File
advertisement

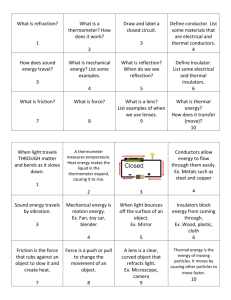
Data Table: Investigation 11 Material Time (minutes:seconds) for each wax dot to melt Wax dot 1 Wax dot 2 Wax dot 3 Wax dot 4 solid steel rod solid brass rod solid glass rod solid aluminum rod hollow brass rod hollow aluminum rod Data Table: Investigation 11 Material solid steel rod solid brass rod solid glass rod solid aluminum rod hollow brass rod hollow aluminum rod Time (minutes:seconds) for each wax dot to melt Wax dot 1 Wax dot 2 Wax dot 3 Wax dot 4 Making Sense of Energy Scientists and engineers have a word, conductivity, which is used to describe how well heat energy moves through a solid. Sometimes the phrase thermal conductivity is used to be sure that there is no confusion with electrical conductivity. If a material has a high conductivity, then heat energy can move through it faster than a material having a low conductivity. Like density, the conductivity is a property of a substance, and is not a property of an object. For example, the conductivity of a steel nail is the same as the conductivity of the steel hull of a huge aircraft carrier. Objects like frying pans and woodstoves are designed to transfer heat energy, so they will be made from materials that are good conductors. Other objects like winter gloves are designed to slow down heat transfer, and are made from materials that are poor conductors. Thermal insulators (poor thermal conductors) are good at keeping hot things hot and also keeping cold things cold. The thermal conductivity of a substance is an important property that must be considered when using the substance to make products. We have seen that some materials conduct heat energy more effectively than other materials. Metals, as a general rule, are good conductors, and glasses are poor conductors. As poor as glasses are at conducting heat energy, they are far from being the worst conductors. There are materials; like wood, foam products, and some fabrics; that are much poorer thermal conductors than glass. These products are so poor at conducting heat energy, they are called thermal insulators, and they are used to help keep heat energy from moving. If it is desirable to keep heat energy from escaping a container, thermal insulators are used to make the walls or line the walls of the container. The container can be as small as a thermos bottle designed to hold hot coffee, or as large as a house. In both cases, the plan is to keep heat energy from leaving the container. It is impossible to completely stop the heat energy from conducting out, but good thermal insulators slow down conduction dramatically, keeping the inside of the container warm or even hot. 1. Which substance tested is the best conductor of heat energy, and which is the poorest conductor? 2. Is there a small difference or a large difference in the conductivity of metals and glass? Explain. 3. How can good insulators help keep the inside of a container cold when it is hot outside, but also keep the inside of a container hot when it is cold outside? 4. Did the wax drops take the same time to melt on the hollow bar as they did on the solid bar that was made from the same material? If the answer is NO, does energy pass through a hollow bar faster or slower than it does through the solid bar of the same material? 5. Can you explain why heat energy moves differently through the hollow bars than it did through the solid bars?