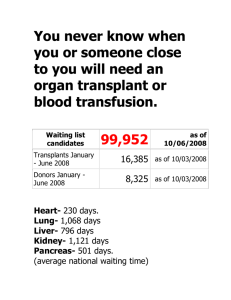
Blood Types and Donation
advertisement

LESSON PLAN 3 Class: Grade 12 Biology Unit: Circulation B11-3-03: Compare and contrast the characteristics of different blood groups. (GLO: D1) Include: ABO and Rh factor B11-3-04: Predict the physiological consequences of blood transfusions involving different blood groups. B11-3-05: Describe the blood donation process and investigate related issues. Materials: Blood type video Canadian Blood Services Video Student online worksheet Class pin up questions Background: Students were introduced to blood types in previous lesson; learning the difference between blood types and which types can donate/receive from others. Procedure Activate: Show blood type video to review what was learned in the previous lesson. Allow students to complete questions from yesterday before answering them as a class. 20 Min Acquire: Watch video on blood donation process from Canadian Blood Services. Have students access the website for Canadian Blood Services to complete student handout on donation requirements and processing. 25 min Apply/Assessment Display 25 questions around the classroom. Students rotate to each question and fill in their answer sheet. To be handed in at the end of the period. 30 Min Close: Tell students they will be having a presentation on blood types April 29th, and at that point will be able to find out their blood type. Remind students of test next week. BLOOD DONATIONS – Student handout Search the Canadian Blood Services Website, www.blood.ca, to answer the following questions: 1. How many units of blood are needed to save someone who a. Needs a hip replacement ____________ b. Is undergoing cancer treatment __________ c. Who was in a car accident __________ 2. Eligibility a. How old must you be to donate blood? _________ b. How much must you weigh to donate? _________ c. How long must you wait between donations? _____________ 3. Temporary Deferrals. How long must you wait to donate blood following a. Getting a tattoo or piercing? ________ b. Being pregnant? __________ c. Having dental work? _________ d. Receiving a flu shot? _________ 4. List 4 reasons, other than those above, that would lead to someone being deferred from donating blood. 5. What are 4 reasons that may lead to an indefinite deferral? 6. What is CJD or vCJD? 7. If you have been to a country with Malaria, can you donate blood? 8. What can you donate: a. What is included in ‘whole blood’? b. What is leukoreduction? c. Why is leukoreduction done? d. What is plasmapheresis? e. What can plasma donations be used to treat? f. What is plateletpheresis? g. What is the shelf life of platelets? Example of Assessment Questions: Station #11 Station #12 What blood type is the universal donor? What blood type is the universal recipient? Station #13 Station #14 What blood type is the universal donor for plasma? What type of antibodies does type O blood have? Station #15 Station #16 What type of antibodies does type AB blood have? Where are antibodies found? Station #17 Station #18 Where are antigens found? Can a person with Rh- blood receive blood from a donor with Rh+ blood? Station #19 Station #20 What happens if two blood types that are not the same mix? What is the function of white blood cells? Station #21 Station #22 What is the purpose of platelets? What blood component makes up the majority of blood? (erythrocytes, thrombocytes, leukocytes, or plasma) Station #23 Station #24 Leukocytes are also known as _________________ blood cells. Erythrocytes are also known as ______________ blood cells Station #25 Station #26 What is the purpose of hemoglobin? Where are red blood cells made? Station #27 Station #28 Where are white blood cells made? Where are platelets made? Station #29 Station #30 Antibodies and antigens are both types Thrombocytes are also known as of ______________________. __________________________.