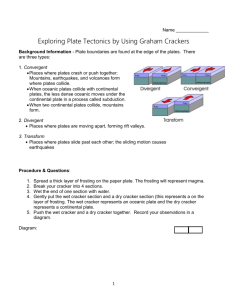
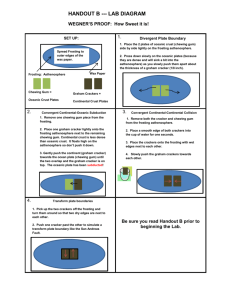
Lab: Graham Cracker Plate Tectonics Purpose: 1) Identify forces that shape features of the Earth 2) Predict land features resulting from gradual changes 3) Represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations Background Information: Type of boundary Movement Convergent Places where plates crash or push together; mountains, volcanoes, and island arcs form where plate collide. Arrows (C-C) (O-O) (C-O) Divergent Transform Places where plates are moving apart (away) from each other, forming rift valleys and midocean ridges. Places where plates slide past each other in opposite directions, the sliding motion causes earthquakes and fault lines to form. Materials: Graham cracker Cup of water Cake frosting Plastic utensil Wax paper Making a prediction: What do you think the cracker will represent in the lab you will be doing today? What do you think the frosting will represent in the lab you will be doing today? Lab: Graham Cracker Plate Tectonics Procedure & Questions: Procedure #1 1. Spread a thick layer of frosting on the wax paper 2. Break your cracker into 4 sections 3. Wet the end of one section with water. 4. Gently put the wet cracker section and a dry cracker section on the layer of frosting. 5. Push the wet cracker and a dry cracker together. Questions: 1. What does the wet cracker represent? 2. What does the dry cracker represent? 3. What type of boundary does this represent? Draw and label a diagram of this process: Procedure #2 1. Place two dry crackers side by side on the frosting. 2. Slide them past each other. Questions: 1. What tectonic process does this model? Draw and label a diagram of this process: Lab: Graham Cracker Plate Tectonics Procedure #3 1. Place a dry cracker end to end with another dry cracker on the frosting. 2. Push them together towards each other. Questions: 1. What type of boundary does this model? 2. What type of plates are involved? Draw and label a diagram of this process: Procedure #4 1. Take two pieces of dry crackers and place them side by side on the frosting. 2. Push the crackers down and out in opposite directions at the same time. Questions: 1. What type of boundary does this model? 2. What type of plates are involved? Draw and label a diagram of this process: