Review for biochemistry
advertisement
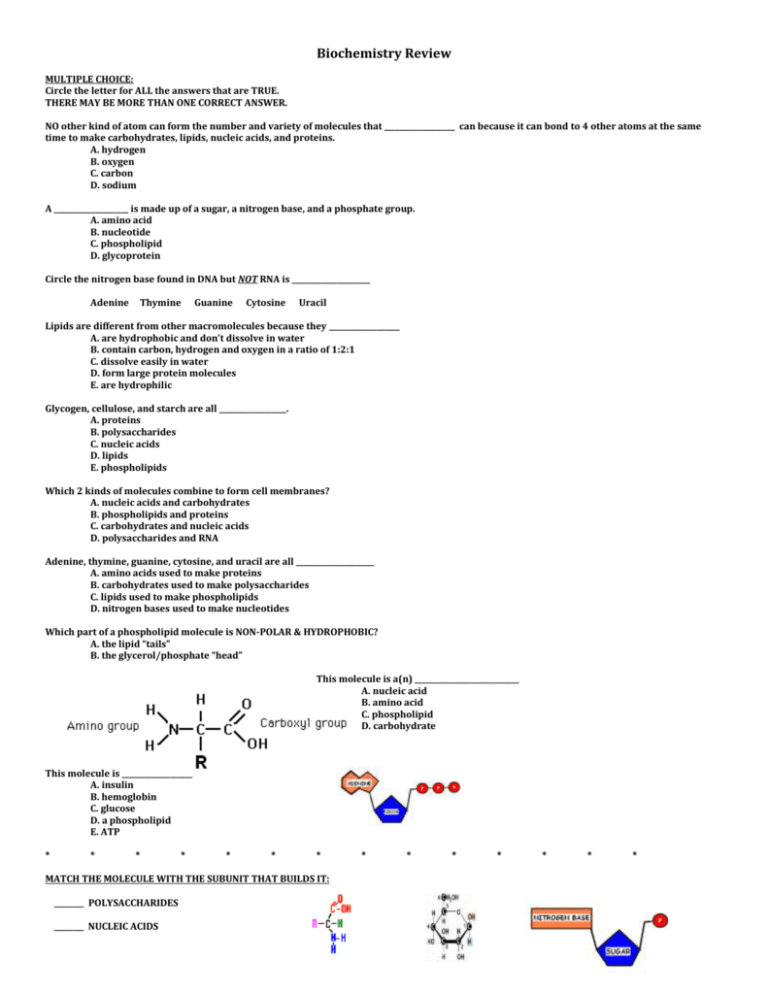
Biochemistry Review MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle the letter for ALL the answers that are TRUE. THERE MAY BE MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER. NO other kind of atom can form the number and variety of molecules that ___________________ can because it can bond to 4 other atoms at the same time to make carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. A. hydrogen B. oxygen C. carbon D. sodium A ____________________ is made up of a sugar, a nitrogen base, and a phosphate group. A. amino acid B. nucleotide C. phospholipid D. glycoprotein Circle the nitrogen base found in DNA but NOT RNA is _____________________ Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytosine Uracil Lipids are different from other macromolecules because they ___________________ A. are hydrophobic and don’t dissolve in water B. contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 C. dissolve easily in water D. form large protein molecules E. are hydrophilic Glycogen, cellulose, and starch are all __________________. A. proteins B. polysaccharides C. nucleic acids D. lipids E. phospholipids Which 2 kinds of molecules combine to form cell membranes? A. nucleic acids and carbohydrates B. phospholipids and proteins C. carbohydrates and nucleic acids D. polysaccharides and RNA Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil are all _____________________ A. amino acids used to make proteins B. carbohydrates used to make polysaccharides C. lipids used to make phospholipids D. nitrogen bases used to make nucleotides Which part of a phospholipid molecule is NON-POLAR & HYDROPHOBIC? A. the lipid “tails” B. the glycerol/phosphate “head” This molecule is a(n) ____________________________ A. nucleic acid B. amino acid C. phospholipid D. carbohydrate This molecule is ___________________ A. insulin B. hemoglobin C. glucose D. a phospholipid E. ATP * * * * * * * MATCH THE MOLECULE WITH THE SUBUNIT THAT BUILDS IT: ________ POLYSACCHARIDES ________ NUCLEIC ACIDS * * * * * * * ________ PROTEINS TRUE or FALSE Circle T if the statement is TRUE Circle F if the statement in FALSE and use the blank provided to correct the underlined word/phrase. T F The 20 different polysaccharides used to make proteins differ in what is attached in their R group position. _____________________ T F Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide that makes plants sturdy. ___________________ T F One function of proteins is to provide insulation. __________________ T F People with diabetes can’t make hemoglobin to control their blood sugar. Match the molecule with its description: LIPIDS CARBOHYDRATES PROTEINS NUCLEIC ACIDS ____________________________ made by joining amino acid subunits in long chains which provide a wide variety of functions in cells ____________________________ made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio ____________________________ made from nucleotide subunits which store and carry information ____________________________ Hydrophobic fats, oils, waxes, & steroids made mainly from carbon and hydrogen atoms in long chains or multiple rings COMPARE: KINDS OF CARBOHYDRATES # of SUGARS it contains GIVE 3 EXAMPLES MONOSACCHARIDES POLYSACCHARIDES MACROMOLECULES CARBOHYDRATES GIVE SOME FUNCTIONS OF EACH 1. 2. NUCLEIC ACIDS LIPIDS 1. 2. 1. 2. 3. PROTEINS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. COMPARE NUCLEIC ACIDS: Is it Single/double stranded? DNA RNA Which Nitrogen bases does it contain? Which Sugar does it contain? Function(s)? NAME THE MOLELCULE DESCRIBED BELOW: Protein hormone that tells animal cells to store blood glucose as glycogen Double stranded nucleic acid made from nucleotides subunits containing A, T, G, and C that stores genetic info in cells Protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body Membrane protein with carbohydrates attached that helps cells identify “self” and plays a role in blood types, organ transplants, and germ recognition Macromolecule with a polar glycerol/phosphate “head” and 2 non-polar hydrophobic “tails” used to make cell membranes Single stranded nucleic acid made from nucleotide subunits containing A, U, C, and G which carries information from the DNA to the cell for protein synthesis Storage form of glucose used by plant cells Storage form of glucose used by animal cells Structural polysaccharide made from glucose subunits that makes plants sturdy Nucleotide subunit made from ribose sugar, adenine, and 3 phosphates which stores and transports ENERGY in cells Polar molecule made from 1 oxygen and 2 hydrogen atoms that is required by all living things ENZYMES MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle the letter of the answer(s) that correctly complete the sentence. THERE MAY BE MORE THAN ONE CORRECT ANSWER. Reactants in an enzyme catalyzed chemical reaction are called __________________ A. polymers B. products C. substrates D. organics Macromolecule that can act as enzymes are ______________________. A. carbohydrates B. lipids C. Nucleic acids D. proteins Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by _________________________. A. decreasing the activation energy B. increasing the activation energy C. making more hydrogen bonds D. changing the pH of the solution Proteins (like enzymes) unwind or ___________________ when placed in extreme pH or temperature conditions. A. desensitize B. polymerize C. depolarize D. denature Enzymes are ___________________________ A. used up during chemical reactions B. unchanged during chemical reactions and reusable * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * MATCH EACH COMPONENT IN THE ENZYME CATALYZED REACTION BELOW WITH ITS NAME BY WRITING THE LETTER ON THE LINE PROVIDED. _____ PRODUCTS _____ SUBSTRATE _____ ACTIVE SITE _____ ENZYME-SUBSTRATE COMPLEX _____ ENZYME Name two (2) environmental conditions that can cause proteins (enzymes) to change their shape. ______________________________ __________________________ Many genetic diseases result from the production of enzymes that are not shaped correctly. How does changing in an enzyme’s shape cause it to work poorly or not at all? DNA polymerase is a molecule found in all cells. Judging by its name, do you think it is an enzyme? YES NO HOW CAN YOU TELL? DNA, RNA, and PROTEINS MULTIPLE CHOICE: The three bases on the tRNA molecule that are complementary to one of the mRNA codons are called the ___________________. A. message matches B. anticodon C. promoter D. exon E. intron According to Chargaff’s rules, which nucleotide is always paired with Adenine IN A DNA MOLECULE? A. Adenine B. Thymine C. Guanine D. Cytosine E. Uracil Ribosomes are made out of __________________________. A. RNA and proteins B. phospholipids and proteins C. glycoproteins and lipids D. DNA and proteins DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, ___________________________________________ A. each with two new strands B. one with two new strands and one with 2 original strands C. each with two original strands D. each with one new strand and one original strand Which type(s) of RNA is/are involved in protein synthesis? A. t-RNA only B. R-RNA only C. r-RNA and m-RNA only D. all 3 kinds of RNA are involved in making proteins Where in the cell does transcription take place? A. in the nucleus B. on ribosomes in the cytoplasm C. in Golgi bodies D. on the nucleosomes Where in the cell does translation take place? A. in the nucleus B. on ribosomes in the cytoplasm C. in Golgi bodies D. on the nucleosomes DNA wraps around histones to form bead-like structures called __________________. A. introns B. exons C. ribosomes D. nucleosomes How many codons are needed to specify THREE AMINO ACIDS? A. 3 B. 6 C. 9 D. 12 What did the Hershey-Chase blender experiment help prove? A. DNA is a double helix. B. Pneumonia causes dead mice. C. Histones are made of DNA. D. The genetic material is made of DNA. Many DNA molecules contain sequences called ____________ that are not involved in coding for proteins and are edited out of the complementary RNA molecule copy before it is used. A. exons B. introns C. nucleosomes D. anticodons The molecule that caused transformation in Griffith’s pneumonia/mouse experiment was ______________. A. DNA B. a bacteriophage C. a protein D. RNA Nitrogen bases with only 1 ring are called ____________________. A. nucleosomes B. purines C. pyrimdines D. histones The place where RNA polymerase binds to start transcribing a gene is called the _______________ A. operator B. promoter C. repressor D. anticodon MATCH THE PROCESS WITH ITS DESCRIPTION: TRANSLATION TRANSCRIPTION REPLICATION _______________________ Making an complementary RNA sequence from a DNA code (DNA RNA) _______________________ Making a DNA copy of a DNA molecule (DNA DNA) _______________________ Making proteins from an RNA message (RNA protein) Use words from the word bank to match the following: messenger-RNA transfer-RNA ribosomal-RNA ___________________ Carries the DNA code from nucleus to cytoplasm ___________________ Made by the nucleolus ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Adds the correct amino acid to the growing protein chain Combines with proteins to form ribosomes Has a CODON region Has an ANTICODON region ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ COMPARE AND CONTRAST CHROMATIN CHROMOSOMES What are DNA/proteins doing? Type of cell seen in? COMPARE AND CONTRAST DNA RNA INTRON EXON Double / Single stranded? Sugar used? List all nitrogen bases it has Which nitrogen base is missing? Location in cell? HOW ARE THEY ALIKE ? What happens to it? SHORT ANSWER: Name the 3 parts of a nucleotide molecule: __________________ _____________________ _____________________ THINK ABOUT IT: Use what you know about heat and enzymes. Why do you think heating the lethal pneumonia bacteria in Griffith’s experiment killed them? Explain the function of the TATA box. Is it found on prokaryotes or eukaryotes ? USING ANALOGIES: If a double helix is compared to a “twisted ladder”, which would the following represent? Sides of the ladder ? ___________________________ Rungs of ladder ? ______________________________ Glue in the middle that holds the ladder together? ____________ DNA, RNA, & PROTEINS REVIEW 1. Making a copy of DNA is called _________________________. 2. Which nitrogen base isn’t used during this process? 3. Name the enzyme you learned about that adds the complementary nucleotides and spell checks to make sure the new copy is correct. 4. This process of making copying an RNA message from the DNA code is called ____________________. 5. Tell where in the cell this happens. (picture to the right) 8. USE THE mRNA CODE WHEEL to tell the amino acid sequence coded for by the following message: UCA AAA UUC 6. Which kind of RNA has an ANTICODON region and carries the amino acids to the ribosome? Name the parts/structures of a cell: A = __________________ B = __________________ C = __________________ D = __________________ E = __________________ F = __________________ 7. Tell several ways DNA is different from RNA. 8. What do we call the small pieces of DNA that are edited out of the mRNA message before it is expressed? 9. DNA that is SPREAD OUT in the nucleus of NON-DIVIDING cells is called ________________. 10. When making DNA, CYTOSINE always pairs with _______________________. 11. Using an RNA message to make a protein is called ________________. 12. Name this subunit used to build DNA and RNA. 13. Name the spot RNA polymerase attaches to DNA during TRANSCRIPTION. 14. Give the complementary DNA strand. A T T G C C A G C 15. NAME THIS KIND OF RNA. 16. Name the molecule attached at the arrow. 17. An experiment conducted by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase showed that: A. pneumonia kills mice B. Proteins carry the genetic code C. DNA can be transferred between bacteria D. DNA carries the genetic code 18. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS could also be called ___________________. 19. Nitrogen bases made up of TWO RINGS are called 20. The process in which one bacterium is changed by the transfer of genetic material from another bacterium is called 21. Name this subunit used to build PROTEINS. 22. Write the anticodon for "E". ___________ 23. Name the nucleic acid that is double stranded and contains deoxyribose sugar. 24. Name the woman whose X-ray images of DNA helped James Watson and Francis Crick to figure out the structure of DNA. 25. Name the enzyme involved with TRANSCRIPTION.







