Paediatric Rashes
advertisement
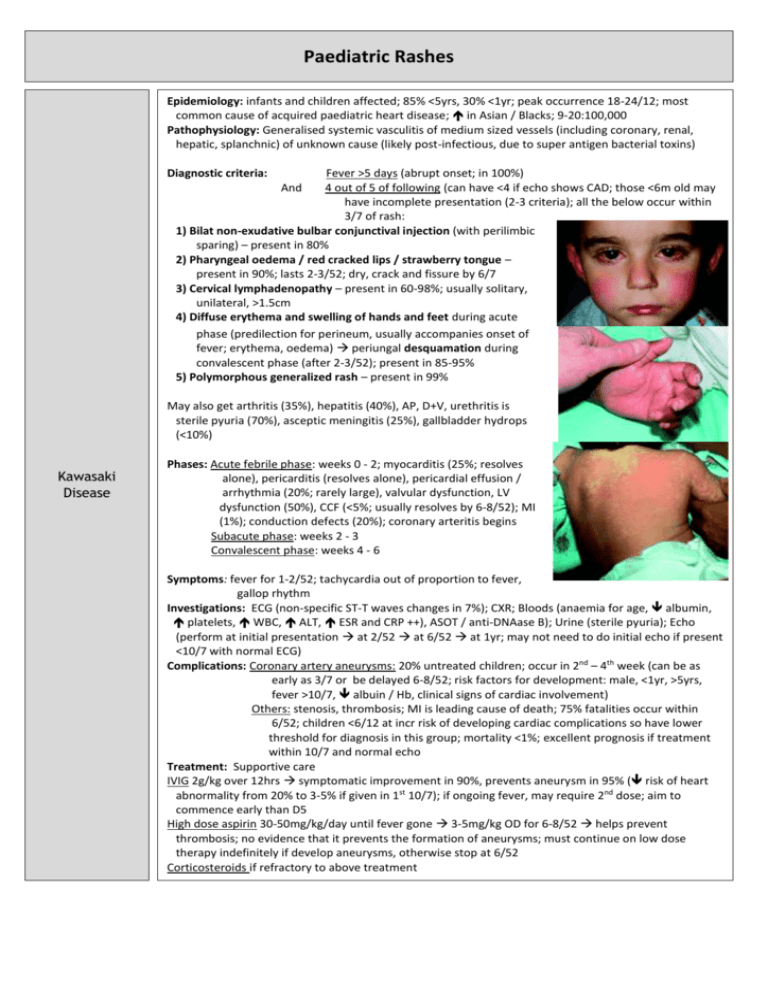
Paediatric Rashes Epidemiology: infants and children affected; 85% <5yrs, 30% <1yr; peak occurrence 18-24/12; most common cause of acquired paediatric heart disease; in Asian / Blacks; 9-20:100,000 Pathophysiology: Generalised systemic vasculitis of medium sized vessels (including coronary, renal, hepatic, splanchnic) of unknown cause (likely post-infectious, due to super antigen bacterial toxins) Diagnostic criteria: Fever >5 days (abrupt onset; in 100%) 4 out of 5 of following (can have <4 if echo shows CAD; those <6m old may have incomplete presentation (2-3 criteria); all the below occur within 3/7 of rash: 1) Bilat non-exudative bulbar conjunctival injection (with perilimbic sparing) – present in 80% 2) Pharyngeal oedema / red cracked lips / strawberry tongue – present in 90%; lasts 2-3/52; dry, crack and fissure by 6/7 3) Cervical lymphadenopathy – present in 60-98%; usually solitary, unilateral, >1.5cm 4) Diffuse erythema and swelling of hands and feet during acute phase (predilection for perineum, usually accompanies onset of fever; erythema, oedema) periungal desquamation during convalescent phase (after 2-3/52); present in 85-95% 5) Polymorphous generalized rash – present in 99% And May also get arthritis (35%), hepatitis (40%), AP, D+V, urethritis is sterile pyuria (70%), asceptic meningitis (25%), gallbladder hydrops (<10%) Kawasaki Disease Phases: Acute febrile phase: weeks 0 - 2; myocarditis (25%; resolves alone), pericarditis (resolves alone), pericardial effusion / arrhythmia (20%; rarely large), valvular dysfunction, LV dysfunction (50%), CCF (<5%; usually resolves by 6-8/52); MI (1%); conduction defects (20%); coronary arteritis begins Subacute phase: weeks 2 - 3 Convalescent phase: weeks 4 - 6 Symptoms: fever for 1-2/52; tachycardia out of proportion to fever, gallop rhythm Investigations: ECG (non-specific ST-T waves changes in 7%); CXR; Bloods (anaemia for age, albumin, platelets, WBC, ALT, ESR and CRP ++), ASOT / anti-DNAase B); Urine (sterile pyuria); Echo (perform at initial presentation at 2/52 at 6/52 at 1yr; may not need to do initial echo if present <10/7 with normal ECG) Complications: Coronary artery aneurysms: 20% untreated children; occur in 2nd – 4th week (can be as early as 3/7 or be delayed 6-8/52; risk factors for development: male, <1yr, >5yrs, fever >10/7, albuin / Hb, clinical signs of cardiac involvement) Others: stenosis, thrombosis; MI is leading cause of death; 75% fatalities occur within 6/52; children <6/12 at incr risk of developing cardiac complications so have lower threshold for diagnosis in this group; mortality <1%; excellent prognosis if treatment within 10/7 and normal echo Treatment: Supportive care IVIG 2g/kg over 12hrs symptomatic improvement in 90%, prevents aneurysm in 95% ( risk of heart abnormality from 20% to 3-5% if given in 1st 10/7); if ongoing fever, may require 2nd dose; aim to commence early than D5 High dose aspirin 30-50mg/kg/day until fever gone 3-5mg/kg OD for 6-8/52 helps prevent thrombosis; no evidence that it prevents the formation of aneurysms; must continue on low dose therapy indefinitely if develop aneurysms, otherwise stop at 6/52 Corticosteroids if refractory to above treatment Scarlet Fever Aetiology: Group A beta-haemolytic strep erythrogenic toxin Incubation: 2-4/7 (ie. Short) Symptoms: Acute onset fever, sore throat, headache, vomiting, abdominal pain exanthem develops over 1-2/7 Red tonsils and pharynx covered in exudates; Bright red / haemorrhagic spots on soft palate Tongue white coating through which red hyptertrophied papillae project (white strawberry tongue) White coating disappears after 4-5/7 red strawberry tongue After 12-48hrs Red, finely punctate 1-2mm blanching papules (rough sandpaper) on neck, axillae and groin Rapidly spreads to trunk and extremities Linear petechial eruptions in antecubital and axillary folds (Pastia’s lines) Facial flushing and circumoral pallor Fades at 6/7 Desquamates at 2/52, on hands and feet 1st Complications: otitis media, sinusitis, rheumatic fever, post-strep glomerulonephritis Investigations: ASOT, swab Treatment: Penicillin 10/7 Aetiology: RNA myxovirus Epidemiology: rare in immunised; now mostly seen in older patients; highly infectious (90% susceptible close contacts will become infected Incubation: 7-18/7 (av 10/7); 14/7 between exposure and rash; patient infectious from 5/7 before rash to 4/7 after rash Measles Case definition: 3-4/7 URTI rash 1. Fever >38 (ie. High) 2. Rash: fever always present at time of onset of rash; behind ears and at hairline spreads from head to feet, inc palms and soles; erythematous maculopapular, red blanching confluence esp on face copper-brownish hue as resolves desquamates after 3/7; lasts 1/52 3. 1 of cough / coryza / conjunctivitis / Koplick spots (white, bluish-white 1mm spots with red base on buccal mucosa; appear 1/7 before rash); may have generalised lymphadenopathy; may be diarrhoea Complications: otitis media (2.5%), pneumonia (4%; responsible for 50% deaths); encephalitis (0.1%; onset 1-2/52 after disease; mortality 10-15%; permanent neuro damage in 40%); subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (can occur 4-10yrs later, progressive mental deterioration and death); myocarditis, nephritis, hepatitis, pericarditis, keratitis Investigations: swab for PCR (will be +ive within few days, when serology may still be negative; also useful in immunocomp); blood for serology (IgM = infection, levels peak at 7-10/7; IgG = immunity; may be negative if <4/7 from onset fever, need to do repeat after 1/52, remains +ive for 3/12, sensitivity 100%, specificity 98%); double bag specs and don’t send through lamsen Treatment: Supportive; need infection control measures; notifiable disease; no school / child care for 5/7; admit if: poor PO intake, respiratory compromise, CNS complications Prophylaxis: Exposed if: enter same room within 2 hours of infected person leaving Non-immune if: not had 2x MMR and born after 1969, from 6/12 to 1st vaccine, if >4yrs and not had 2nd vaccine, pregnant, immunocomp, or prem <28/40 Offer MMR if <72hrs (not if pregnant); if immunocompromised / pregnant / >72hrs, consider Ig Henoch Scholein Purpura (HSP) is NOT a platelet problem Epidemiology: 2:1000; more Asian / Indian; usually 4-6yrs (2-11yrs) Aetiology: Allergic vasculitis, follows URTI, IgA mediated; associated with infection, drugs, vaccines; may be post Grp A strep Pathology: Small vessels (skin, GI tract, kidneys, joints) Symptoms: Palpable purpura on buttocks and legs (extensor surface) – presenting symptom in 50%; maybe also erythematous, urticarial, echymoses, petechaie Abdominal pain (+ nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea; in 60-80%; diffuse and colicky; occurs after rash; 50% have blood in stool; 5% get acute GI haemorrhage; 3% get intussusception) Migratory polyarthralgia (66-80%; presenting symptom in 25%; usually resolves after 24-48hrs; in gravity dependent joints) Renal failure (in 20-50%) – nephritic syndrome Generalized oedema (eg. Feet; often painful) Investigations: haematuria and proteinuria in 90%; urine, FBC (platelets normal); U+E’s Complications: Nephritic / nephrotic syndrome, ARF (<1%), HTN; if proteinuria = more severe and needs follow up; Intussusception (5%); bowel perforation Management: Usually resolves in 3-4/52; supportive; monitor BP and urine for 6/12; IV fluids if ill; NSAIDS; Consider prednisone 1mg/kg for 2/52 (if abdominal, joint or scrotal disease; may prevent renal complications (2% get long term renal impairment); helps joint pain, abdominal pain, oedema) Admit if: abdominal, renal complications; symptomatic relief Echovirus 9, Coxsackie virus A9 Enteroviruses Enterovirus (hand, foot and mouth disease) Coxsackie virus (herpangina) Transmission: Fecal-oral, oral-oral, respiratory-oral Symptoms: Non-specific febrile illnesses, respiratory tract infection, GI symptoms, meningitis; variety of rashes; Maculopapular rash beginning on face and neck, extending to trunk and feet; may be lesions on buccal mucosa and soft palate (resemble Koplik spots); maybe petechiae, vesicles, urticaria Duration: 5/7 Symptoms: Fever, anorexia, malaise, sore mouth 1-2/7 later, oral lesions then cutaneous lesions Oral lesions: painful 4-8mm vesicles on erythematous base on buccal mucosa, tongue, soft palate, gingiva ulcerate Cutaneous lesions: 3-7mm red papules grey vesicles on palms and soles (may be dorsum of feet and buttocks) heal in 7-10/7 Treatment: Hydration, analgesia, mouthwash Symptoms: Fever, mouth pain, oral ulcers Similar ulcers to hand, foot and mouth, but no skin lesions Rubella Erythema Infectiosum (Fifth Disease, Slapped Cheek) Incubation: 12-25/7 Symptoms: 1-5/7 fever, malaise, headache, sore throat irregular pink macules and papules on face, spreading to neck, trunk and arms; coalesces then clears Forchheimer spots: pinpoint petechiae on soft palate that coalesce Suboccipital and posterior auricular lymphadenopathy Treatment: Supportive Symptoms: Abrupt appearance of rash fiery red rash on cheeks; diffuse erythema of closely grouped tiny papules on erythematous base; edges slightly raised; circumoral pallor; sparing of eyelids and chin; lasts 4-5/7 1-2/7 after face rash nonpruritic macular/maculopapular erythema on trunk and upper limbs spreads; lasts 1/52; spares palms and soles; fades with central clearing Associated with fever, malaise, headache, sore throat, cough, coryza, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, myalgia Treatment: Supportive Herpes Transmission: HSV-2 genital, HSV-1 oral Symptoms: Herpes labialis, gingivostomatitis – painful umbilicated vesicles unroof and crust over Eczema herpiticum – break out on area previously affected by eczema Herpetic whitlow – distal fingers Treatment: Consider sexual abuse; Oral acyclovir; supportive Chickenpox Symptoms: Pruritic generalized vesicular exanthem with mild systemic symptoms; starts on trunk / scalp as faint red macules vesicular in 24hrs, on erythematous base dry and crust; widespread, palms and soles spared; may occur on mucous membranes Treatment: Supportive if uncomplicated; cleanse lesions to prevent secondary infection; antivirals only if immunocompromised If neonate exposed: nil treatment, present if develops chickenpox then treat with IV aciclovir Roseola Infantum (Sixth Disease) Impetigo Staph Scalded Skin Syndrome Erysipelas Scabies Symptoms: Abrupt onset of fever lasting 3-5/7, cough, coryza, anorexia, abdominal discomfort fever settles appearance of rash over 1-2/7. Erythematous, blanching, macular/maculopapular eruption, discrete rose / pale pink 2-5mm lesions; most on neck, trunk and buttocks; can also involve face and arms. No mucous membrane involvement. Lasts 1-2/7 fades rapidly. Treatment: Supportive Aetiology: Staph aureus, beta-haemolytic strep Symptoms: Lesions on face, neck, and extremities; usually no systemic symptoms Nonbullous: small erythematous macules and papules thin walled vesicles pustules rupture golden yellow crust smooth red surface underneath; may become confluent; local adenopathy Bullous: local; toxin causes separation of skin and bullae; thin walled bullae 0.5-3cm, filled with clear-yellow fluid, rupture easily Treatment: Nonbullous: topical; oral only if severe Symptoms: systemic; malaise, fever, irritability, tender skin; extensive areas of exfoliation; Nikolsky Treatment: inpatient, IVABx; may require admission to Burns unit Aetiology: Group A beta-haemolytic strep Symptoms: Fever, chills, malaise, vomiting; Local redness, heat, swelling; raised indurated border; well demarcated Treatment: Penicillin / erythromycin Symptoms: Severe pruritis; generalized eruption of linear burrows, papules, pustules, vesicles; mostly affect hand, feet, groin; excoriation from scratching Treatment: Permethrin Erythema Toxicum Seborrhoeic Dermatitis Symptoms: Erythematous macules 2-3cm on face, trunk, extremities; central 1-3mm pustules Treatment: None Symptoms: Greasy yellow/red scales, mostly on scalp; not pruritic Treatment: Mineral oil