Rocks Resources and Scenery Module Sheet
advertisement
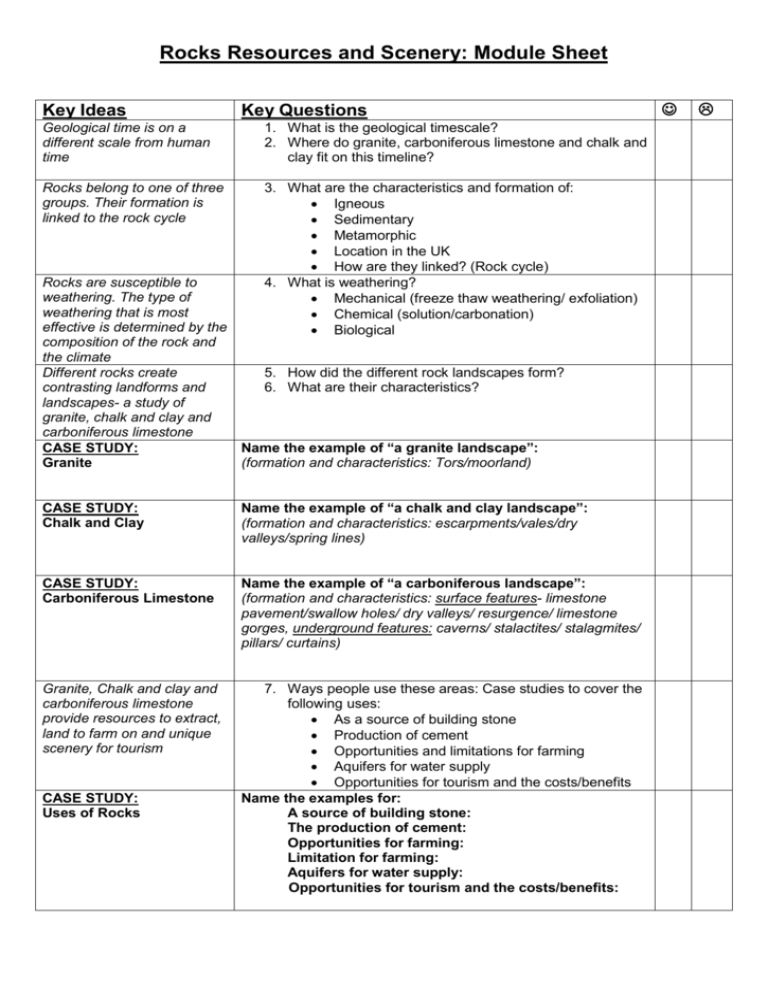
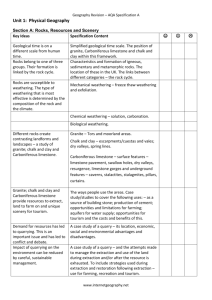
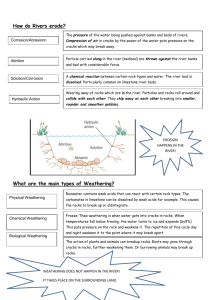
Rocks Resources and Scenery: Module Sheet Key Ideas Key Questions Geological time is on a different scale from human time 1. What is the geological timescale? 2. Where do granite, carboniferous limestone and chalk and clay fit on this timeline? Rocks belong to one of three groups. Their formation is linked to the rock cycle 3. What are the characteristics and formation of: Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Location in the UK How are they linked? (Rock cycle) 4. What is weathering? Mechanical (freeze thaw weathering/ exfoliation) Chemical (solution/carbonation) Biological Rocks are susceptible to weathering. The type of weathering that is most effective is determined by the composition of the rock and the climate Different rocks create 5. How did the different rock landscapes form? contrasting landforms and 6. What are their characteristics? landscapes- a study of granite, chalk and clay and carboniferous limestone CASE STUDY: Name the example of “a granite landscape”: Granite (formation and characteristics: Tors/moorland) CASE STUDY: Chalk and Clay Name the example of “a chalk and clay landscape”: (formation and characteristics: escarpments/vales/dry valleys/spring lines) CASE STUDY: Carboniferous Limestone Name the example of “a carboniferous landscape”: (formation and characteristics: surface features- limestone pavement/swallow holes/ dry valleys/ resurgence/ limestone gorges, underground features: caverns/ stalactites/ stalagmites/ pillars/ curtains) Granite, Chalk and clay and carboniferous limestone provide resources to extract, land to farm on and unique scenery for tourism 7. Ways people use these areas: Case studies to cover the following uses: As a source of building stone Production of cement Opportunities and limitations for farming Aquifers for water supply Opportunities for tourism and the costs/benefits Name the examples for: A source of building stone: The production of cement: Opportunities for farming: Limitation for farming: Aquifers for water supply: Opportunities for tourism and the costs/benefits: CASE STUDY: Uses of Rocks Rocks Resources and Scenery: Module Sheet Demand for resources has led to quarrying. This is an important issue and has led to conflict and debate CASE STUDY: A Quarry Impact of quarrying on the environment can be reduced by careful sustainable management CASE STUDY: Sustainable Management of a Quarry 8. Case study of a quarry: location, economic, social and environmental advantages and disadvantages Name the example of “quarry” for the aspects above: 9. Case study of a quarry: Attempts made to manage the extraction and use of the land during extraction and/or after the resource is exhausted. To include strategies used during extraction and restoration following extraction- use for farming, recreation and tourism Name the example of “quarry” for the aspects above: