Lecture 1
advertisement

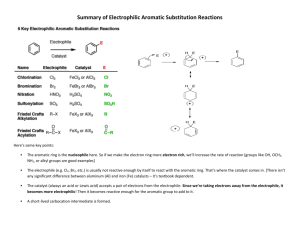
[Year] ORGANIC II TEAM Lecture 1 Clinical 2020 Cairo University 2014/2015 /Clinical2020CU Organic Chemistry II Lecture 1 aromatic compounds اللي هنتكلم فيه عن كذا موضوع أولهمOrganic 2 بسم هللا نبدأ أول محاضرة في منهج how to obtain certain وهنعرف مين دول وبنحضرهم إزاي وبنعمل بيهم تقاعالت إزاي ونتعود على سؤال ); finalعزة قالت هتجيبه في الـ. اللي دcompound Aromatic compounds They are compounds containing one or more benzene or benzene-like ring. وعلى شكلdouble bonds يعني فيهم..دول عبارة عن مركبات فيهم حلقة أو أكتر من البنزين أو حلقات شبه البنزين . بس مش بنزينrings Kekule proved that 1,3,5-cyclohextriene has C6H6 unsaturated formula “triene”, cyclo and is very stable compound. The structure contained a six-membered ring of carbon atoms with alternating single and double bonds. According to Resonance theory: -The actual structure (III) is hybrid between the 2 Kekule structures (I) & (II). -Structures (I) & (II) are imaginary contributes in the actual structure III so they are not present. وشكله حلقة وهو3 double bonds عنده1,3,5-cyclohextriene أثبت إن البنزين شكله بس زيKekule العالم وإن البنزين نظريا..single & double bonds في البنزين طاقتها وطولها بينbonds كمان أثبت إن،مركب ثابت جدا .(III) اللي في شكلPi bonds ( سوا وتتكون حلقة الـII) ( وI) بيتكون من مركب In cyclohextriene: single bond 14 Angstrom, double bond 7 Angstrom. CLINICAL 2020 2 In benzene: intermediate bond 10 Angstrom. Each C—C bond is single in one structure & double in the other C—C bond in benzene intermediate between single and double, and differs from 1,3,5-cyclohextriene which has taller sigma bonds than pi bonds. The 6 π e’s are delocalized on the 6 carbons “resonance” that appears later as stabilization of the compound. ) بيفضلوا يتنقلوا جوه الحلقة ومش ثابين في مكانهم وده3x2 من التالتةpi bond على كل2 e’s( 6π electrons الـ . للمركب عموماstability بتعملresonance واحنا عارفين إنresonance بينتج عنه . resonance جدا بسببstable بس هو مركب، في البنزينdouble bonds *نستنتج من الكالم ده إن برغم الـ ... بدل اللخبطة1,3,5-cyclohextrieneعايزين نفرق بين البنزين كده و Bond length Benzene 10 Angstrom “intermediate” Stability Type of reactions More stable. Substitution. 1,3,5-cyclohextriene Single bond: 14 Angstrom. Double bond: 7 Angstrom. Less stable. Addition (as alkenes). From Molecular Orbital explanation of structure of benzene we conclude that: Benzene is: 1- Planar hexagon. 2- Bond angle = 120 degree. 3- Each carbon is SP2 hybridized. Aromaticity Aromaticity which means aromatic characters used to describe certain properties in benzene or compounds like benzene. These properties are: The ring stability resonance stabilization. Reaction by substitution not addition. CLINICAL 2020 3 NMR spectroscopy 7-9. C—C bond length all the same intermediate between single & double. Aromaticityدي كلمة بتعبر عن خصائص aromatic compoundsزي البنزين وكده.. من الخصائص دي- :ثبات حلقة البنزين بسبب .resonance تفاعل البنزين بيتم بـ substitution reactionمش additionزي األلكين.لها rangeمن 9-7في حاجة اسمها * NMR spectroscopyدي هناخدها في محاضرتين قدام لسه*.-طول الروابط بين الكربونات في البنزين هو هو وبيبقى بين طول single & double bondsزي ما قلنا فوق. Requirements of aromaticity It must fulfill 4 conditions: (from cyclopropene “3Cs” to cyclo octane “8Cs”). Monocyclic Planar SP2 hybridized Aromatic compound Obeys Huckel's rule .1 .2 .3 .4 4 :Monocyclicالزم يكون مركب من حلقة واحدة مش أكتر ..زي بنزين مثال. :Planarيكون المركب عادي زي اللي متعودين عليه ،ما يكونش شكله 3Dأو معاق كدة. :SP2 hybridizedالشرط ده يعني يا فيه double bondيا المركب بيحمل شحنة سواء موجبة أو سالبة (.)C=C, C+, C- هتقوللي إزاي C-يعني carboanionو SP2واحنا خدنا إنها SP3الترم اللي فات ؟؟! هقوللك عادي إنسى اللي فات ده عشان مش دايما كده وهناخد الكالم ده لسه قدام حوار hybridizationعموما. :Obeys Huckel’s ruleبتقول الـ ruleدي إن الزم عدد الـ Pi-electronsيكون ( )4n+2و (.)n=0,1,2.. فالـ aromatic cpdsيكون عدد الـ 2,6,10,14,18… : pi-electrons CLINICAL 2020 Types of compounds Aromatic Antiaromatic Nonaromatic Aromatic: fulfill 4 conditions, highly stable. Anti-Aromatic: fulfill 1st 3 conditions but doesn’t obey Huckle’s rule (contain 4n pi electrons), highly unstable. “no. of pi-e’s: 4,8,12,16…” Non-aromatic: fail in one of 1st 3 conditions, stable. Cyclic, planar, not all Cs are SP2.. Therefore, non-aromatic. What will happen if we remove H+ or H- ? A) Removal of H- (hydride): forming carbocation. .carbocation ويتكونbond بتوع الـ2 electrons خرجت ومعهاHydrogen CLINICAL 2020 5 Cyclic, planar, All Cs are SP2 , obeys Huckel’s rule π e’s = 2 (4n+2 = 2).. Therefore, aromatic. B) Removal of H+(proton): forming carboanion. . carboanion ويتكونbond بتوع الـ2 e’s خرجت لوحدها وسابت الـHydrogen Cyclic, planar, All Cs are SP2 , doesn’t obey Huckel’s rule π e’s = 4 (4n+2 ≠ 4).. Therefore, anti-aromatic. Classify the following compounds (aromatic, anti-aromatic & **الجزء ده ممكن ييجي سؤال non-aromatic) and why** ;) slides يال نكمل باقي األمثلة اللي في الـ CLINICAL 2020 6 CLINICAL 2020 7 !! هنا دهcyclo octatetraene إيه الكالم الكبير اللي مكتوب على الـ ودهnon-planar بس في الحقيقة شكلها بيبقى معوق كدهplanar هنا مكتوب إن شكل المركب نظريا إنه..بص معايا .120 وهي المفروض تبقىbond angle = 135 نتيجة إن So the compound is present in tub shape ) (الشكل الغريب ده non-planar.. Therefore, nonaromatic. Substituted benzene derivatives Nomenclature A) Monosubtituted benzene derivatives: Benzene is considered as parent when derivative is for example Halogen X or Nitro group NO2. Some monosubstituted derivatives have special names as: CLINICAL 2020 8 طب دول األولوية لمين في المجموعات دي على التانية؟؟ Priority: SO3H > COOH > CHO “in benzaldehyde” > OH > NH2. B) Disubstituted benzene derivatives مين Ortho, meta, paraدول ؟! دي زي األرقام اللي بنستخدمها في nomenclatureلما ييكون في derivatives بس دي طريقة قديمة عن ( ortho ،)1,2,3..بتعبر عن المكان الـ adjacentاللي جنب أول meta ،substituentبتعبر عن تاني مكان أول para ،substituentبتعبر عن تالت مكان بالنسبة للـ substituentبيبقى قدامه كده. 9 CLINICAL 2020 C) Trisubstituted benzene derivatives: Reactions Benzene is considered as nucleophile, so it reacts by electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction not addition. +ve ألنها محتاجةnucleophile فبنعتبرهاelectron cloud– سهل تتفاعل نتيجة الـve charge البنزين عليها .substitution reaction اللي هتتفاعل معاه بـelectrophile اللي هتاخدها منcharge : خطوات3 التفاعل بيتم علىMechanism Step 1: Generation of electrophile from reagent. *we will know types of E+ & reagents later* E—Z E+ (electrophile) + ZStep 2: Addition of electrophile to benzene to give intermediate carbocation (sigma-complex) in which aromaticity is lost “less stable”. This is rate limiting step. sigma- اسمهintermediate ويتكونelectrophile تهجم الكترونات البنزين على الـelectrophileتكون الـ ّ بعد ما .less stable )وبيبقىbonds بس الشحنة بتفضل تتنقل بين الـcarbocation (عبارة عنcomplex Step 3: It is deprotonation of anion Z- to regenerate aromaticity & give substitution product. وينتجreagent اللي كان في الـZ anion تخرج معHفي الخطوة دي الكترونات الهيدروجين بتفضل و .Monosubstituted benzene derivative CLINICAL 2020 10 في األلكين مثال؟؟double bond زي أيaddition مشsubstitution طب ليه بقى البنزين بيتفاعل بـ ودخل مكانaddition) اتفاعل بالـstep 2( sigma-complex اللي هوintermediate carbocationعشان لو الـ ده بيرجعproton ألن لما بنشيل..less stable أصال والمركب هيبقىaromatic مش هيطلع+ve of carbocation . جداااااstable ويخلي الناتج اللي طلعaromaticity character By another words, because if the intermediate carbocation undego addition of anion, the resulting product is not aromatic but the loss of proton restores aromaticity & gives a product more stable than the reactant. Let’s start mechanisms of substitution reactions ;) But first we should know generally types of electrophiles used in those reactions: -For nitration NO2 -Sulphonation SO3 -Halogenation Cl2 or Br2 -lewis acid complex. -Alkylation Alkyl halide- AlCl3 complex. -Acylation Acylium ion CH3 – C Ξ O+ CLINICAL 2020 11 1) Nitration of benzene Reagent used: Conc. HNO3/H2SO4 Electrophile: NO2 + Nitronium ion. Product of the reaction: nitrobenzene. ****ممكن ييجي الجزء ده سؤال Mechanism: STEP 1: Formation of electrophile by reaction of sulphuric acid H2SO4 & nitric acid HNO3 to form NO2 HONO2 (HNO3) + HOSO3H (H2SO4) تهجم عليها عشانnitric acid ) فيO( بما إنها األقوى هتخليsulphuric acid الهيدروجين في:اللي هيحصل كالتالي احنا عارفين إن..+ve charge هنا عليهproducts اللي احنا شايفينه في الـcomplex وتكون، lone pair عندها فالمياه هتطلع لوحدها فيdehydrating بيعملsulphuric acid وكده كدهwater is good leaving group .electrophile وكده نكون كونّا الـHSO4- لوحدها ويطلعNO2+ وتسيبproductsالـ STEP 2: Addition of electrophile NO2+ to form intermediate carbocation CLINICAL 2020 12 الهجوم دايما.NO2+ بتاعت البنزين هتاخدelectron cloud وattraction عليها شحنة موجبة هيحصلNO2+ بما إن لحد ماsigma-complex تفضل تتنقل ويتكون+ve charge وresonance ويحصل...من سالب لموجب مش العكس .)step 3( في األخرnitrobenzene تدخل تاخد هيدروجين وتخرج وتنتجHSO4- Step 3: Deprotonation of intermediate carbocation by base to regenerate aromaticity: 2) Sulphonation of benzene “Reversible reaction” Reagent used: SO3/ H2SO4 “fuming sulphuric acid”. Electrophile: SO3. Product of the reaction: Benzene sulphonic acid. Conc. Sulphuric alone can be used, but the reaction is slow. Mechanism STEP 1: Electrophile in fuming H2SO4 is SO3 but by using conc. Sulphuric alone, SO3 is produced as follows: e’s بتسحبhigh electronegativity ) فيه عندهاO( ** طب ليه ؟؟ علشان+ve charge مافيش عليهاSO3 ناخد بالنا . electrophile فتبقى زيpartial +ve ) عليهاS( ناحيتها وتخلي CLINICAL 2020 13 STEP 2: Addition of electrophile E+: .intermediate carbocation فالكترونات البنزين هتهجم عليها وتكونpartial +ve ) عليهاS( زي ما قلنا Step 3: Deprotonation of intermediate carbocation by base to regenerate aromaticity: . طلع زي ما دخلH2SO4 وH في الخطوة دي بنشيل Step 4: Proton transfer water + benzene ويطلّعH3O+ منproton الخطوة الزيادة دي بس زي إعادة ترتيب لشكل المركب بإنه بياخد .sulphonic acid Sulphonation is reversible but nitration is irreversible Desulphonation by H3O+ “passing steam through the reaction mixture”. CLINICAL 2020 14