Supplemental Instruction Leader Training
advertisement

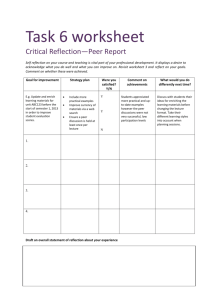
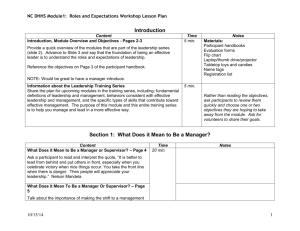
Supplemental Instruction Leader Training Supervisor Mrs. Angelica B. Nevin Supervisor Dr. Jennifer Bebergal Email anevin@fau.edu Email bebergal@fau.edu Phone 561-297-0945 or 561-445-0011 Phone 561-297-2432 or 954-298-0269 Definition and history of Supplemental Instruction: Supplemental Instruction (SI) is an academic support model developed by Dr. Deanna Martin[1] at the University of Missouri-Kansas City (UMKC)[2] in 1973 that uses peer assisted study sessions to improve student retention and success within targeted historically difficult courses.[3] The SI program provides peer support by having students who succeeded in traditionally difficult academic courses (e.g., Organic Chemistry, Biology 101, Logic) help other students complete these courses. SI is a non-remedial approach that provides regular review sessions outside of class, in which students work collaboratively by discussing readings, comparing notes, working together to predict test items, and sharing ideas for improving class material. Courses selected for SI tend to be “gatekeeper” courses for first and second year students—generally those classes that have a 30% or higher proportion of students who receive a “D”, fail, or withdraw (the DFW rate) from the course. Out-of-class review sessions are led by “SI leaders,” students who took the class already and did well. SI leaders attend all class lectures, take notes, and act as models to those currently taking the course. The SI model is used for selected courses at the undergraduate, graduate, and professional school levels, and has been adopted by colleges and universities in the United States and internationally.[4] The International Center for SI hosts and conducts regular trainings [10] on the SI model and has trained people in over 1,500 institutions in more than 29 countries. Outside of the United States, SI is also known as PASS (Peer Assisted Study Sessions) and PAL (Peer Assisted Learning). Page 1 Description: Training is an integral part of being an SI leader. The training process is an intensive, semester long journey. Certain aspects are mandatory while others are voluntary. Much of the training process incorporates the SI model, which will bring together the entire SI team to work in groups to solve problems, discuss topics, and solidify content knowledge in a fun, interactive way. Other parts of the training process will begin on an individual basis through guided readings and discussion posts on Blackboard. However, the use of Blackboard lends itself to a collaborative, online experience that may take place at the learners pace. Timely posts and professional feedback is expected. Goals of training: Training is meant to prepare SI leaders: To facilitate SI sessions. To assist students in acquiring content knowledge while reinforcing appropriate study skills for future success. To increase retention within targeted historically difficult courses. To improve student grades in targeted historically difficult courses. To increase the graduation rates of students. To comply with the high caliber of expectations set forth by the University and CRLA certification standards. Training Elements: One week before classes begin: Mandatory 2 day training, 9am-5pm. Lunch is provided. Day 1: Tasks, relationships, contract review, Blackboard intro, making announcements and introductions, etc. Day 2: Cone of experience, parts of a session, creating lesson plans and handouts, mock sessions based on FAU lecture recording, redirecting questions, office tour, etc. Total Time: 14 hours Every Month (4 times each semester): Mandatory Team meetings for additional in-service training. Guided Reflections, group interactions, brainstorming, team building, etc. Total Time: 6 hours First Month of Classes: Mandatory Completion of 2 peer evaluations Page 2 Visit at least 2 SI sessions and provide congratulatory and constructive feedback for your colleague, reflect on your own sessions and possible changes. All peer reviews must be documented on our peer evaluation sheet and handed into the office for compilation and disbursement to evaluated leaders. Total Time: 2 hours Throughout the semester: Voluntary Blackboard Modules 1. Active Listening 2. Adult Learners 3. Learning Styles 4. Critical Thinking 5. Plagiarism and the Honor Code 6. Role of Learning Centers in Higher Education 7. Self-regulated Learning 8. Brain Learning and Memory For adequate time for reflection and feedback, it is suggested that each module be completed every two weeks. Modules typically take 2-3 hours to adequately complete. Total Time: 16-24 hours Completion of all trainings: 38-46 hours/semester Typical Time spent with Students: SI sessions= 3-4x/wk x 15 weeks= 45-60 hours/semester SI office hours= 3x/wk x 15 weeks= 45 hours/semester Total student contact hours/semester= 90-105/semester Evaluation of SI leaders: Peer Evaluations Supervisor and CLASS staff observations of SI sessions and office hours Appraisal of lesson plans and handouts 1. By supervisor 2. By SI course faculty member(s) 3. By peers Review of participation and Blackboard posts (through a star rating system) 1. By supervisors 2. By SI team members End-of-Term Evaluation completed by faculty member(s) End-of-Term Evaluation by supervisors and CLASS staff Completion of Training as per the CRLA training rubric for each Level (1,2 &3) Page 3 LEVEL I: TOPICS, MATERIALS, AND DOCUMENTATION (SUMMARY CHART) Topic When Covered Amount of time Methods Materials Used/ Documentation Definition of Tutoring and Responsibilities Pre-Term Training 45 min. Individual Reading and Reflection, Group Discussion UMKC Leader Guide (pp.10-13 & 28) PDF file pp. 2-5 & 25 Basic Guidelines Do’s & Don’ts Pre-Term Training 1.5 hours Pre-Term Training 1.25 hours Individual Reading and Reflection, Group Discussion Individual Reading and Reflection, Group Discussion UMKC Leader Guide (pp. 12-13) PDF pp. 4-5 UMKC Leader Guide (pp. 29, 34-35, 53-65, 72) PDF pp. 13,18-19,2639 Individual Reading and Reflection, Group Discussion Andragogy and SelfDirected Learning: Pillars of Adult Learning Theory Sharan B. Merriam Group Discussion UMKC Leader Guide (pp. 16-23, 29-30) PDF pp. 6-11, 13-14 Techniques: Beginning & ending session Adult Learners Blackboard 2-3 hours Module Assertiveness/Han dling Difficult Situations 1 hr. Pre-term and inservice Role Modeling All Trainings 1.5 hrs. (Pre-term, in-service Individual Reading, Reflection, Group Discussion and individual meetings with supervisors It is our program’s goal to tie appropriate rolemodeling into every and discussion, reading Blackboard modules) and interaction. As SI leaders, our group is expected to be a model peer in all respects. Personal examples are used whenever possible. Setting Goals/Planning Pre-term training 1 hr. Homework, in-service Personal reflection, group discussion and Parameters are set on the agenda of our individual meetings with supervisor(s) pre-term training. Goals are tied to past participation trends for individuals (attached). Communication Skills Pre-term and inservice, on- 1 hr. Ice-breakers, group discussions, etc. Document: Icebreakers Oral: Introductions to Peer and Supervisor Page 4 Completed Y/N Date Completed Initials going class, observed by supervisors and team Evaluations members. Written: Guide to a well written email, handouts, etc. Active Listening Blackboard and Paraphrasing 2 hrs. Individual Reading, Active Listening Module, pre-term Reflection, Group Discussion, Redirection Rogers, C. and Farson, R.E. training, on- of questions “Whose Line is it Anyway?” Activity going Referral Skills Study Skills Pre-term All 30 min. 2 hrs. Trainings (Pre-term, in-service and Supervisor led Document: discussion University Resource List Individual Reading, Reflection, Group Discussion and individual meetings with supervisors UMKC Leader Guide Individual Reading, Collaborative Reflection, Group Learning Enhances Discussion Critical Thinking. Gokhale, A.A. Individual Reading, Reflection, Group Discussion and individual meetings with supervisors University Honor Code (54-87) PDF pp. 27-58 Top 25 ways to weave in study skills Blackboard modules) Critical Thinking Blackboard Skills Module Ethics, Philosophy, All Trainings Harassment and (Pre-term, Plagiarism in-service and 2 hrs. 2 hrs. Blackboard modules) Total Time for Level I: 18.5-19.5 hours Page 5 LEVEL II: TOPICS, MATERIALS, AND DOCUMENTATION (SUMMARY CHART) Topic When Covered Probing Questions Pre-Term Amount of time 1.5 hr. and inservice Methods Materials Used/ Documentation Group Discussion, UMKC Leader Guide (all Role-playing presented as such) “Whose line is it anyway?” activity Leading by example Cultural Awareness Pre-term, in- and Diversity service, Blackboard 2.5hrs. Supervisor led Expertise of guest speaker discussion, guest speaker, reflection, from Office for Students with Disabilities role-playing, Leader discussion of Blackboard Module Documentation diversity Discussion of diverse populations at FAU Identifying and using resources Pre-term 30 min. Supervisor led discussion Document: University Resource List (located in Specific Skill/Subject Areas Pre-term, inservice, 3 hrs. Individual Reading, Reflection, Group Discussion and individual meetings with supervisors and professors Past session plans, current and past textbooks, weekly Supervisor led UMKC Leader Guide (pp. discussion, reflection, role-playing 31, 35, 49-51, 53-87) PDF pp. 15,19,22-24,26-64) ‘Informational pages) professor office hours Assessing or Pre-term and Changing Study Habits In-service and 2-3.5 hrs. Blackboard Modules scheduled meetings with professor(s), weekly attendance at lecture Encouraging Student Success: The Instructional Challenges, Response Strategies, and Study Skills of Contemporary Undergraduates Kuo, J., Hagie, C. & Miller, M.T. Staying Motivated Blackboard, Reflection, Group Quotes from past members, Individual 2 hrs. Discussion and motivational primer from meetings for follow-up individual meetings with supervisors supervisor, group sharing of coping and time management strategies from fellow leaders. Total Time for Level II: 11.5-13 hours Page 6 Completed Y/N Date Completed Initials LEVEL III: TOPICS, MATERIALS, AND DOCUMENTATION (SUMMARY CHART) Topic When Covered Target Population Dealings Pre-term and In-service Amount of time 2 hrs. Methods Individual Reading, Reflection, Group Discussion and individual meetings with supervisors and professors Materials Used/ Documentation UMKC Leader Guide (pp.10-11,18-19, 30-33, 49-51) PDF pp. 2-3,8-9,14-17,2224 Weekly scheduled meetings with professor(s) Discussion with leader team at monthly meetings Role of Learning Blackboard Centers in Higher Ed. Module Structuring the Learning Pre-term and In-service 2 hrs. 1.5 hrs. Experience Educational Outcomes of Reading, Reflection, Group Tutoring: A meta-analysis of Findings. Cohen, P.A., Discussion Kulik, J.A., Kulik, C.C. The Effectiveness of Peer Tutoring in Further and Higher Education: A Typology and Review of the Literature. Topping, K.J. Pre-term training is structured in the SI UMKC Leader Guide (pp. 12-13,1819,29-35,49-51) model fashion with PDF pp. 4-5,8-9,13-19,22- opening, closing and content 24 Scheduled meetings with techniques. supervisor(s) Training/Supervisin Individual Discussion, Peer Observation Sheet g other tutors meetings with reflection, role- Supervisor Evaluation supervisor playing Sheet Individual Reading, Reflection, Group Discussion and individual meetings with supervisors and professors Individual UMKC Leader Guide Reading, Reflection, Group Theories of Education. Kneller, G.F. Group Pre-term and Management Skills In-service Theory and Blackboard Practice Module 2.5 hrs. Individual 1.5 hrs 2 hrs. Discussion Total Time for Level III: 11.5 hours References Page 7 Four Twentieth Century Completed Y/N Date Completed Initials References http://www.crla.net/itpc/index.htm Elder, L. & Paul, R. (1996). Critical Thinking Development: A Stage Theory. Foundation for Critical Thinking, 1-11. Retrieved from http://www.criticalthinking.org/print- page.cfm?pageID=483 Fitchburg State University. (2000-2011). Tutor Training Guidebook: Philosophy and Code of Ethics. Retrieved from http://www.fitchburgstate.edu/tutoring/tutorguidebook/philosophy.cfm Kneller, G. F. (1964). Twentieth Century Theories of Education. Introduction to the Philosophy of Education. Retrieved from http://people.morehead-st.edu/fs/w.willis/fourtheories.html Merriam, S.B. (2001). Andragogy and Self Directed Learning: Pillars of Adult Learning Theory. New Directions for Adult and Continuing Education, 89, 3-13 Rogers, C., & Farson, R. (2007). Active Listening. Gordon Training International, 1-8 Supplemental Instruction. (2011, January 25). In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 14:11, January 25, 2011, from http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index. php?title=Supplemental_Instruction&oldid=409963027 http://www.umkc.edu/cad/si/overview.shtml Page 8