IS Help Sheet
advertisement
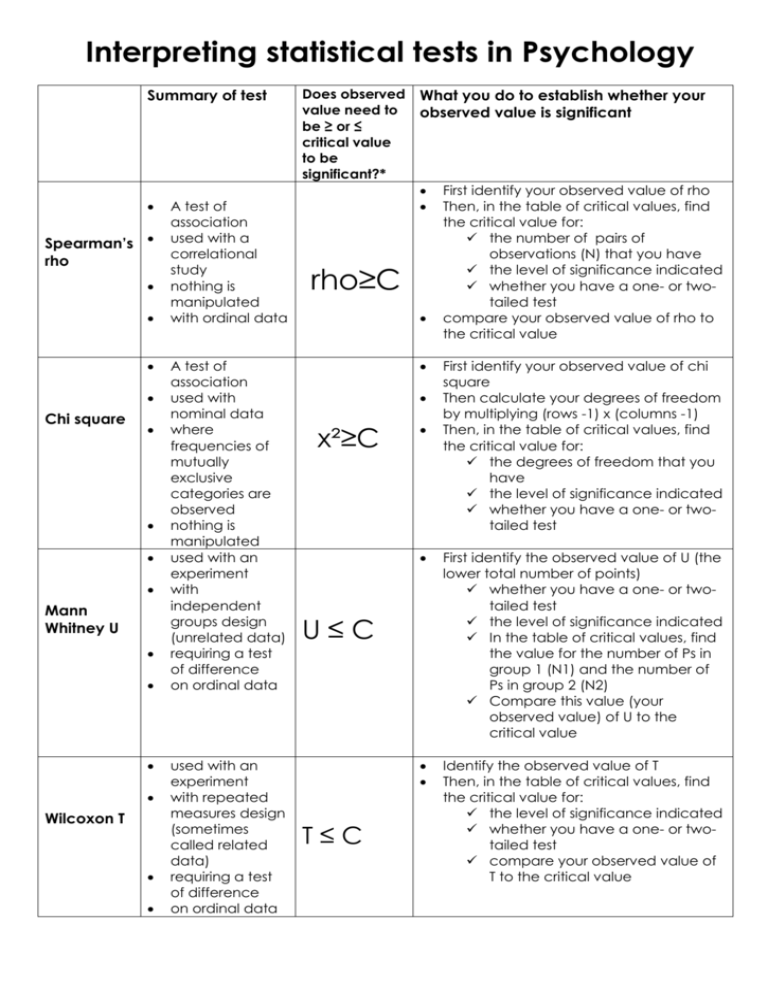
Interpreting statistical tests in Psychology Summary of test Spearman’s rho Chi square Mann Whitney U Wilcoxon T A test of association used with a correlational study nothing is manipulated with ordinal data A test of association used with nominal data where frequencies of mutually exclusive categories are observed nothing is manipulated used with an experiment with independent groups design (unrelated data) requiring a test of difference on ordinal data used with an experiment with repeated measures design (sometimes called related data) requiring a test of difference on ordinal data Does observed value need to be ≥ or ≤ critical value to be significant?* What you do to establish whether your observed value is significant rho≥C x²≥C First identify your observed value of chi square Then calculate your degrees of freedom by multiplying (rows -1) x (columns -1) Then, in the table of critical values, find the critical value for: the degrees of freedom that you have the level of significance indicated whether you have a one- or twotailed test First identify the observed value of U (the lower total number of points) whether you have a one- or twotailed test the level of significance indicated In the table of critical values, find the value for the number of Ps in group 1 (N1) and the number of Ps in group 2 (N2) Compare this value (your observed value) of U to the critical value Identify the observed value of T Then, in the table of critical values, find the critical value for: the level of significance indicated whether you have a one- or twotailed test compare your observed value of T to the critical value U≤C T≤C First identify your observed value of rho Then, in the table of critical values, find the critical value for: the number of pairs of observations (N) that you have the level of significance indicated whether you have a one- or twotailed test compare your observed value of rho to the critical value