View
advertisement

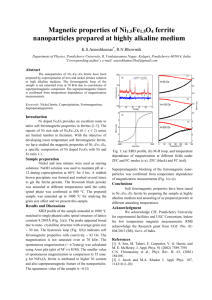
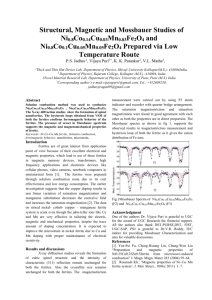
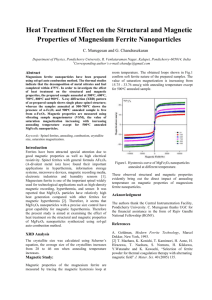
Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Solvothermal Synthesized Ni-Zn Ferrites Nivedita L. Raveendran1, P. Saravanan2, R. T. Rajendrakumar3* 1 Advanced Materials and Devices Laboratory, Department of Physics, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore 46, India. 2 Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory, Hyderabad 500058, India 3 Reader, Department of Nanoscience and Technology, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore 46, India. *Corresponding author’s e-mail:rtrkumar@buc.edu.in, Tel.: +91-9789757888 Nickel-zinc ferrite nanoparticles were prepared by solvothermal technique by varying the precursor molar ratio. The as-prepared and annealed particles were subjected to various characterization techniques. The XRD analysis confirmed the formation of cubic spinel structure; while magnetization measurements demonstrated superparamagnetic behaviour with maximum Ms value of 33.7 emu/g for Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles. Keywords: Ni-Zn ferrite, solvothermal, superparamagnetic, EMI suppression. Introduction Nickel-zinc ferrite with spinel structure is one of the most widely studied materials due to its high versatility in industrial use and its suitability in biomedical fields, high frequency applications and electronic devices for EMI suppression. They are magnetically soft materials and possess high saturation magnetization, low coercivity, high resistivity and low dielectric loss. While the processing of Ni-Zn ferrite nanoparticles was widely investigated by means of many soft-chemical methods, the applicability of solvothermal technique is very less explored. The purpose of the present study is to investigate the effect of this preparation technique on the properties of mixed spinel ferrite for improving its functional properties. Experimental methodology Nickel-zinc ferrite particles (NixZn1-xFe2O4; x = 0.0-1.0) were synthesized by varying the precursor molar ratio of nitrate precursors using solvothermal method with diethylene glycol as the solvent [1]. The precursor mixture solution was sealed in a Teflon lined stainless steel autoclave and kept at 130oC for 20 h. The particles were prepared without the benefit of any surfactants. The synthesized particles were annealed at different temperatures. The as-prepared and annealed ferrite nanoparticles were characterized by XRD, UVvis spectroscopy and VSM. Results The XRD diffraction results confirmed the spinel structure of the as-prepared nanocrystalline ferrites with average crystallite size in the range of 40 – 50 nm, as calculated from the Debye-Scherrer’s formula. From the optical analysis, it was observed that the band gap decreases as the percentage of Nisubstitution increases. The magnetic hysteresis curves obtained at room temperature for the as-prepared samples are shown in Fig. 1. All the curves exhibit negligible coercivity and remanence magnetization at 300K -indicating the presence of superparamagnetic behavior [2]. The Ms values 23.6, 28.7 and 33.7 emu/g were estimated for the nickel-zinc ferrite particles corresponding to the Ni-precursor molar ratio of 0.7, 0.3 and 0.5, respectively and these values are superior than that of those obtained for pure zinc (17.5 emu/g)and nickel ferrites (20.9 emu/g). 40 30 Magnetization (emu/g) Abstract 20 10 0 NiFe2O4 -10 Ni0.7Zn0.3Fe2O4 -20 Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4 Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 -30 ZnFe2O4 -40 -20000 -10000 0 10000 20000 Applied Field (Oe) Fig.1: Room temperature M-H curves NixZn1-xFe2O4 prepared by solvothermal method. for References [1] Wei Yan etal., Materials Science and Engineering B 171 (2010) 144–148 [2] R. Ortega-Zempoalteca et. Al., Phys. Status Solidi A, 1–5 (2014)