Density of Earth Materials Study Guide
advertisement

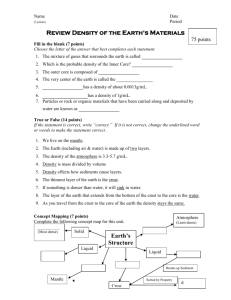
Density of Earth Materials Study Guide Read this! Make sure you understand… 1. Examine the effects of density and particle size on the behavior of materials in mixtures. a. Compare the density of various objects to the density of known earth materials. b. Calculate the density of earth materials (e.g., rocks, water, air). c. Observe and describe the sorting of earth materials in a mixture based on density and particle size (e.g., sorting grains of sand of the same size with different densities, sort materials of different particle size with equal densities). d. Relate the sorting of materials that can be observed in streambeds, road cuts, or beaches to the density and particle size of those materials. 2. Analyze how density affects Earth's structure a. Compare the densities of Earth's atmosphere, water, crust, and interior layers. b. Relate density to the relative positioning of Earth's atmosphere, water, crust and interior. c. Model the layering of Earth's atmosphere, water, crust, and interior due to density differences. d. Distinguish between models of Earth with accurate and inaccurate attributes. Vocabulary 1. Atmosphere: The layers of air that surround Earth. The most dense atmospheric layers are closer to Earth and the least dense layers are far away from Earth. 2. Density: A comparison of the mass of a substance with its volume. Mathematically, density is calculated as: D=M/V. An object or liquid tends to sink in a liquid with less density than the object. 3. Model: A larger or smaller representation of an item. Study Questions: Answer in complete and thoughtful sentences! 1. A beach is composed of particles of sand of the same size. Why doesn't the beach have materials of all sizes? Answer: The particles have been sorted by size and density 2. Earth’s interior is divided into at least 4 layers. What are the four major divisions in order of least dense to most dense? Answer: Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core 3. Put the following items into a test tube, shake it up, and predict the layering from bottom to top of the outcome of your investigation. Earth materials: air, gravel, water, sand and gold dust. Answer: From bottom to top: water mixed in with layered gravel, sand, and gold dust, with air above the mixture 4. In an experiment, students shook jars of water with soil and rock in them. What does the shaking model in nature? Answer:A stream environment 5. A student collected data about the density of air. She found that .1 g of air had a volume of 100 cm3. What is the density of the air? Answer: .001 g/ cm3 6. As technology get metter, what weill change with the models of the Earth’s structure? Answer: Models will probably change because new technology will provide better information about the structure of Earth. 7. Water has a density of 1 gram/milliliter. There are four rocks that all have the same volume of 5 cubic centimeters. What must the mass be less than for the rock to float when placed in water? Answer: less than 5 grams 8. Why are iron and nickel found in Earth's core? Answer: They have a higher density than most of Earth's substances 9. In winter, a layer of cold air settles in the valleys and warmer air is often found higher in the mountains. What might account for this condition? Answer: Cold air is denser than warm air 10. In the past, many people thought that Earth was hollow. Why is this model of Earth not accepted now? Answer: Today scientists have collected data that support a layered model of Earth. 11. A balloon filled with helium rises into the air. Why? Answer: The helium is less dense than air 12. A square chunk of plastic has a length of 5 cm, width of 5 cm and height of 5 cm. It has a mass of 200 g. What is its density Answer: 1.6 g/cm3 13. A streambed contains round rocks, all about the same size. Why are there no smaller particles of sand and clay? Answer: Sand and clay have washed away 14. A group of students designed an experiment to test the effect of density on the sorting of Earth materials. They added particles of various sizes: sand, gravel and clay. They were mixed in a jar and water was added. They shook the mixture and then let it settle. The jar looked like this when they were done: Their conclusion was "Gravel is the most dense because it sank to the bottom first. Sand is less dense than gravel and clay is least dense." How good is the group's conclusion? Answer: poor, they did not measure density