Economics Reading Questions: Modules 74 & 75
advertisement

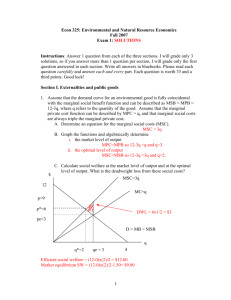
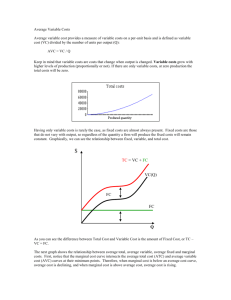
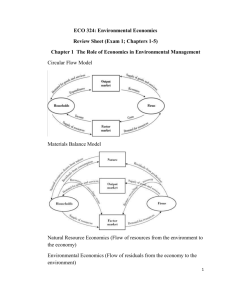
Economics Mr. Bekemeyer Section 14 Reading Questions (Modules 74 & 75) Module 74 (Pages 723 - 729) Check Your Understanding 1. 2. Wastewater runoff from large poultry farms adversely affects residents in neighboring homes. Explain the following: a. why this is considered an externality problem b. the efficiency of the outcome with neither government intervention nor a private deal c. how the socially optimal outcome is determined and how it compares with the nointervention, no-deal outcome. According to Yasmin, any student who borrows a book from the university library and fails to return it on time imposes a negative externality on other students. She claims that rather than charging a modest fine for late returns, the library should charge a huge fine, so that borrowers will never return a book late. Is Yasmin's economic reasoning correct? Tackle the Test: Multiple-Choice Questions 1. The socially optimal level of pollution is A) B) C) D) E) 2. Which of the following is a source of negative externalities? A) B) C) D) E) 3. Less than that created by the market, but not zero More than that created by the market Whatever the market creates Determined by firms Zero Loud conversations in a library Smokestack scrubbers A beautiful view National defense A decision to purchase dressy but uncomfortable shoes Inefficiencies created by externalities can be dealt with through A) B) C) D) E) Government actions only Private actions only Market outcomes only Either private or government actions Neither private nor government actions 4. The Coase theorem asserts that, under the right circumstances, inefficiencies created by externalities can be dealt with through A) B) C) 5. Lawsuits Vigilante actions Mediation D) E) Private bargaining Government policies Which of the following makes it more likely hat private solutions to externality problems will succeed? A) B) C) High transaction costs Delays in the bargaining process Loosely defined legal rights D) E) High prices for legal services A small number of affected parties Tackle the Test: Free-Response Questions 1. Draw a correctly labeled graph showing the market-determined quantity of pollution, and explain why that quantity will be chosen n the absence of intervention and private deals. On the same graph, show the socially optimal level of pollution. 2. a. Define the marginal social cost of pollution. b. Define the marginal social benefit of pollution, and explain whey polluting more can provide benefits to a firm even when it could produce the same quantity of output without polluting as much. c. Define the socially optimal level of pollution. Module 75 (Pages 731 - 740) Check Your Understanding 1. Some opponents of tradable emissions permits object to them on the grounds that polluters that sell their permits benefit monetarily from their involvement in polluting the environment. Assess this argument. 2. For each of the following cases, explain whether an external cost or external benefit is created and identify an appropriate policy response. a. Trees planted in urban areas improve air quality and lower summer temperatures. b. Water-saving toilets reduce the need to pump water from rivers and aquifers. The cost of a gallon of water to homeowners is virtually zero. c. Old computer monitors contain toxic materials that pollute the environment when improperly disposed of. Tackle the Test: Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Which of the following policy tools is inefficient even when correctly administered? A) B) C) 2. external cost. marginal external cost . price at which MSC = MSB. D) E) marginal social benefit. marginal external benefit. MSC > MSB MSB > MPB MSC > MPC D) E) MPB > MSC MPB > MSB One example of a source of external benefits is A) B) C) 5. Emissions taxes Pigouvian taxes Which of the following is true in the case of a positive externality A) B) C) 4. D) E) An efficient Pigouvian subsidy for a good is set equal to the good’s A) B) C) 3. Environmental standards Tradable emissions permits Cap and trade programs Technology spillover D) Pollution E) Taxes on environmental conservation Traffic congestion Subsidies for polluters Marginal social benefit equal marginal private benefit plus A) B) C) Marginal external benefit Total external benefit Marginal social cost D) E) Marginal private cost Total external cost Tackle the Test: Free-Response Questions 1. The purchase of antivirus software by one person provides benefits to other people because they are less likely to receive a virus from the software purchaser. Draw a correctly labeled graph showing how the market will determine the quantity of antivirus software purchased. On the same graph, show the socially optimal quantity of antivirus software. List two different government policies that could be used to achieve the optimal quantity of antivirus software. 2. The use of plastic water bottles creates external costs as the result of plastic production, bottle transportation, litter, and waste disposal. Draw a correctly labeled graph showing how the market will determine the quantity of water bottles purchased. On the same graph, show the marginal external cost, the socially optimal quantity of water bottles, and the size of a Pigouvian tax that could be used to achieve the socially optimal quantity of water bottles.