Analytical Chemistry - Spectroscopy STUDENT
advertisement

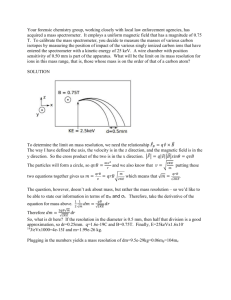
Analytical Chemistry – Spectroscopy (multiple choice) 1. Which pair of substances could be distinguished from one another by using a flame test? A Butane and octane B Sodium chloride and potassium chloride C Calcium carbonate and calcium chloride D Chlorophyll A and chlorophyll B 2. Which of the following components of a UV-visible spectrometer is used to focus the light from the lamp into a single beam? A Monochromator B Slit C Cuvette D Mirror 3. When an electron has been excited from the 5th shell to the 2nd shell and then returns to the ground state, the number of different possible wavelengths of light emitted is: A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6 4. Which one of the following bands of the electromagnetic spectrum is involved in analysis of substances by NMR spectroscopy? A Radio waves B Microwaves C UV waves D X-rays 5. A diluted solution of a lime-flavoured cordial containing the blue dye FCF (no. 133) showed the following absorbance spectrum when tested in a UV-visible spectrometer. What wavelength is likely to be selected for the analysis of the blue dye in the cordial, and in what region of the spectrum for visible light would this wavelength be located? A 660 nm; in the orange–red region of visible light B 660 nm; in the blue region of visible light C 600 nm; in the orange–red region of visible light D 600 nm; in the blue region of visible light 6. The calibration curve for the analysis of the blue dye FCF (no. 133) in foods using UV-visible spectrophotometry is shown below. A student dissolved 3.0 g of quandong favoured jelly crystals that contain this dye, and made up 100 mL of solution. The absorbance of the solution was 0.31. What was the concentration of the blue dye in the jelly crystals in %(w/w)? A 0.0020 %(w/w) B 0.020 %(w/w) C 0.20 %(w/w) D 2.0 %(w/w) 7. Propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol are structural isomers that are drawn below. Which of the following peaks will occur on the mass spectrum of propan-1-ol but not that of propan-2-ol? A 15 B 29 C 45 D 60 8. A forensic chemist was asked to analyse some tablets found by sporting officials during a routine check of the changing rooms at a sports stadium during an international event. Suspecting that the active ingredient was a performance-enhancing drug, the chemist first separated it from the mixture in the tablet and then analysed the isolated substance to deduce its structure. An instrument that could be used to separate the active ingredient from the mixture in the tablet and an instrument that could then be used to identify the functional groups present in molecules of the suspect substance are, respectively: A gas chromatograph; atomic absorption spectrometer B mass spectrometer; infrared spectrometer C high performance liquid chromatograph; infrared spectrometer D mass spectrometer; NMR spectrometer 9. Suppose an AAS is used to determine the concentration of iron ions in a can of soup to assess the extent to which the steel can has corroded. Which of the following is NOT an essential feature of the light emitted by the lamp used for this analysis? A It must be rapidly turned on and off (pulsed). B It must consist of wavelengths that are only absorbed by iron atoms. C Only a strongly absorbed wavelength present in this light can reach the detector. D It must be passed through a transparent cell containing the test sample. 10. In UV-visible spectrophotometry and atomic absorption spectroscopy, what does absorbance measure? A The fraction of light of a particular wavelength absorbed by a sample B The fraction of light of a particular wavelength transmitted by a sample C The total amount of light energy absorbed by a sample D The intensity of light that emerges from a sample 11. In order to determine the iron content of a sample of canned tuna, analysts first established a calibration curve for the absorbance of a series of standard solutions of iron(III), using an atomic absorption spectrometer. This is shown below. They then finely ground the contents of a can of tuna and added a 25-g sample of the tuna mixture to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and made up the volume to 100.00 mL. They determined its absorbance to be 8 %. What was the concentration of iron in the original tuna sample in ppm(w/w)? A 80 ppm(w/w) B 20 ppm(w/w) C 8 ppm(w/w) D 2 ppm(w/w) 12. With what is a sample bombarded when it is introduced into a mass spectrometer? A X-rays B Particles of the carrier gas C High-speed electrons D Gamma rays from a radioactive isotope 13. A mass spectrometer can also be used to determine the number of isotopes of an element, their relative isotopic masses and percentage abundance. Chlorine has two isotopes: chlorine-35, which has a percentage abundance of 75.8 %, and chlorine-37. What would be the mass/charge ratio of the principal peaks on the mass spectrum of chlorine molecules, Cl2, and which peak would be the highest peak? A 35, 37; highest peak 35 B 35, 37, 70, 74; highest peak 35 C 35, 37, 70, 74; highest peak 70 D 35, 37, 70, 72, 74; highest peak 70 14. What occurs at the molecular level when molecules are irradiated with infrared radiation? A The energy of the radiation is sufficient to cause the molecules to fragment. B The molecules absorb the energy of the radiation and begin to vibrate. C The molecules absorb the energy of the radiation and stretch out. D The bonds in the molecules absorb discrete amounts of energy. 15. How many absorption bands would you expect to see in the infrared spectrum of ethene, CH2=CH2? A 2 C 4 B 3 D 5 16. What is the meaning of the term wavenumber, which is used in IR spectroscopy? A It is the reciprocal of the wavelength of radiation of particular energy. B It is the number of waves that pass through a particular point each second. C It is another term for the energy of radiation in the IR band. D It is the total number of wavelengths of IR radiation absorbed by the compound. 17. Proteins and peptide are biomolecules consisting of chains of amino acid monomers. However, peptide molecules are much smaller than protein molecules. Which of the following types of analysis can give the most information about the 3-D structure of a particular peptide? A High performance liquid chromatography and X-ray crystallography B X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy C Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mass spectrometry D Infrared spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy 18. What is the main nucleus present in organic compounds that is used in analysis by NMR spectroscopy? A Hydrogen-1 nucleus B Hydrogen-2 nucleus C Carbon-12 nucleus D Carbon-13 nucleus 19. How many peaks would you expect to see on the low resolution NMR spectrum of 1-chloroethane, CH3CH2Cl? (Disregard the signal due to TMS.) A 1 C 3 B 2 D 5 20. Shown below is the structure of ethyl benzene. t has three peaks on its low-resolution NMR spectrum, not including the peak due to TMS. From left to right on this spectrum, the integration curve shows that the areas under the peaks are in the ratio 5 : 2 : 3. Into how many peaks will the third peak (the peak furthest on the right) split in the high-resolution NMR spectrum of this compound? A 2 C 4 B 3 D 5