NGSS Topic Progression Comparison with MI HSCE/GLCE NGSS
advertisement

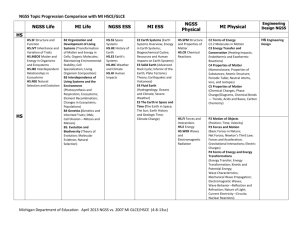
NGSS Topic Progression Comparison with MI HSCE/GLCE NGSS Life HS Topics/Standards HS.SF Structure and Function HS.IVT Inheritance and Variation of Traits HS.MEOE Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems HS.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems HS.NSE Natural Selection and Evolution HS MI Life NGSS ESS MI ESS Standards (Content Statements) B2 Organization and Development of Living Systems (Transformation of Matter and Energy in Cells; Organic Molecules; Maintaining Environmental Stability; Cell Specialization; Living Organism Composition) B3 Interdependence of Living Systems and the Environment (Photosynthesis and Respiration; Ecosystems; Element Recombination; Changes in Ecosystems; Populations) B4 Genetics (Genetics and Inherited Traits; DNA; Cell Division – Mitosis and Meiosis) B5. Evolution and Biodiversity (Theory of Evolution; Molecular Evidence; Natural Selection) Topics/Standards Standards (Content Statements) E2 Earth Systems (Earth Systems Overview; Energy in Earth Systems; Biogeochemical Cycles; Resources and Human Impacts on Earth Systems) E3 Solid Earth (Advanced Rock Cycle; Interior of the Earth; Plate Tectonics Theory; Earthquakes and Volcanoes) E4 Fluid Earth (Hydrogeology; Oceans and Climate; Severe Weather) E5 The Earth in Space and Time (The Earth in Space; The Sun; Earth History and Geologic Time; Climate Change) HS.SS Space Systems HS.HE History of Earth HS.ES Earth’s Systems HS.WC Weather and Climate HS.HI Human Impacts NGSS Physical MI Physical Topics/Standards Standards (Content Statements) HS.SPM Structure and Properties of Matter HS.CR Chemical Reactions C2 Forms of Energy C2.2 Molecules in Motion C3 Energy Transfer and Conservation (Heating Impacts; Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions) C4 Properties of Matter (Nomenclature; Properties of Substances; Atomic Structure; Periodic Table; Neutral Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes) C5 Properties of Matter (Chemical Changes, Phase Change/Diagrams, Chemical Bonds — Trends, Acids and Bases, Carbon Chemistry) HS.FI Forces and Interactions HS.E Energy HS.WER Waves and Electromagnetic Radiation P2 Motion of Objects (Position; Time; Velocity) P3 Forces and Motion (Basic Forces in Nature; Net Forces; Newton’s Third Law; Forces and Acceleration; Gravitational Interactions; Electric Charges) P4 Forms of Energy and Energy Transformations (Energy Transfer; Energy Transformation; Kinetic and Potential Energy; Wave Characteristics; Mechanical Wave Propagation; Electromagnetic Waves; Wave Behavior –Reflection and Refraction; Nature of Light; Current Electricity –Circuits; Nuclear Reactions) Michigan Department of Education April 2013 NGSS vs. MI HSCE(2006) and GLCE (2009) (4-8-13sc) Engineering Design NGSS HS Engineering Design NGSS Topic Progression Comparison with MI HSCE/GLCE NGSS Life MI Life MS.SFIP Structure, Function and Information Processing MS.MEOE Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems MS.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems MS.NSA Natural Selection and Adaptations MS.GDRO Growth, Development, and Reproduction of Organisms 6.OL Organization of Living Things (Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers) 7.OL Organization of Living Things (Cell Functions; Growth and Development; Photosynthesis) 6.EC Ecosystems (Interactions of Organisms; Relationships of Organisms; Biotic and Abiotic Factors; Environmental Impact of Organisms) 7.HE Heredity (Reproduction) NGSS ESS MI ESS NGSS Physical MI Physical Engineering Design NGSS 8 MS 6-8 MS.SS Space Systems MS.HE History of Earth MS.ES Earth’s Systems MS.WC Weather and Climate MS.HI Human Impacts 6.ST Earth in Space and Time (Fossils; Geologic Time) 6.SE Solid Earth (Soil; Rock Formation; Plate Tectonics; Magnetic Field of Earth) 7.ES Earth Systems (Solar Energy; Human Consequences; Weather and Climate; Water Cycle) 7.FE Fluid Earth (Atmosphere) MS.SPM Structure and Properties of Matter MS.CR Chemical Reactions MS.FI Forces and Interactions MS.EN Energy MS.WER Waves and Electromagnetic Radiation 7 6 Michigan Department of Education April 2013 NGSS vs. MI HSCE(2006) and GLCE (2009) (4-8-13sc) 6.CM Changes in Matter (Changes in State) 7.PM Properties of Matter (Chemical Properties; Elements and Compounds) 7.CM Changes in Matter (Chemical Changes) 6.EN Energy (Kinetic and Potential Energy; Energy Transfer) 7.EN Energy (Waves and Energy; Energy Transfer; Solar Energy Effects) MS Engineering Design NGSS Topic Progression Comparison with MI HSCE/GLCE 5.MEOE Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems 5.OL Organization of Living Things (Animal Systems) 5.HE Heredity (Inherited and Acquired Traits) 5.EV Evolution (Species Adaptation and Survival; Relationships Among Organisms) 4.OL Organization of Living Things (Life Requirements) 4.EV Evolution (Survival) 4.EC Ecosystems (Interactions; Changed Environment Effects) 5.ES Earth’s Systems 5.SS Space Systems: Stars and the Solar System 5.ES Earth Systems (Seasons) 5.EST Earth in Space and Time (Solar System; Solar System Motion) 5.SPM Structure and Properties of Matter 5.FM Force and Motion (Force Interactions, Force, Speed) 4.ES Earth’s Systems: Processes that Shape the Earth 4.ST Earth in Space and Time (Characteristics of Objects in the Sky; Patterns of Objects in the Sky; Fossils) 4.E Energy 4.W Waves: Waves and Information 3.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems 3.IVT Inheritance and Variation of Traits: Life Cycles and Traits 3.OL Organization of Living Things (Structures and Functions; Classification) 3.EV Evolution (Environmental Adaptation) 3.WC Weather and Climate 3.ES Earth Systems 3.FI Forces and (Natural Resources; Interactions Human Impact) 3.SE Solid Earth (Earth Materials; Surface Changes; Using Earth Materials) 2 2.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems 2.ES Earth’s Systems: Processes that Shape the Earth 2.SE Solid Earth (Surface Changes) 2.FE Fluid Earth (Water; Water Movement) 2.SPM Structure and Properties of Matter 1 1.SFIP Structure, Function and Information Processing 2.OL Organization of Living Things (Life Requirements; Life Cycles) 2.HE Heredity (Observable Characteristics) 1.OL Organization of Living Things (Life Requirements; Life Cycles) 1.HE Heredity (Observable Characteristics) K.OL Organization of Living Things (Life Requirements) 4. EN Energy (Forms of Energy; Energy and Temperature; Electrical Circuits) 4.PM Properties of Matter (Physical Properties; States of Matter; Magnets; Conductive and Reflective Properties) 4.CM Changes in Matter (Changes in State) 3.FM Force and Motion (Gravity; Force; Speed) 3.EN Energy (Forms of Energy; Light Properties; Sound) 3.PM Properties of Matter (Conductive and Reflective Properties) 2.PM Properties of Matter (Physical Properties; Material Composition) 1.SS Space Systems: Patterns and Cycles 1.ES Earth Systems (Solar Energy; Weather; Weather Measurement) 1.SE Solid Earth (Earth Materials) K.SE Solid Earth (Earth Materials) 1.W Waves: Light and Sound 1.PM Properties of Matter (Physical Properties; States of Matter; Magnets) K.FI Forces and Interactions: Pushes and Pulls (Forces, Position, Direction) K.FM Force and Motion (Position; Gravity; Force) 5 4.SFIP Structure, Function, and Information Processing 4 3 K K.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems: Animals, Plants, and Their Environment K.WC Weather and Climate Michigan Department of Education April 2013 NGSS vs. MI HSCE(2006) and GLCE (2009) (4-8-13sc) 3-5 Engineering Design K-2 Engineering Design NGSS Topic Progression Comparison with MI HSCE/GLCE Organization/Structure of GLCE/HSCE (p. 10 HSCE) The Science Expectations are organized into Disciplines, Standards, Content Statements, and specific Performance Expectations. Disciplines HS Disciplines – Earth Science, Biology, Physics, Chemistry K-7 Disciplines – Earth Science, Life Science, Physical Science Organization of Each Standard Each standard includes three parts: • A standard statement that describes what students who have mastered that standard will be able to do. • Content statements that describe Prerequisite, Essential, Core, and Recommended science content understanding for that standard. • Performance expectations that describe Prerequisite, Essential, Core, and Recommended performances for that standard. NOTE: Boundary statements that clarify the standards and set limits for expected performances, technical vocabulary, and additional discipline-specific inquiry and reflection expectations are included in a companion document. HSCE Standards Organization – Standards (number of content statements within each) Earth Science Biology Physics Chemistry E1 Inquiry, Reflection, and Social Implications (2) E2 Earth Systems (4) P1 Inquiry, Reflection, and Social Implications (2) P2 Motion of Objects (3) C1 Inquiry, Reflection, and Social Implications (2) C2 Forms of Energy (5) P3 Forces and Motion (8) C3 Energy Transfer and Conservation (5) E4 The Fluid Earth (3) B1 Inquiry, Reflection, and Social Implications (2) B2 Organization and Development of Living Systems (6) B3 Interdependence of Living Systems and the Environment (5) B4 Genetics (4) P4 Forms of Energy and Energy Transformations (12) C4 Properties of Matter (10) E5 Earth in Space and Time (4) B5 Evolution and Biodiversity (3) E3 The Solid Earth (4) C5 Changes in Matter (7) GLCE Standards Organization (K-4 and 5-7) – Standards (number of content statements within each) Science Processes Earth Science Life Science Physical Science Inquiry Process IP (1) Earth Systems (ES) (5 - Solar Energy, Weather, Weather Measurement, Natural Resources, Human Impact) Solid Earth (SE) (3 – Earth Materials, Surface Changes, Using Earth Materials) Fluid Earth (FE) (2 – Water, Water Movement) Organization of Living Things (OL) (4 – Life Requirements, Life Cycles, Structures and Functions, Classification) Force and Motion (FM) (4 - Position, Gravity, Force, Speed) Heredity (HE) (1 – Observable Characteristics) Earth in Space and Time (ST) (3 – Characteristics of Objects in the Sky, Patterns of Objects in the Sky, Fossils) Ecosystems (EC) (2 – Interactions, Changed Environment Effects) Energy (EN) (5 – Forms of Energy, Light Properties, Sound, Energy and Temperature, Electrical Circuits) Properties of Matter (PM) (5 – Physical Properties, States of Matter, Magnets, Material Composition, Conductive and Reflective Properties Changes in Matter (CM) (1 – Changes in State) Inquiry Analysis and Communication IA (1) Reflection and Social Implications RS (1) Evolution (EV) (2 – Environmental Adaptation, Survival) Michigan Department of Education April 2013 NGSS vs. MI HSCE(2006) and GLCE (2009) (4-8-13sc) NGSS Topic Progression Comparison with MI HSCE/GLCE Organization/Structure of the NGSS The NGSS Performance Expectations are organized by Topic – In order to eliminate potential redundancy, seek an appropriate grain size among Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs) identified within the Framework for K-12 Science Education, the NGSS writers identified NGSS topics around which to develop the standards. The standards include Performance Expectations that incorporate three dimensions (articulated in Foundations Boxes) – Science and Engineering Practices, Disciplinary Core Ideas, and Crosscutting Concepts. Each standard (topic) also includes connections to other NGSS and to the CCSS (identified in Connections Boxes). NGSS Topic Organization -- Topics/Standards (and number of PEs) Life Science (LS) High School LS (5 Topics/Standards) HS.SF Structure and Function HS. IVT Inheritance and Variation of Traits HS.MEOE Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems HS.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems HS.NSE Natural Selection and Evolution Middle School LS (5 Topics/Standards) MS.SFIP Structure, Function and Information Processing MS.MEOE Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems MS.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems MS.NSA Natural Selection and Adaptations MS.GDRO Growth, Development, and Reproduction of Organisms Elementary (K-5) LS (4 Topics/7 Standards) 5.MEOE Matter and Energy in Organisms and Ecosystems 4.SFIP Structure, Function and Information Processing 3.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems 3.IVT Inheritance and Variation of Traits: Life Cycles and Traits 2.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems 1.SFIP Structure, Function and Information Processing K.IRE Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems: Animals, Plants, and Their Environment Earth and Space Science (ESS) High School ESS (5 Topics/Standards) HS.SS Space Systems HS.HE History of Earth HS.ES Earth’s System HS.WC Weather and Climate HS.HI Human Impacts Physical Science (PS) High School PS (5 Topics/Standards) HS.SPM Structure and Properties of Matter HS.CR Chemical Reactions HS.FI Forces and Interactions HS.E Energy HS.WER Waves and Electromagnetic Radiation Engineering Design (ED) High School ED (1 Topic/Standard) HS.ED Engineering Design Middle School ESS (5 Topics/Standards) MS.SS Space Systems MS.HE History of Earth MS.ES Earth’s Systems MS.WC Weather and Climate MS.HI Human Impacts Middle School PS (5 Topics/Standards) MS.SPM Structure and Properties of Matter MS.CR Chemical Reactions MS.FI Forces and Interactions MS.E Energy MS.WER Waves and Electromagnetic Radiation Middle School ED (1 Topic/Standard) MS.ED Engineering Design Elementary (K-5) ESS (3 Topics/7 Standards) 5.ES Earth’s Systems 5.SS Space Systems: Stars and the Solar System 4.ES Earth’s Systems: Processes that Shape the Earth 3.WC Weather and Climate Elementary (K-5) PS (4 Topics/7 Standards) 5.SPM Structure and Properties of Matter Elementary Engineering Design (ED) (1 Topic/2Standards) 3-5.ED Engineering Design 2.ES Earth’s Systems: Processes that Shape the Earth 1.SS Space Systems: Patterns and Cycles K.WC Weather and Climate 2.SPM Structure and Properties of Matter 4.E Energy 4.W Waves: Waves and Information 3.FI Forces and Interactions 1.W Waves: Light and Sound K.FI Forces and Interactions: Pushes and Pulls Michigan Department of Education April 2013 NGSS vs. MI HSCE(2006) and GLCE (2009) (4-8-13sc) K-2.ED Engineering Design