Chapter 15 Crustal Deformation review sheet
advertisement

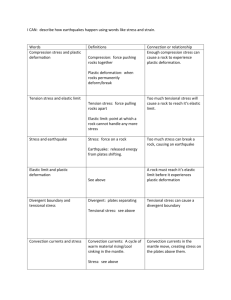
Earth Systems 3209 Chapter 15 - Review Sheet Key Terms Crustal deformation Compressional stress Elastic deformation Faulting Folding force tensional stress brittle deformation dip-slip fault anticline fold stress shear stress ductile deformation strike slip (transform) fault syncline fold Key Topics p. 415 – 416: Understand the difference between force, stress, and strain. Explain how each of the three types of stress (compressional, tensional, and shear) can cause crustal deformation but in different ways. p. 416 – 418: Describe the differences between the three types of deformation (elastic, brittle, and ductile) and know the conditions that cause each to occur. p. 416 – 419: Understand how each of the following factors affects deformation: a. temperature b. confining pressure c. rock type d. time p. 425 – 432: Explain why faults occur and describe the differences between dip-slip faults and strike-slip faults. Know that there are several types for each and be able to explain the differences between them. A. Dip-slip 1. normal (tensional) 2. horst and graben (tensional) 3. reverse (compressional) 4. thrust (compressional) B. Strike-slip (transform 1. left-lateral (shear) 2. right-lateral (shear) p. 421 – 425: Understand that folding of rock is caused by slow, continual, compressional forces, usually at great depth. Describe the differences between the two most common types of folds: a. anticline folds b. syncline folds