Using ALL your remaining m&m atoms, construct molecules of O2. Remember O2 contains double bonds. Show the O2 molecules to your teacher and have your teacher initial the paper. How many O 2 molecules have you made? DO NOT BREAK APART MOLECULES UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. 6. You have just created glucose and oxygen. What organisms normally produce glucose and oxygen? 7. What is the name of the process that produces glucose and oxygen? 8. This process occurs in what cell organelle? 9. The number of molecule products of photosynthesis are: _____C6H12O6 + _____O2. 10. Now an animal comes along and inhales the oxygen produced by the plant, and eats the glucose that created the plant’s body. Why does the animal need to eat the plant? 11. To represent what occurs in the animal’s cells, break apart your glucose and oxygen molecules and erase the covalent bonds you have drawn. Using ALL your m&m atoms, create as many CO 2 and H2O molecules as you can. Remember to draw the double bonds between the C and O molecules. What is the name of this process you represented on your whiteboard? (Note that although this process was represented by an animal, this process also occurs in plants.) 12. How many molecules of CO2 did you create? How many molecules of H2O did you create? 13. Breaking apart the bonds of glucose releases energy stored in those bonds. This energy is called chemical energy. This is how both plants AND animals obtain the energy they need for life. What cell organelle breaks down food molecules to release energy? 14. Breaking apart the bonds of glucose and oxygen to reform the bonds of carbon dioxide and water is a chemical reaction. What protein molecule in cells speeds up chemical reactions (acts as a catalyst)? 15. The reactants of respiration are glucose and oxygen. The products are the CO 2 and H2O you just created. Rewrite the equation for respiration using the number using the number of molecules you created. This is called a balanced equation, because the numbers of atoms in the reactants are equal to the numbers of atoms in the products. C6H12O6 + _____O2 + sunlight energy _____CO2 + _____H2O 16. Remember that photosynthesis and respiration are opposite equations. Write a balance equation for photosynthesis. _____CO2 + _____H2O C6H12O6 + _____O2 + chemical energy Post-lab Questions: 1. What is the equation for combustion and how is it similar/different to respiration? 2. In your own words, describe photosynthesis and its purpose for plants. 3. In your own words, describe cellular respiration and its purpose organisms. 4. The products of photosynthesis are the ________________ of respiration. 5. The products of respiration are the _________________ of photosynthesis. 6. What happens to the products of respiration produced by organisms? 7. Write the balanced equation for photosynthesis. What type of energy is required by plants to form glucose molecules? What reactant of photosynthesis provides the carbon molecules in glucose? 8. Write the balanced equation for respiration. What type of energy is released by the breakdown of glucose? What do the carbon molecules in glucose become in the products of respiration? 9. The chlorophyll needed for photosynthesis is found in what organelle? 10. The release of energy from food molecules during cellular respiration happens in what organelle? Name: _____________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: ________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ The Chemistry of Respiration and Photosynthesis Answer Sheet Pre-lab Answers: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Procedure Answer: a. Carbon color: 1 b. Oxygen color: c. Hydrogen color: 2 a. # of electrons: b. # of bonds in Carbon: 3 c. # of bonds in Oxygen: d. # of bonds in Hydrogen: 4 Teacher Initial: _________ Teacher Initial: _________ 5 # of O2 molecules: 6 7 8 a. # of C6H12O6: 9 b. # of O2: 10 11 a. # of CO2: 12 b. # of H2O: 13 14 15 C6H12O6 + _____O2 + sunlight energy _____CO2 + _____H2O 16 _____ O2 + C6H12O6 ______CO2 + ______H2O + Energy Post-Lab Answer Combustion Equation: 1 Comparison: 2 3 4 5 6 Balanced equation: 7 Energy Type: Reactant Molecule: Balanced equation: 8 Energy Type: Product Molecule: 9 10