Roadmap for the year
advertisement

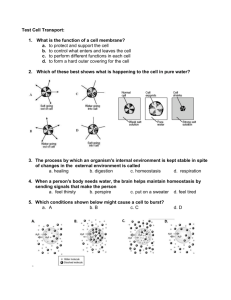
UNIT 3: CELLULAR BIOLOGY 3B: Cell Membrane & Transport Roadmap for the year: Unit 1: Chemical Basis of Life Unit 2: Ecology and Human Impact Unit 3: Cell Biology 3A Origin of Life 3B Cellular Membrane and Transport 3C Cell Structure and Function Unit 4: Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology Unit 5: Genetics and Evolution Unit 6: Human Body Systems Themes for the year: How does this unit contribute to your understanding of the following themes? Life on Earth has various Levels of Organization The Structure of Living Things leads to their Function The Big Picture… Evidence supports that earth and the organisms that inhabit it have changed greatly over time. The diversity of life is the result of ongoing evolutionary change. Species alive today have evolved from ancient common ancestors. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all living things. Cells in a multicellular organism are interdependent upon each other. Cells are dynamic and constantly work towards maintaining homeostasis. Processes that occur at the cellular level provide the energy and basic structure organisms need to survive. Evidence supports that earth and the organisms that inhabit it have changed greatly over time. The diversity of life is the result of ongoing evolutionary change. Species alive today have evolved from ancient common ancestors. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all living things. Cells in a multicellular organism are interdependent upon each other. Cells are dynamic and constantly work towards maintaining homeostasis. Processes that occur at the cellular level provide the energy and basic structure organisms need to survive. Form (structure) leads to function. Suggested Resources… Homework Assignments Classwork Assignments Laboratory Activities Note Packet Textbook Chapter 7 (Section 7.3) Online Textbook Activities: Interactive Art (Passive Transport, Diffusion, Osmosis) and Art in Motion (Protein Pumps, Endocytosis, Exocytosis) Directions: Below are check lists of things you should know and things you should be able to do by the end of the unit. Use this tool to help you prepare for the unit assessment. By the conclusion of this unit, you should know the following: 1. A cell membrane is a selectively permeable boundary that helps cells maintain homeostasis by regulating what enters/leaves cells. 2. Specialized molecules like transport proteins and cholesterol can be found in the cell membrane. 3. Substances such as oxygen and basic nutrients must be able to enter cells; waste products must be able to exit cells through the cell membrane. 4. Both active and passive transport mechanisms allow substances to enter/leave cells according to concentration gradients and/or the cell’s needs. 5. Passive transport (including diffusion and osmosis) is the movement of materials across the cell membrane without cellular energy. 6. The movement of materials against a concentration difference is known as active transport. Active transport requires energy. 7. Water moves into or out of cells by osmosis. A solution is a mixture consisting of a solute uniformly dissolved in a solvent. The solvent is identified as that component which makes up the bulk of the solution. By the conclusion of this unit, you should be able to do the following: 1. Describe the different types of biological molecules and their functions that make up the cell membrane. 2. Give examples of substances that are normally moved across cell membranes. 3. Relate the structure of the cell membrane to its function in selective permeability. 4. Distinguish between passive and active transport. 5. Compare and contrast passive transport (diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion) with active transport (including molecular active transport and endocytosis/exocytosis). 6. Solve problems involving the movement of solutes and/or water across selectively permeable membranes, along their concentration gradients, including the identification of hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic solutions. 7. Predict what type of transport would be expected for the movement of certain molecules into/out of cells. Cell Membrane & Transport Key Terms Words found in the textbook (not all are in the glossary): 1) Diffusion: 2) Facilitated Diffusion : 3) Osmosis : 4) Isotonic : 5) Hypertonic : 6) Hypotonic : 7) Active Transport (pg. 212) : 8) Endocytosis (pg. 213) : 9) Exocytosis (pg. 213) : 10) Homeostasis : 11) Selectively Permeable : 12) Lipid Bilayer : 13) Solute : 14) Solvent : 15) Cell membrane: