Name ______ Exploring Plate Tectonics by Using Graham Crackers
advertisement
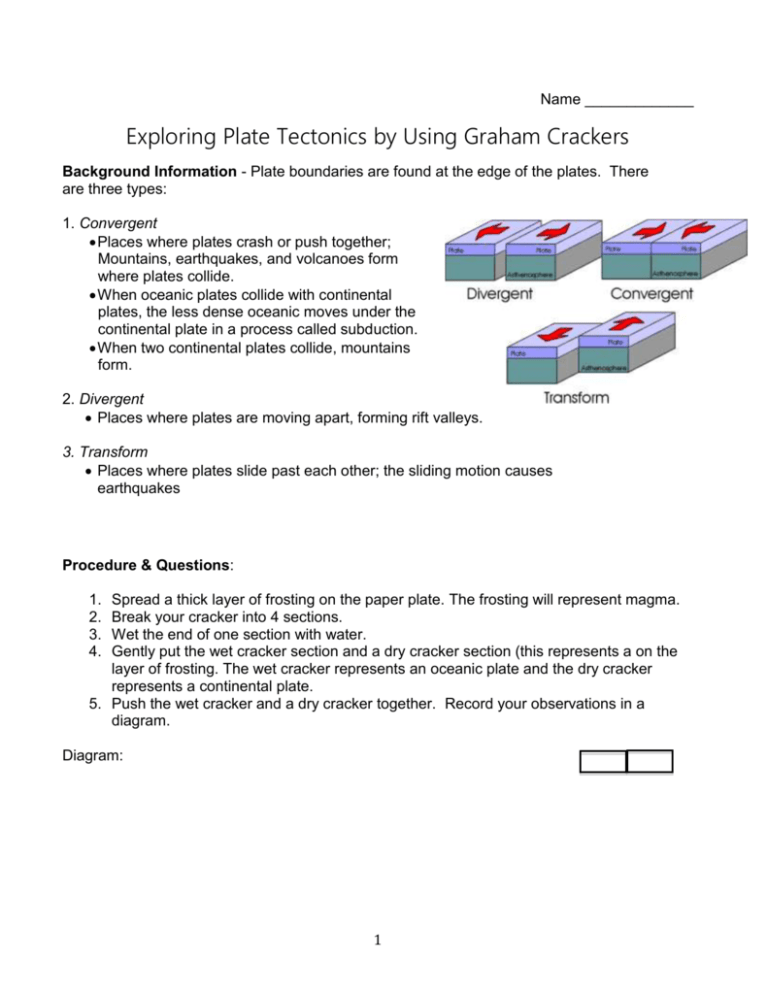
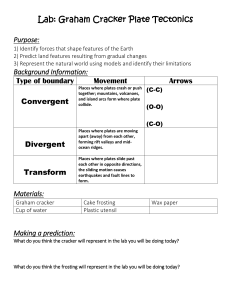
Name _____________ Exploring Plate Tectonics by Using Graham Crackers Background Information - Plate boundaries are found at the edge of the plates. There are three types: 1. Convergent Places where plates crash or push together; Mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes form where plates collide. When oceanic plates collide with continental plates, the less dense oceanic moves under the continental plate in a process called subduction. When two continental plates collide, mountains form. 2. Divergent Places where plates are moving apart, forming rift valleys. 3. Transform Places where plates slide past each other; the sliding motion causes earthquakes Procedure & Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Spread a thick layer of frosting on the paper plate. The frosting will represent magma. Break your cracker into 4 sections. Wet the end of one section with water. Gently put the wet cracker section and a dry cracker section (this represents a on the layer of frosting. The wet cracker represents an oceanic plate and the dry cracker represents a continental plate. 5. Push the wet cracker and a dry cracker together. Record your observations in a diagram. Diagram: 1 What tectonic process(s) does this model? What do you think happens as a continental and oceanic plate push together? What is a limitation of this model? 6. Place two pieces of dry cracker side by side on the frosting. Slide them past each other. The dry crackers represent continental plates. Record your observations in a diagram. Diagram: What tectonic process(s) does this model? What do you think happens when two continental plates slide past one another? What is a limitation of this model? 7. Place two pieces of dry crackers end to end with one another. Push them together. Record your observations in a diagram. Diagram: 2 What tectonic process(s) does this model? What do you think happens when two plates push together? What is a limitation of this model? 8. Pull the two pieces of dry crackers away from each other. Record your observations in a diagram. Diagram: What tectonic process(s) does this model? What do you think happens when two plates move away from each other? What is a limitation of this model? 3