Incomplete Dominance PPT
advertisement
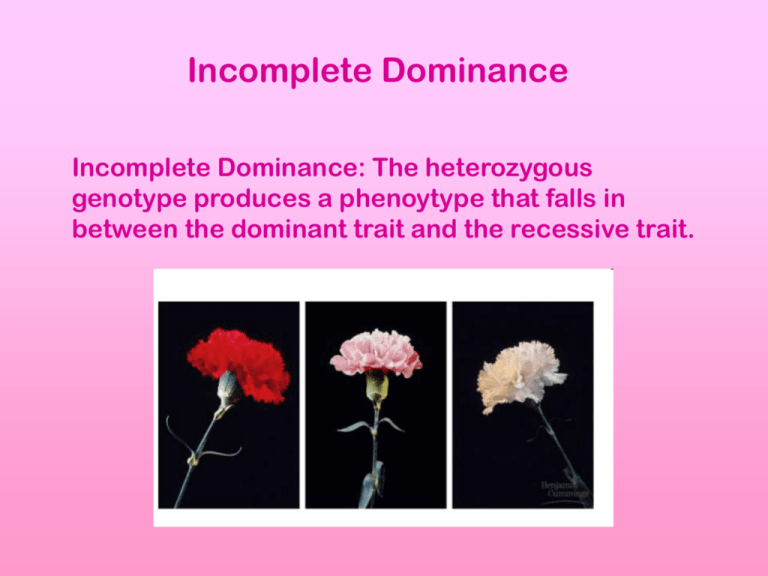
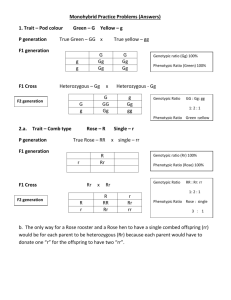
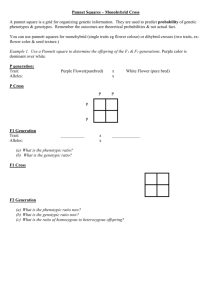
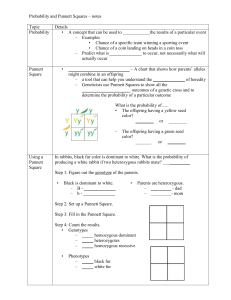
Incomplete Dominance Incomplete Dominance: The heterozygous genotype produces a phenoytype that falls in between the dominant trait and the recessive trait. Example: In flowers, petal color demonstrates incomplete dominance. Red results when a flower has homozygous dominant alleles for the trait. White results when a flower has homozygous recessive alleles for the trait. A flower that is heterozygous for this trait will be pink. Predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring for the following: 1. Red and white R RR x rr R Genotypic Ratio: 100% Rr r Rr Rr Phenotypic Ratio: r Rr Rr 100% pink flowers Example: In flowers, petal color demonstrates incomplete dominance. Red results when a flower has homozygous dominant alleles for the trait. White results when a flower has homozygous recessive alleles for the trait. A flower that is heterozygous for this trait will be pink. Predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring for the following: 2. Red and pink R r RR x Rr Genotypic Ratio: 50% RR 50% Rr R R RR RR Phenotypic Ratio: Rr 50% Red flowers, 50% Pink flowers Rr White and Pink rr x Rr Genotypic Ratio: r r R Rr r Pink and Pink Rr 50% Rr 50% rr Phenotypic Ratio: 50% Pink flowers 50% White flowers rr rr Rr x Rr Genotypic Ratio: R r RR Rr R r Rr rr 25% RR 50% Rr 25% rr Phenotypic Ratio: 25% Red flowers 50% Pink flowers 25% White flowers Codominance Codominance: condition in which both alleles of a gene are expressed in heterozygous offspring. Example 1: In cows black coat color and white coat color are codominant. Heterozygous offspring will be spotted. 1. Black cow and White cow B BB x WW B Genotypic Ratio: W 100% BW BW BW Phenotypic Ratio: W BW BW 100% Spotted cow Example 1: In cows black coat color and white coat color are codominant. Heterozygous offspring will be spotted. 2. Black cow and Spotted cow B B W BB B BB BB x BW Genotypic Ratio: 50% BB 50% BW Phenotypic Ratio: BW BW 50% Black cow 50% Spotted cow Example 1: In cows black coat color and white coat color are codominant. Heterozygous offspring will be spotted. 3. Both Spotted cows BW x BW Genotypic Ratio: B B BB W 25 % BB 50% BW 25% WW BW Phenotypic Ratio: W BW WW 25% Black cow 50% Spotted cow 25% White cow Example 2: In blood typing, the gene for type A and the gene for type B are codominant. The gene for type O is recessive. Blood Type (phenotype) Genotype A AA or AO B BB or BO AB AB O OO Determine the possible blood types of the offspring when: 1. Mother is type O, Father is type A (homozygous) O O Genotypic Ratio: A AO AO 100% AO Phenotypic Ratio: A AO AO 100% Type A Blood Determine the possible blood types of the offspring when: 2. Mother is type AB, Father is Type A (heterozygous) A A B Genotypic Ratio: 25 % AA 25% AB AA 25% AO 25% BO AB Phenotypic Ratio: O AO BO 50% Type A Blood 25% Type AB Blood 25% Type B Blood Determine the possible blood types of the offspring when: 3. Mother is type A (heterozygous), Father is type B (heterozygous) A B O Genotypic Ratio: 25 % OO 25% AB AB 25% AO 25% BO BO Phenotypic Ratio: O AO OO 25% Type O Blood 25% Type A Blood 25% Type AB Blood 25% Type B Blood Determine the possible blood types of the offspring when: 4. Mother is type B (homozygous), Father is type A (homozygous) B B Genotypic Ratio: A AB AB 100% AB Phenotypic Ratio: A AB AB 100% Type AB Blood