Practice Problems for Exam 2 A study was conducted to determine
advertisement
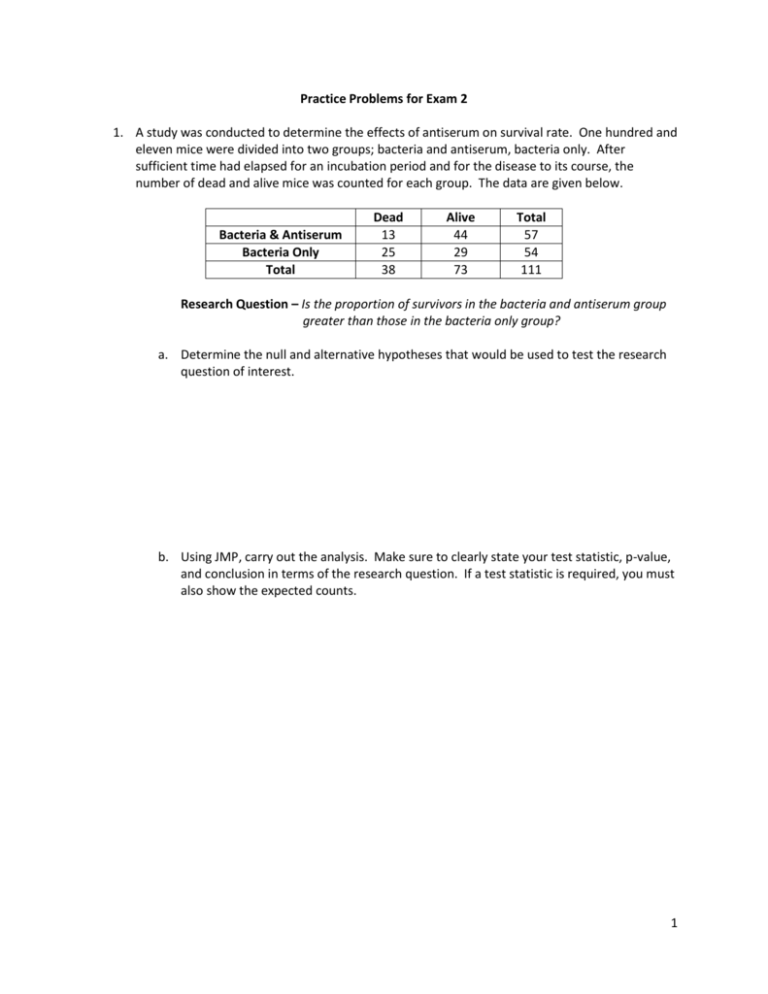
Practice Problems for Exam 2 1. A study was conducted to determine the effects of antiserum on survival rate. One hundred and eleven mice were divided into two groups; bacteria and antiserum, bacteria only. After sufficient time had elapsed for an incubation period and for the disease to its course, the number of dead and alive mice was counted for each group. The data are given below. Bacteria & Antiserum Bacteria Only Total Dead 13 25 38 Alive 44 29 73 Total 57 54 111 Research Question – Is the proportion of survivors in the bacteria and antiserum group greater than those in the bacteria only group? a. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses that would be used to test the research question of interest. b. Using JMP, carry out the analysis. Make sure to clearly state your test statistic, p-value, and conclusion in terms of the research question. If a test statistic is required, you must also show the expected counts. 1 2. Toschke et al. (American Journal of Epidemiology, 2003) collected data on the smoking status of mothers during pregnancy and whether their child was born premature (37 weeks or fewer of gestation) or full term. 3970 mothers participated in the study and of the 406 mothers who were smokers, 36 had premature babies, while 168 of the mothers who were non-smokers had premature babies. a. Fill in the contingency table for the scenario. Premature Baby Full Term Baby Total Smoker Non-Smoker Total b. Using JMP, find the relative risk of having a premature baby for the smokers compared to the non-smokers. c. Interpret the relative risk found in part b. d. Using JMP, find and interpret the odds ratio for this scenario. e. According to the relative risk found in part b and the odds ratio found in part d, can a relationship/association between smoking status and having a premature baby be concluded? Explain. 2 3. Sickle-cell anemia is a heredity chronic blood disease that is extremely severe when an individual carries two copies of the defective gene. It is particularly common in countries plagued by malaria, a parasitic infection transmitted by mosquitos. A study in Africa tested 543 children for the sickle-cell gene and malaria. Of the children tested, 136 had the sickle-cell gene and 407 did not possess the gene. Of those with the sickle-cell gene, 36 had heavy malaria infections whereas 139 of the children without the sickle-cell gene had heavy malaria infections. Research Question – Is the proportion of children with heavy malaria infections different for those with the sickle-cell gene compared to those without? a. Fill in the contingency table for the scenario. Malaria No malaria Total Sickle-cell No Sickle-cell Total b. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses that would be used to test the research question of interest. c. Using JMP, carry out the analysis. Make sure to clearly state your test statistic, p-value, and conclusion in terms of the research question. If a test statistic is required, you must also show the expected counts. 3 4. Twenty-four male strain A/J mice (6 – 8 weeks old) were randomly assigned to be exposed to simulated environmental tobacco smoke that consisted of a mixture of 89% sidestream and 11% mainstream smoke from Kentucky 1R4F reference cigarettes, at a chamber concentration of 87 mg/m3total suspended particulate matter. All mice were exposed in 0.44 m3stainless steel inhalation chambers for 6 h/day, 5 days/week for 5 months. Another 24 mice were randomly assigned to be kept in clean air during this time period. Then, all of the mice were allowed to recover further for 4 months in filtered air before being killed for analysis of lung tumor incidence. Of the mice exposed to smoke, 20 had a tumor; of the controls kept in air, 9 had a tumor. a. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the difference in proportions. b. Interpret the confidence interval found in part a. 4