Osmosis, diffusion, and active transport modeling
advertisement

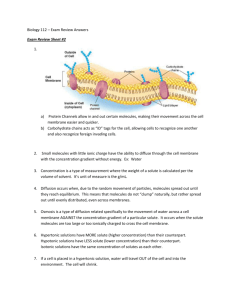
Modeling – Osmosis, Diffusion, and Active Transport Purpose: To explain how a concentration gradient causes diffusion of molecules across the cell membrane. Materials: Model cut-outs (cut-out) Cell membrane drawing Modeling Procedures - Osmosis: 1. Set-up your model by showing 10 sodium molecules inside the cell and 6 sodium molecules outside the cell. You also need o place 6 water molecules inside the cell and 10 water molecules outside the cell. 2. Demonstrate osmosis. 3. Draw the before and after diagrams below. 4. Color the water molecules blue and the sodium molecules red. 5. Include arrows showing which way movement is occurring. Before After Modeling Procedures – Passive Diffusion 1. Set-up your model by showing 2 oxygen molecules inside the cell and 6 oxygen molecules outside the cell. 2. Show how molecules move by passive diffusion using your model pieces. 3. Draw the before and after diagrams below. 4. Color the oxygen molecules green. 5. Include arrows showing which way movement is occurring. Modeling Procedures – Facilitated Diffusion 1. Set-up your model showing 1 glucose molecule inside the cell and 5 glucose molecules outside the cell. 2. Demonstrate active diffusion by showing the movement of glucose through the protein channel. 3. Draw the before and after below. You will need to draw in the protein channel using a brown pencil. 4. Color the glucose molecules yellow. 5. Include arrows showing which way movement is occurring. Modeling Procedures – Active Transport 1. Set-up your model by showing 7 sodium molecules and 3 water molecules on the inside of the cell. You should have 3 sodium molecules, 3 water molecules, and an ATP molecule on the outside of the cell. 2. Demonstrate active transport by moving the sodium molecules, out of the cell, across the cell membrane. (You will need to place the ATP molecule on the protein channel to model the use of energy. You can move 3 sodium molecules with 1 ATP molecule.) 3. Draw the before and after. You will need to draw in the protein channel using a brown pencil. 4. Color the water molecules blue, sodium molecules red, and ATP molecule purple. 5. Include arrows showing which way movement is occurring.. Conclusion Questions: Osmosis 1. In the beginning, there is more sodium _________________ the cell. There is more water __________________ the cell. 2. Explain why water molecules move across the membrane. 3. After the diffusion of water, how much water is inside the cell compared to outside the cell? Why? How much sodium? Why? Passive Diffusion 4. Explain what causes oxygen molecules to move across the membrane. 5. What is passive diffusion? 6. What are some molecules that can move by passive diffusion? Facilitated Diffusion 7. Why do glucose molecules require a channel protein? 8. How is the transport of glucose the same as passive diffusion? How is it different? 9. Why is the diffusion of glucose “facilitated”? Active Transport 10. Describe and explain how sodium molecules move across the membrane. 11. What is necessary for a molecule to move with active transport? 12. Why do molecules like sodium enter the cell by active transport and not passive diffusion? 13. Give an example of a cell that uses active transport to move molecules across its membrane.