"How to Understand and Use the Wind Chill Factor" Edited by
advertisement

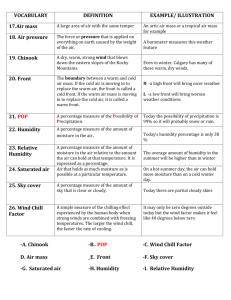
"How to Understand and Use the Wind Chill Factor" Edited by Flickety, Ben Rubenstein, Travis Derouin, Lillian May and 6 others Wind chill is the meteorological term used for explaining how the wind can make us feel even colder (chillier) than the actual temperature. While in many parts of the world knowing the wind chill can be a fun exercise, in some places it is essential to know, to ensure that you don't expose your skin to the cold air too long. Over-exposure to the cold without adequate protection can lead to frostbite, hypothermia and freezing to death. Here are some tips on how to understand and use the wind chill factor in your daily activities. 1. Understand what wind chill is. Wind chill is the effect that wind has on ''our skin'' in cold weather. It is not something that makes the actual outside temperature less but it is the combination of the cold air and wind impacting on our skin. It does not have any temperature-reduction effect on non-living objects (although the wind itself can obviously affect things like camping stoves for mountaineers etc.). Our skin feels colder because its internal body heat that usually generates a "boundary layer" of heat surrounding our body is "blown away" by the wind hitting it. Removal of this tiny layer of warm air from around our body leaves us exposed directly to the cold air. It is even more evident if your skin is wet because this draws away the heat very quickly and leaves you with the feeling of "bone-chilling". 2. Understand what the wind chill factor is. The wind chill factor is a way of calculating the impact of a wind on a human body. Recent wind chill factor measurements are provided in a temperature format for the public because this is the easiest way for us to understand it. 3. Calculate the wind chill factor. This is a formula that is easiest to calculate using an online calculator. Search for a wind chill calculator to use. Or, if you're mathematically minded, you could try it the hard way, which involves using a formula; see, for instance: USA Today wind chill formulas 4. Use the wind chill factor to take evasive action. When you hear the wind chill factor, it is safest to assume that the wind chill temperature is the temperature for which you should prepare. Wear clothes appropriate to that temperature, sun screen, hats, gloves/mittens, boots, etc. Stay indoors if the weather is going to be too cold with the wind chill factored in. 5. Stay warm. Apart from having good clothing as a barrier between you and the cold, you can help reduce heat loss through exercising constantly (walking, skiing, snowshoeing etc.). You'll notice how quickly you cool down when you stop moving after activity. Try eating high protein/energy foods such as nuts, energy bars etc. and drink hot drinks - even hot water with a dash of cayenne pepper is known to provide an instant heat spike that will help your body glow in the cold. Tips: Carry hot drinks and energy bars if you're skiing, snowshoeing etc. They are small but provide a good energy boost for their size and can mean the difference between a miserable outing and a fun time. If you do get caught up in a vicious cycle of feeling very cold because of the temperature, the wind and inadequate or even wet clothing, try to get back to a warm place extremely quickly; failing which, dig into the snow and try to get out of the wind for a time. You'll still feel cold but it'll give your body a break during which time you can try to rally up some energy, maybe eat an energy bar and drink something hot and then return to a warm hut, car etc. to thaw again. Carry hand and feet warmers if you are going to be outside for a long time. Cover up thoroughly in cold weather that has a wind chill factor warning. Make sure your clothing is of good quality, with excellent insulation barriers between you and the outside cold. Seek advice from sports, ski or hiking stores if you aren't sure what to get. Seek the sun! If there is sunshine during a cold day, it will keep you a lot warmer than a grey day - try leaving the skiing etc. for the sunny days (but don't forget the sun screen, sun glasses and hat). Warnings Avoid using alcohol as a source of warming; contrary to how it feels, alcohol reduces your temperature and if you have too much, it will also reduce your capacity to realize how cold you actually feel. Never stay outdoors in extremely cold weather for long periods of time; even a short period of time can be dangerous when the wind chill is severe. Skin can begin to freeze at -25ºC/ -13ºF and it can freeze within minutes at -35ºC/ -31ºF. Do not skip meals. Food is your source of energy (fuel) and you use energy to generate heat. This is important whether you're walking between office blocks in the city or skiing from one end of a park to the other. You'll adapt more to the cold as winter progresses; as such, acclimatize yourself to winter progressively, spending time outdoors throughout autumn and leading into winter, so that your body is gradually getting used to the falling temperatures. It is a worse shock for those indoors all day who only venture out on weekends!