Projectile Trajectory CEPA
advertisement

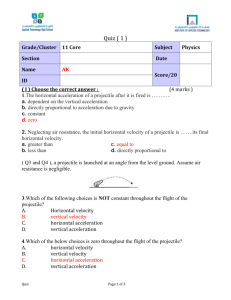
Projectile Trajectory CEPA Purpose: To model landing the human cannon ball in the net while keeping the velocity of the cannon and the distance constant. Description: To better engage the crowd, Emmanual Zacchini of Ringling Brothers and Barnum Bailey circus proposed launching himself at a low angle and then, to dazzle the crowd, a greater angle as Mr. Zacchini launches over the flying trapeze. While liking the act, the ring master was concerned about the liability and asked Mr. Zacchini to model his act first and prove that the calculations would work reliably. Students will measure the time and be given the distance to calculate the velocity of the projectile launcher. They will be given the smaller of two angles of launch. They must calculate the distance away that the net must be placed to catch scale shaped Mr. Zachinni. Next a second launch at the complimentary angle will be completed to dazzle the crowd. Students must prove mathematically what the correct distance should be for the nets placement and then prove it with three actual launches. Students will write up their research in a manner that is clear for others to understand and they will write a conclusion that defends their data. Next Gen Science Standards HS-PS2-1 HS-PS2-4 Analyze data to support the claim that Newton’s second law of motion describes the mathematical relationship among the net force on a macroscopic object, its mass, and its acceleration Use mathematical representations of Newton’s Law of Gravitation and Coulomb’s Law to describe and predict the gravitational forces between objects. From the Massachusetts Frsmeworks 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, work). 1.2 Distinguish between displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. Solve problems involving displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and constant acceleration. 1.3 Create and interpret graphs of 1-dimensional motion, such as position vs. time, distance vs. time, speed vs. time, velocity vs. time, and acceleration vs. time where acceleration is constant. 1.4 Interpret and apply Newton’s three laws of motion. 1.5 Use a free-body force diagram to show forces acting on a system consisting of a pair of interacting objects. For a diagram with only co-linear forces, determine the net force acting on a system and between the objects. 1.6 Distinguish qualitatively between static and kietic friction, and describe their effects on the motion of objects. 1.7 Describe Newton’s law of universal gravitation in terms of the attraction between two objects, their masses, and the distance between them. Materials Provided Launcher, stand, 2 timer gates, 1 timer, net, ball to symbolize Mr. Zacchini, calculator with trig functions Accommodations/ Modifications As identified in either the IEP or 504 plan for a given student. Typical accommodations to include but not limited to; definitions for vocabulary, a formula sheet, and extra time. However students will have no more than 1 extra time period to complete the data collection and calculation. Overview of Task The ringmaster has asked you Mr. Zacchini to liven up your performance. While a low angle trajectory is interesting for the audience to watch, The ringmaster has suggested you being shot over the flying trapeze act while it is in progress. Since setup time for the net takes so long, the ringmaster doesn’t want you to move it between the two different launches. On a scale model you will need to do the calculations to prove where the net should be located with a 20 degree and complimentary angle trajectory and after calculating the velocity you will need to find the apex of the path. Accuracy is critical as Mr. Zacchini’s life depends upon you. Your task requires you to correctly calculate and measure time, distance, velocity, apex height and horizontal distance, then record the data in an organized manner for others to understand. Calculations should be completed to three significant figures. Do not round off. Record time, velocity, horizontal distance, and the apex both calculated and measured where possible. Prove to the trapeze artists that you will safely sail over their heads knowing the maximum height the trapeze artists achieve is 1.5 meters. Product to Hand In 1. Detailed procedure of how you accomplished this exercise. 2. All calculations completes using KUESA 3. Calculate the percent of error between the measured and calculated results with possible areas identified that could be the cause of the error. 4. Write a conclusion that is defended by your data You have three class periods to complete your product for this Projectile Lab. Evaluation Rubric Category 4 3 2 1 Procedure Detailed Detailed procedure identifying the steps needed in the proper order to accomplish this task. Steps are numbered. The correct vocabulary is used Calculations Calculations were performed correctly using KUESA and laid out in the report in a clear logical linear manner. Answers are accurate to three significant figures. Procedure is either not detailed or a step is missing. Steps might not be numbered. Incorrect vocabulary is used at least twice. Calculations were done correctly but KUESA was not used or calculations were not laid out in a logical order. Procedure will not lead to success. Several steps are either missing or incorrect. Vocabulary is either missing or used incorrectly Calculations were not done correctly and the sequence followed by the student is unclear. Measurement Measurements were performed correctly and laid out in the report in a clear logical linear manner. Measurements are reported to three significant figures. Measurements were performed correctly were not laid out in a clear logical linear manner. At least two measurements were not reported to three significant figures. Procedure is missing several steps or the steps are unclear. Incorrect vocabulary is used. Steps might not be numbered. Calculations were not done correctly but are laid out in a clear manner allowing for the reader to determine where the lab technician made their error. KUESA was attempted. Measurements were not done correctly but are laid out in a clear manner allowing for the reader to determine where the lab technician made their error. Measurements were not reported to three significant figures. Conclusion Conclusion includes what was learned about calculating and measuring the Apex Height and Horizontal Projectile Distance. It points to a percent of error of less than 10%. The proper vocabulary is used in the conclusion. Sources for the discrepancies between calculated are identified. Conclusion includes what was learned about calculating and measuring the Apex Height and Horizontal Projectile Distance. It points to a percent of error of less than 13%. The proper vocabulary is mostly used in the conclusion. Sources for the discrepancies between calculated are identified. Conclusion includes what was learned about calculating and measuring the Apex Height and Horizontal Projectile Distance. It points to a percent of error of less than 18%. The proper vocabulary is missing. Sources for the discrepancies between calculated are not identified. Conclusion does not include what was learned about calculating and measuring the Apex Height and Horizontal Projectile Distance. Percent of error is either missing or > 18%. The proper vocabulary is missing. Sources for the discrepancies between calculated are not identified. Measurements were not done correctly and the sequence followed by the student is unclear. Measurements were not reported to three significant figures. Student Score Teacher Score Teacher Notes This is an end of unit summative assessment for projectile motion. Students should be able to complete this with little difficulty as they have read about projectile motion, had several quizzes on projectile motion, taken a written exam, and completed three labs on the subject. The CEPA should be introduced shortly after the start of the unit so students will become familiar with the terminology, and equipment they will need to complete this assessment. Vocabulary: Sine Function- The ratio of the side opposite the angle described to the Hypotenuse Distance- As measured in meters Time- as measured in seconds Velocity- As measured in meters per second Acceleration- This is gravitational acceleration on earth at a rate of 9.8 meters/second2 Trajectory- The path the projectile will travel Projectile- an object that moves through air or space acted on only by gravity (in this case earth’s gravity) air resistance will be ignored in this example. Apex- the maximum height achieved. Theta – The term used in place of an unknown acute angle.