Ch. 5 notes, metamorphic rock
advertisement

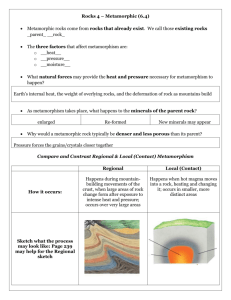
CH 5: HOW EARTH'S ROCKS WERE FORMED Part 3: Metamorphic Rocks I.METAMORPHIC ROCKS A.What Metamorphic Rocks Are T19 1.Meta = change morph = form 2.Formed from existing rock by a.Heat b.Pressure c.Chemicals B.Regional (Dynamic) Metamorphism T20 1.Forms most metamorphic rock 2.Occurs during mountain building 3.Large areas of rock under intense heat/pressure causing change a.Heat source (1)Existing heat in deeply buried rock (2)Friction of moving rock layers b.Pressure source (1)Great weight of overlying rock (2)Squeezing pressure of moving rock masses c.Result of Change (1)Grains squeezed closer together (2)Rock more dense/less porous (3)Minerals reformed or formed by heat/chemical action d.Rock examples (1)Marble (metamorphosed limestone) (2)Quartzite (metamorphosed sandstone) C.Metamorphism of Shale T21 1.Shale changes w/ dynamic/regional metamorphism a.More dense b.More crystalline c.New minerals formed ex. mica, hornblende d.Foliation occurs (1) Squeezed into parallel layers along which rock easily splits 2.Rocks formed from shale a.Slate: 1st formed/micro thin layers b.Phyllite: 2nd formed/shiny c.Schist: 3rd (most intense metamorphism) (1)Layers seen easily (2)Flaky/mica sparkles 3.Rocks formed from non-shale source a.Schist from basalt/sandstone b.Gneiss from granite/conglomerate (1)Coarsest foliation of all metas (2)Thick/parallel bands D.Thermal (Contact) Metamorphism T22 1.Occurs when hot magma forces way into overlying rock a.Heat bakes contacted rock 2.Affects much less rock than dynamic metamorphism 3.Less drastic changes/no foliation 4.Ex: Hornfels (from shale), fine grained/dense/hard