The Debate Behind US Intervention in World War II
advertisement

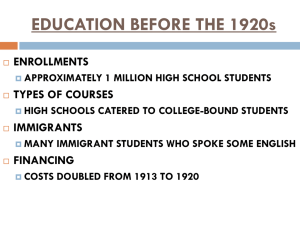
was no longer seasonable as the unimaginable dangers he had barely The Debate Behind U.S. Intervention in World War II By Susan Dunn From The Atlantic glimpsed in 1936 erupted into what he termed a "hurricane of events." On the evening of Sunday, May 26, 1940, days after the Germans began their thrust west, as city after city fell to the Nazi assault, a somber Roosevelt delivered a fireside chat about the dire events in Europe. Earlier that evening, the president had distractedly prepared drinks for a small group of friends in his study. There was none of the usual banter. Dispatches were pouring into the White House. "All bad, all bad," Roosevelt grimly muttered, handing them to Eleanor to read. But in his talk, as he tried to prepare Americans for what might lie ahead, he set a reflective, religious tone. "On this Sabbath evening," he said in his reassuring voice, "in our homes in the midst of our American families, let us calmly consider what we have Left: President Roosevelt signs the declaration of war against Germany; right: Charles Lindbergh in the done and what we must do." But before talking about his decision to vastly famous photo from Lambert Field, St. Louis, Missouri, 1923 (Library of Congress) increase the nation's military preparedness, he hurled an opening salvo at the "DEAR FRISKY," President Roosevelt wrote in May 1940 to Roger isolationists. Merriman, his history professor at Harvard and the master of Eliot House. "I like your word 'shrimps.' There are too many of them in all the Colleges and Universities -- male and female. I think the best thing for the moment is to call them shrimps publicly and privately. Most of them will eventually get in line if things should become worse." They came in different sizes and shapes, he explained. One group of them constituted a Trojan horse of pro-German spies, saboteurs, and traitors. While not naming names, he singled out those who sought to arouse people's "hatred" and "prejudices" by resorting to "false slogans and emotional appeals." With fifth columnists who sought to "divide and weaken us in the To designate young isolationists, who deluded themselves into believing that face of danger," Roosevelt declared, "we must and will deal vigorously." America could remain aloof, secure, and distant from the wars raging in Another group of isolationists, he explained, opposed his administration's Europe, Roosevelt liked the amusing term "shrimps"-- crustaceans policies simply for the sake of opposition -- even when the security of the possessing a nerve cord but no brain. In that critical month of May 1940, he nation stood at risk. finally realized that it was probably a question of when, not if, the United States would be drawn into war. Talk about neutrality or noninvolvement The president recognized that some isolationists were earnest in their beliefs and acted in good faith. Some were simply afraid to face a dark and foreboding reality. Others were gullible, eager to accept what they were told the "gods of force and hate" would endanger all democracies in the western by some of their fellow Americans, that what was happening in Europe was world. In this time of crisis, America could no longer pretend to be "a lone "none of our business." These "cheerful idiots," as he would later call them in island in a world of force." Indeed, the nation could no longer cling to the public, naively bought into the fantasy that the United States could always fiction of neutrality. "Our sympathies lie with those nations that are giving pursue its peaceful and unique course in the world. their life blood in combat against these forces." Then he outlined his policy. They "honestly and sincerely" believed that the many hundreds of miles of salt water would protect the nation from the nightmare of brutality and violence gripping much of the rest of the world. Though it might have been a comforting dream for FDR's "shrimps," the president argued that the isolationist fantasy of the nation as a safe oasis in a world dominated by fascist terror evoked for himself and for the overwhelming majority of Americans not a dream but a "nightmare of a people without freedom -- the nightmare of a people lodged in prison, handcuffed, hungry, and fed through America was simultaneously pursuing two courses of action. First, it was extending to the democratic Allies all the material resources of the nation; and second, it was speeding up war production at home so that America would have the equipment and manpower "equal to the task of any emergency and every defense." There would be no slowdowns and no detours. Everything called for speed, "full speed ahead!" Concluding his remarks, he summoned, as he had in 1933 when he first took the oath of office, Americans' "effort, courage, sacrifice and devotion." the bars from day to day by the contemptuous, unpitying masters of other It was a "fighting speech," wrote Time magazine, "more powerful and more continents." determined" than any the president had yet delivered about the war in Two weeks after that fireside chat, on June 10, 1940, Roosevelt gave another Europe. But the reality was actually more complicated. key address about American foreign policy. This time it was in the Memorial On the one hand, the president had taken sides in the European conflict. No Gymnasium of the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, to an audience more illusions of "neutrality." And he had delivered a straightforward that included his son Franklin, Jr., who was graduating from the Virginia statement of the course of action he would pursue. On the other hand, he was Law School. That same day, the president received word that Italy would not free to make policy unilaterally; he still had to contend with isolationists declare war on France and was sending four hundred thousand troops to in Congress. On June 10, the day of his Charlottesville talk, with Germans invade the French Mediterranean coast. In his talk, FDR deplored the "gods about to cross the Marne southeast of Paris, it was clear that the French of force and hate" and denounced the treacherous Mussolini. "On this tenth capital would soon fall. France's desperate prime minister, Paul Reynaud, day of June, 1940," he declared, "the hand that held the dagger has plunged it asked Roosevelt to declare publicly that the United States would support the into the back of its neighbor." Allies "by all means short of an expeditionary force." But Roosevelt But more than a denunciation of Mussolini's treachery and double-dealing, the speech finally gave a statement of American policy. It was time to "proclaim certain truths," the president said. Military and naval victories for declined. He sent only a message of support labeled "secret" to Reynaud; and in a letter to Winston Churchill, he explained that "in no sense" was he prepared to commit the American government to "military participation in support of the Allied governments." Only Congress, he added, had the joy-mad city, draped in flags and drenched in confetti and ticker tape. "No authority to make such a commitment. conqueror in the history of the world," wrote one newspaper, "ever received a "We all listened to you last night," Churchill wired the president the day after welcome such as was accorded Colonel Charles A. Lindbergh yesterday." the Charlottesville address, pleading, as he had done earlier in May, for more On May 19, 1940, a week before the president gave his fireside chat arms and equipment from America and paring down his request for denouncing isolationists and outlining plans to build up American defenses, destroyers from "forty or fifty" to "thirty or forty." "Nothing is so important," Lindbergh had made the isolationist case in his own radio address. The he wrote. In answer to Churchill's urgent appeal, the president arranged to United States was not in danger from a foreign invasion unless "American send what he cleverly called "surplus" military equipment to Great Britain. people bring it on" by meddling in the affairs of foreign countries. The only Twelve ships sailed for Britain, loaded with seventy thousand tons of bomber danger to America, the flier insisted, was an "internal" one. planes, rifles, tanks, machine guns, and ammunition-- but no destroyers were included in the deal. Sending destroyers would be an act of war, claimed Senator David Walsh of Massachusetts, the isolationist chairman of the Senate Naval Affairs Committee. Walsh also discovered the president's plan to send twenty torpedo boats to Britain. Flying into a rage, he threatened legislation to prohibit such arms sales. Roosevelt backed down -- temporarily -- and called off the torpedo boat deal. Though the president had explained that the Atlantic and Pacific oceans could no longer provide safe boundaries and could not protect the American continent from attack, Lindbergh insisted that the two vast oceans did indeed guarantee the nation's safety. "There will be no invasion by foreign aircraft," he stated categorically in his reedy voice, "and no foreign navy will dare to approach within bombing range of our coasts." America's sole task, he underscored, lay in "building and guarding our own destiny." If the nation Even as Nazi troops, tanks, and planes chalked up more conquests in Europe, stuck to a unilateral course, avoided entanglements abroad, refrained from the contest between the shrimps and the White House was not over. On the intervening in European affairs, and built up its own defenses, it would be contrary, the shrimps still occupied a position of formidable strength. impregnable to foreign incursions. In any case, he stressed, it was pointless The glamorous public face and articulate voice of the isolationist movement belonged to the charismatic and courageous Charles Lindbergh. His solo flight across the Atlantic in May 1927 had catapulted the lanky, boyish, 25- for the United States to risk submerging its future in the wars of Europe, for the die had already been cast. "There is no longer time for us to enter this war successfully," he assured his radio audience. year- old pilot onto the world stage. "Well, I made it," he said with a modest Deriding all the "hysterical chatter of calamity and invasion," Lindbergh smile upon landing at Le Bourget airfield in Paris, as thousands of delirious charged that President Roosevelt's angry words against Germany would lead French men and women broke through military and police lines and rushed to "neither friendship nor peace." toward his small plane. When he returned to New York two weeks later, flotillas of boats in the harbor, a squadron of twenty- one planes in the sky, and four million people roaring "Lindy! Lindy!" turned out to honor him in a Friendship with Nazi Germany? Surely Lindbergh realized that friendship between nations signifies their mutual approval, trust, and assistance. But so starry- eyed was he about German dynamism, technology, and military might and so detached was he from the reality and consequences of German centuries-old anti-Semitic myth of Jews as stateless foreigners, members of aggression and oppression that even on that day of May 19, when the an international conspiratorial clique with no roots in the "soil" and interested headline in the Washington Postread, "NAZIS SMASH THROUGH only in "transportable" paper wealth. BELGIUM, INTO FRANCE" and when tens of thousands of desperate Belgian refugees poured across the border into France, Lindbergh said he believed it would make no difference to the United States if Germany won the war and came to dominate all of Europe. "Regardless of which side wins this war," he stated in his May 19 speech without a whiff of hesitation or misgiving, "there is no reason . . . to prevent a continuation of peaceful relationships between America and the countries of Europe." The danger, in his opinion, was not that Germany might prevail but rather that Roosevelt's antifascist statements would make the United States "hated by victor and vanquished alike." The United States could and should maintain peaceful diplomatic and economic relations with whichever side won the war. Fascism, democracy-- six of one, half a dozen of the other. His defeatist "The Lindberghs and their friends laugh at the idea of Germany ever being able to attack the United States," wrote radio correspondent William Shirer, stationed in Berlin. "The Germans welcome their laughter and hope more Americans will laugh." Also heartened by Lindbergh's words was the German military attaché in Washington, General Friedrich von Boetticher. "The circle about Lindbergh," von Boetticher wrote in a dispatch to Berlin, "now tries at least to impede the fatal control of American policy by the Jews." The day after Lindbergh's speech, the defiant Hollywood studio heads, Jack and Harry Warner, wrote to Roosevelt to assure him that they would "do all in our power within the motion picture industry . . . to show the American people the worthiness of the cause for which the free peoples of Europe are making such tremendous sacrifices." speech could not have been "better put if it had been written by Goebbels himself," Franklin Roosevelt remarked two days later. Who could have foreseen in 1927 that Lindbergh, whose flight inspired a sense of transatlantic community and raised idealistic hopes for international As the mighty German army broke through French defenses and thundered toward Paris, the dominance of Germany in Europe seemed obvious, inevitable, and justified to Lindbergh. Why, then, he wondered, did Roosevelt persist in his efforts to involve the nation in war? "The only reason that we are in danger of becoming involved in this war," he concluded in his May 19 speech, "is because there are powerful elements in America who desire us to take part. They represent a small minority of the American people, but they control much of the machinery of influence and propaganda." It was a veiled allusion to Jewish newspaper publishers and owners of major Hollywood movie studios. He counseled Americans to "strike down these elements of personal profit and foreign interest." While his recommendation seemed to border on violence, he was also reviving the cooperation, would come to embody the fiercest, most virulent brand of isolationism? Two years after his feat, Lindbergh gained entrée to the Eastern social and financial elite when he married Anne Morrow, the daughter of Dwight Morrow. A former J. P. Morgan partner and the ambassador to Mexico, Dwight Morrow would be elected as a Republican to the United States Senate in 1930, just before his death in 1931. Charles and Anne seemed to lead charmed lives-- until their 20- month- old son was snatched from his crib in their rural New Jersey home in March 1932. Muddy footprints trailed across the floor in the second-floor nursery to an open window, beneath which a ladder had stood. "The baby's been kidnapped!" cried the nurse as she ran downstairs. The governor of New York, Franklin Roosevelt, immediately placed all the resources of the state police at the disposal of the New Jersey authorities. Two months later, the small body was were wined and dined by Hermann Goering, second only to Hitler in the found in a shallow grave. A German- born carpenter who had served time in Nazi hierarchy, and other members of the party elite. Goering personally led prison for burglary, Bruno Hauptmann, was charged with the crime; Lindbergh on an inspection tour of aircraft factories, an elite Luftwaffe Lindbergh identified his voice as the one he heard shouting in the darkness of squadron, and research facilities. The American examined new engines for a Bronx cemetery when he handed over $50,000 in ransom. dive bombers and combat planes and even took a bomber up in the air. It was Carrying a pistol visible in a shoulder holster, Lindbergh attended the trial in January 1935, sitting just a few seats away from the accused. After Hauptmann's conviction and move for an appeal, Eleanor Roosevelt oddly and gratuitously weighed in, second- guessing the jury and announcing that she was a "little perturbed" that an innocent man might have been found guilty. But the conviction stood, and Hauptmann would be executed in the electric chair in April 1936. a "privilege" to visit modern Germany, the awestruck Lindbergh said afterward, showering praise on "the genius this country has shown in developing airships." Photographers snapped pictures of Charles and his wife, relaxed and smiling in Goering's home. Lindbergh's reports on German aviation overflowed with superlatives about "the astounding growth of German air power," "this miraculous outburst of national energy in the air field," and the "scientific skill of the race ." The aviator, however, showed no interest in speaking with foreign correspondents in Germany, "who have a In December 1935, in the wake of the trial, Charles and Anne, harassed and perverse liking for enlightening visitors on the Third Reich," William Shirer sometimes terrified by intrusive reporters as well as by would- be dryly noted. blackmailers, fled to Europe with their 3-year-old son, Jon. "America Shocked by Exile Forced on the Lindberghs" read the three-column headline on the front page of the New York Times. In Berlin, Lindbergh's wife, Anne, was blinded by the glittering façade of a Potemkin village. She was enchanted by "the sense of festivity, flags hung out, the Nazi flag, red with a swastika on it,everywhere, and the Olympic Would the crowd- shy Lindbergh and his wife find a calm haven in Europe? flag, five rings on white." The Reich's dynamism was so impressive. "There The Old World also has its gangsters, commented a French newspaper is no question of the power, unity and purposefulness of Germany," she columnist, adding that Europe "suffers from an additional disquieting force, wrote effusively to her mother, adding that Americans surely needed to for there everyone is saying, 'There is going to be war soon.'" The Nazi press, overcome their knee-jerk, "puritanical" view that dictatorships were "of however, took a different stance. "As Germans," wrote the Deutsche necessity wrong, evil, unstable." The enthusiasm and pride of the people Allgemeine Zeitung with an absence of irony, "we cannot understand that a were "thrilling." Hitler himself, she added on a dreamy, romantic note, "is a civilized nation is not able to guarantee the safety of the bodies and lives of very great man, like an inspired religious leader-- and as such rather its citizens." fanatical-- but not scheming, not selfish, not greedy for power, but a mystic, For several years the Lindberghs enjoyed life in Europe, first in England, in a a visionary who really wants the best for his country and on the whole has house in the hills near Kent, and later on a small, rocky island off the coast of rather a broad view." Brittany. In the summer of 1936, the couple visited Germany, where they On August 1, 1936, Charles and Anne attended the opening ceremonies of and eugenicist who instructed the flier in his scientific racism. In his 1935 the Olympic Games in Berlin, sitting a few feet away from Adolf Hitler. As book Man, the Unknown, Carrel had laid out his theories, his criticism of the band played "Deutschland über alles," blond- haired little girls offered parliamentary democracy and racial equality. Asserting that the West was a bouquets of roses to the Führer, the delighted host of the international games. "crumbling civilization," he called for the "gigantic strength of science" to Theodore Lewald, the head of the German Organizing Committee, declared help eliminate "defective" individuals and breeds and prevent "the the games open, hailing the "real and spiritual bond of fi re between our degeneration of the [white] race." In the introduction to the German edition German fatherland and the sacred places of Greece founded nearly 4,000 of his book, he praised Germany's "energetic measures against the years ago by Nordic immigrants." Leaving the following day for propagation of retarded individuals, mental patients, and criminals." Copenhagen, Lindbergh told reporters at the airport that he was "intensely pleased" by what he had observed. His presence in the Olympic Stadium and his warm words about Germany helpfully added to the luster and pride of the Nazis. Also present at the Olympic games, William Shirer overheard people in Nazi circles crow that they had succeeded in "making the Lindberghs 'understand' Nazi Germany." In the fall of 1938, Charles and Anne returned to Germany. In October, at a stag dinner in Berlin hosted by the American ambassador and attended by the Italian and Belgian ambassadors as well as by German aircraft designers and engineers, Goering surprised the aviator by bestowing on him, "in the name of the Führer," Germany's second- highest decoration, a medal-- the Service Cross of the Order of the German Eagle-- embellished with a golden cross In truth, Lindbergh had glimpsed a certain unsettling fanaticism in Germany, and four small swastikas. Lindbergh wore it proudly that evening. Afterward, but, as he reasoned to a friend, given the chaotic situation in Germany after when he returned from the embassy, he showed the medal to Anne, who World War I, Hitler's achievements "could hardly have been accomplished correctly predicted that it would become an "albatross." without some fanaticism." Not only did he judge that the Führer was "undoubtedly a great man," but that Germany, too, "has more than her share of the elements which make strength and greatness among nations." Despite some reservations about the Nazi regime, Lindbergh believed that the Reich was a "stabilizing factor" in Europe in the 1930s. Another visit to Germany in 1937 confirmed his earlier impressions. German aviation was "without parallel in history"; Hitler's policies "seem laid out with great intelligence and foresight"; and any fanaticism he had glimpsed was offset by a German "sense of decency and value which in many ways is far ahead of our own." The Lindberghs wanted to spend the winter in Berlin, and Anne even found a suitable house in the Berlin suburb of Wannsee. They returned to Illiec to pack up for the move, but changed their plans when they learned of Kristallnacht. "My admiration for the Germans is constantly being dashed against some rock such as this," Lindbergh lamented in his diary, expressing dismay at the persecution of Jews at the hands of Nazi thugs. Concerned that their taking up residence in Berlin might cause "embarrassment" to the German and American governments, he and Anne rented an apartment in Paris instead. And yet, Lindbergh's deep admiration for Germany was not In the late spring of 1938, Lindbergh and his wife moved to the tiny Breton seriously dampened. On the contrary, crossing the border from Belgium into island of Illiec, where Charles could carry on lengthy conversations with his Germany in December 1938, Lindbergh was captivated by the fine-looking neighbor and mentor, Dr. Alexis Carrel, an award-winning French scientist young German immigration officer whose "air of discipline and precision," he wrote, was "in sharp contrast to the easygoing pleasantness of Belgium On April 20, 1939, Lindbergh had a busy day in Washington: first a meeting and France." Germany still offered the striking image of the virility and with Secretary of War Harry Woodring and then one with President modern technology he prized. The spirit of the German people, he told John Roosevelt at the White House. After waiting for forty-five minutes, the Slessor, a deputy director in Britain's Air Ministry, was "magnificent"; he aviator entered the president's office. "He is an accomplished, suave, especially admired their refusal to admit that anything was impossible or that interesting conversationalist," Lindbergh wrote later that day in his diary. "I any obstacle was too great to overcome. Americans, he sighed, had lost that liked him and feel that I could get along with him well." But he suspected strength and optimism. Strength was the key to the future. It appeared that they would never agree on "many fundamentals" and moreover sensed eminently rational and fair to Charles Lindbergh that Germany should that there was "something about him I did not trust, something a little too dominate Europe because, as he wrote, "no system . . . can succeed in which suave, too pleasant, too easy. . . . Still, he is our President," Lindbergh the voice of weakness is equal to the voice of strength." concluded. He would try to work with him, he noted, cautiously adding that In April 1939, Lindbergh returned to the United States, his wife and two "I have a feeling that it may not be for long." young sons following two weeks later. A few years earlier he had discussed Emerging after half an hour from a side exit of the executive mansion, with his British friends the possibility of relinquishing his American Lindbergh found himself besieged by photographers and reporters. The citizenship, but now he decided that if there was going to be a war, he would boisterous scene was "disgraceful," the camera- shy aviator bitterly judged. remain loyal to America. Even so, on the same day that he and Anne "There would be more dignity and self-respect among African Savages." discussed moving back to America, he confessed in his diary that, of all the After their meeting, neither Lindbergh nor the White House would shed any countries he had lived in, he had "found the most personal freedom in light on what had been discussed. Rumors would later surface that, at that Germany." Moreover, he still harbored "misgivings" about the United States; April meeting or several months later, the president had offered the aviator a critical of the shortsightedness and vacillation" of democratic statesmen, he cabinet appointment, but such rumors were never substantiated. was convinced that, in order to survive in the new totalitarian world, American democracy would have to make "great changes in its present practices." From the White House that April day, Lindbergh went to a session of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) and spoke about the importance of establishing a program to develop technologically advanced Back on American soil in April, Lindbergh immediately launched into a aircraft. While he backed the NACA's recommendation that the government tireless round of meetings with scientists, generals, and government officials, allocate $10 million for a West Coast research center, not even that spreading the word about the remarkable advances in aviation he had seen in represented sufficient progress in Lindbergh's mind. It would still leave the Germany and pushing for more research and development of American air United States "far behind a country like Germany in research facilities," he and military power. Though he believed in American isolation, he also wrote in his diary. "We could not expect to keep up with the production of believed in American preparedness. European airplanes as long as we were on a peacetime basis." Lindbergh was unrelenting in his message about military preparedness. One In June 1940, as France fell to Nazi troops and planes, Lindbergh turned to scientist who listened carefully to him was Vannevar Bush, the chairman of memories of his father for reassurance and wisdom. "Spent the evening the NACA and head of the Carnegie Institution, a research organization in reading Father's Why Is Your Country at War?" he wrote in his diary. That Washington. After several more meetings that spring, the two men agreed 1917 book justified the son's alarm at the prospect of America's entry into that a plan was needed to revive the NACA. Bush "soaked up" Lindbergh's another European war. Charles Lindbergh, Sr., a progressive Minnesota opinions, wrote Bush's biographer G. Pascal Zachary. Indeed, so impressed Republican who died in 1924, had served in the House of Representatives was Bush that he offered Lindbergh the chairmanship or vice chairmanship from 1907 to 1917. His young son, Charles, ran errands and addressed letters of the NACA-- an offer he aviator declined. Early in 1940 Bush received for him and occasionally was seen in the House gallery, watching his father another report from Lindbergh that repeated his alarm about a serious lack of on the floor below. Although Lindbergh, Sr., had been a follower of engine research facilities in the United States and called for "immediate steps Theodore Roosevelt, on the question of American participation in the First to remedy this deficiency." World War, he and the bellicose TR parted company. Deeply concerned after reading Lindbergh's recommendations, Bush drafted Why Is Your Country at War? was a long- winded, turgid antiwar tract, a proposal for the creation of a National Defense Research Council (NDRC), arguing that the United States had been drawn into the war by the an organization that would supervise and fund the work of American machinations of "cowardly politicians," wealthy bankers, and the Federal engineers and scientists. On June 12, 1940, Bush met for the first time with Reserve Bank. The senior Lindbergh did not oppose the violence of war per President Roosevelt in the Oval Office. He handed him his memo--four short se. Rather, this midwestern agrarian railed against the injustice of a war paragraphs on a single sheet of paper. It was enough, one of Bush's organized and promoted as a for-profit enterprise by the "wealth grabbers" of colleagues later wrote, to convince the president of the need to harness Wall Street, people like the Morgans and the Rockefellers. Ironically, the technology for possible war. Taking out his pen, he wrote on the memo the men of the "power elite" whom he most despised might have included his magical words, "OK-- FDR." son's future father- in-law, Dwight Morrow, a Morgan partner-- though During the war, two thirds of the nation's physicists would be working under Vannevar Bush. One of the secret projects he supervised until 1943, when it was turned over to the army, was known as Section S1. The S1 physicists sought to unlock energy from the fission of atoms of a rare isotope of Lindbergh, Jr., later told an interviewer that he believed that his father and Dwight Morrow would probably have liked each other. At bottom, the elder Lindbergh's screed was a rambling, populist, socialist primer that offered radical remedies for the twin evils of war and capitalism. uranium. And among the starting places for that work as well as for Bush's When his book appeared in print, Lindbergh, Sr., had to defend himself--not creation of the NDRC were his informative and disturbing conversations against the charge that he was anticapitalist, which would have been true, but with Charles Lindbergh. rather against the charge that he was pro- German. He was hung in effigy and taunted as a "friend of the Kaiser." Though there was nothing pro-German in the book, the accusations contributed to his defeat when he ran for governor of Minnesota in 1918. "If you are really for America first," he wrote in his for Nazi Germany. "Perhaps it is the conservatism of his friends and the own defense, "then you are classed as pro-German by the big press[es] which aristocratic racial doctrines of Carrel that have made him sympathetic to are supported by the speculators." Nazism," Rodman wrote. "Perhaps it is the symbolism of his lonely flight Like his father, Charles Lindbergh, Jr., would also face allegations that he was pro-German. But in his case the indictment rang true. and the terrible denouement of mass-worship and the kidnapping that have driven him to the unpopular cause because it is unpopular; that always makes the Byronic hero spurn fame and fortune for guilt and solitary persecution." In the aviator's mind, Germany had it made. In England there was "organization without spirit," he would tell a radio audience in August 1940. "In France there was spirit without organization; in Germany there were both." Indeed, the more Lindbergh had lived among the English people, the less confidence he had in them. They struck him, he wrote, as unable to connect to a "modern world working on a modern tempo." And sadly, he judged that it was too late for them to catch up, "to bring back lost opportunity." Britain's only hope, as he once mentioned to his wife, was to learn from the Germans and to adopt their methods in order to survive. Nor did he have confidence or respect for democracy in the United States. On the American continent, he felt surrounded by mediocrity. Writing in his diary in the summer of 1940, he bemoaned the decline of American society--"the superficiality, the cheapness, the lack of understanding of, or interest in, fundamental problems." And making the problems worse were the Jews. "There are too many places like New York already," he wrote, alluding to that city's Jewish population. "A few Jews add strength and character to a country, but too many create chaos. And we are getting too many." For his part, Lindbergh knew that many of his views were unpopular in certain circles, but, as he told a nationwide radio audience in 1940, "I would far rather have your respect for the sincerity of what I say than attempt to win your applause by confining my discussion to popular concepts." Mistaking sincerity for intelligence and insight, he considered himself a realist who grasped that German technological advances had profoundly and irrevocably altered the balance of power in Europe. The only issue, he once explained to Ambassador Joseph Kennedy, was "whether this change will be peaceably accepted, or whether it must be tested by war." Priding himself on his cleareyed understanding of military strength, he darkly predicted in June 1940, before the Battle of Britain had even begun, that the end for England "will come fast." The playwright Robert Sherwood, whom FDR would draft in the summer of 1940 to join his speechwriting team, may have come closest to the truth about Lindbergh. The aviator, he dryly commented, had "an exceptional understanding of the power of machines as opposed to the principles which animate free men." As Sherwood suggested, Lindbergh may simply have been naive about politics, ignorant about history, uneducated in Was Lindbergh a Nazi? He was "transparently honest and sincere," remarked foreign policy and national security, and deluded by his infatuation with Sir John Slessor, the Royal Air Force marshal who met several times with German technology and vigor. Perhaps he did not fully appreciate, Sherwood Lindbergh. It was Lindbergh's very "decency and naiveté," Slessor later said, said, the extent to which the German people "are now doped up with the that convinced him that the aviator was simply "a striking example of the cocaine of world revolution and the dream of world domination." effect of German propaganda." One of Lindbergh's acquaintances, the journalist and poet Selden Rodman, also tried to explain the aviator's affinity Despite his exuberant enthusiasm for Germany, his disenchantment with democracy, the zealous applause he received from fascists in the United States and in Germany, his admiration for the racial ideas of Alexis Carrel, his increasingly extremist and anti- Semitic speeches, and the fact that his simplistic views mirrored Nazi propaganda in the United States, Lindbergh seemed to want what he believed was best for America. And yet Franklin Roosevelt may have been instinctively correct in his own less nuanced view. "I am absolutely convinced that Lindbergh is a Nazi," FDR said melodramatically to his secretary of the treasury and old Dutchess County neighbor and friend, Henry Morgenthau, in May 1940, two days after Lindbergh's May 19 speech. "If I should die tomorrow, I want you to know this." The president lamented that the 38-year-old flier "has completely abandoned his belief in our form of government and has accepted Nazi methods because apparently they are efficient." Others in the White House shared that assessment. Lindbergh, Harold Ickes sneered, pretentiously posed as a "heavy thinker" but never uttered "a word for democracy itself." The aviator was the "Number 1 Nazi fellow traveler," Ickes said. The delighted German embassy wholeheartedly agreed. "What Lindbergh proclaims with great courage," wrote the German military attaché to his home office in Berlin, "is certainly the highest and most effective form of propaganda." In other words, why would Germany need a fifth column in the United States when it had in its camp the nation's hero, Charles Lindbergh? This is an excerpt from 1940: FDR, Willkie, Lindbergh, Hitler--the Election amid the Storm, by Susan Dunn, published by Yale University Press, 2013.