Pediatric Donor Management Made Simple
advertisement

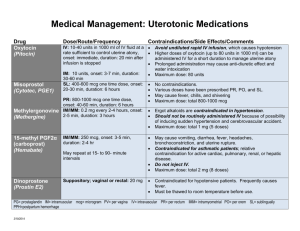
Pediatric Donor Management Guidelines
Pediatric Glascow Coma Scale
Child
Infant
Score
MOTOR
RESPONSE
Obeys Commands
Localizes
Withdraws (Pain)
Flexion (Pain)
Extension (Pain)
None
Spontaneous Movement
Withdraws to touch
Withdraws to pain
Flexion (Pain)
Extension (Pain)
None
6
5
4
3
2
1
VERBAL
RESPONSE
Oriented
Confused
Inappropriate Words
Incomprehensible
None
Coos and Babbles
Irritable Cry
Cries to pain
Moans to pain
None
5
4
3
2
1
EYE OPENING
Opens spontaneous
Opens to speech
Opens to pain
None
Opens spontaneous
Opens to speech
Opens to pain
None
4
3
2
1
Normal Pediatric Vital Signs
Age
Newborns and Infants
Toddlers
Preschoolers
School-Aged Children
Adolescents
Heart Rate
(beats/min)
120-160
90-140
80-110
75-100
60-90
Respirations
(breaths/min)
30-60
24-40
22-34
18-30
12-16
Blood Pressure
Systolic Diastolic
74-100
50-70
80-112
50-80
82-110
50-78
84-120
54-80
94-140
62-88
Hemodynamics
Parameter
Central Venous Pressure (CVP)
(Right Atrial Pressure)
Left Atrial Pressure (LAP)
(Pulmonary Wedge Pressure)
Normal Value
4-8 mmHg
6-11 mmH2O
6-12 mmHg
2 x diastolic pressure
+ systolic pressure ÷
3
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
Pulmonary Artery Pressure (PAP)
Formula
Systolic 15-30 mmHg
Diastolic 5-10 mmHg
Mean 12-18 mmHg
Temperature Conversions
Fahrenheit = (9/5 x Centigrade Temperature) + 32
Centigrade = (Fahrenheit Temperature – 32) x 5/9
Centigrade
Fahrenheit
Centigrade
Fahrenheit
34.0
93.2
38.0
100.4
35.0
95.0
39.0
102.2
36.0
96.8
40.0
104.0
37.0
98.6
41.0
105.8
Toe Temperature monitoring is common in Pediatrics…TT should be >30C
It is an indicator of perfusion-if TT is low CO may also be low or pt may be febrile and
clamped down
Average Dimensions of Endotracheal Tubes
Internal Diameter
Oral: mouth to mid
Nasal: nares to mid
(mm)
trachea
trachea
Premature
2.5-3.0
9
10
Full term
3.0-3.5
10
11
6 months
4.0
11
13
12-24 months
4.5
13-14
16-17
4y
5.0
15
17-18
6y
5.5
17
19-20
8y
6.0
19
21-22
10y
6.5
20
22-23
12y
7.0
21
23-24
14y
7.5
22
24-25
Adults
8.0-9.5
23-25
25-28
**The above sizes are baseline average sizes for age of uncuffed tubes. If a
tube is cuffed it should be 0.5-1 size smaller. Ex: Average 6yo would require 5.5 uncuffed
or 4.5-5.0 cuffed. In pediatrics most used to be uncuffed (kids have an anatomical cuff with
their cricoid cartilage anatomy) however, most current practice is to place cuffed tubes
(for VAP) though keep in mind, not all facilities are doing this yet
Age
Serologies
For any child <18 months- do disease marker testing on mother
Children >18 months- only do disease marker testing on mother if child has been
breast-fed within the last 12 months. Otherwise, testing can be done only on child’s
pre-transfusion blood
Blood from pediatric donors should not exceed 10% of total blood volume
Total blood volume is 80 ml blood/kg of body weight
Example 11.7 kg child 80x11.7=936 ml total blood volume
10% of 936= 93.6 ml of blood
Med/Soc History
Ask full med/soc of both child and mother for children less than 18 months
of age or for those children older than 18 months of age who have been
breast fed within the past 12 months
Donor Management Initial Orders:
Transfer care to Gift of Life with time noted
D/C all previous orders, except pressors, antibiotics, and insulin
VS with CVP and U/O q 1 hour
Maintain body temp 36.5-37.5 (97-99.5)- use warming or cooling blanket
NGT-LIWS
SCD’s
HOB elevated to at least 30 degrees if hemodynamically stable
Q 1-2 hour tilting side to side, ET Tube suctioning, Oral care, Chest PT
Place patient on specialty bed if possible. (Percussion and rotation)
No ETT cuff leak
Place Central line and Arterial Line (no PA catheter under 15 years of agePatients ages 15-18 yrs evaluate on a case by case basis and consult
intensivist at facility, medical manager, and resource.)
Vasoactive drugs to maintain normal SBP for age
EKG
Consult Cardiology for echo and official EKG read
Before Initial ECHO
See Cardiac Algorithm
o Correct metabolic abnormalities
o Correct Anemia
o Correct Volume Status: CVP: 6-10
o Adjust Inotropes: Wean off Neo/Levo, in favor of
T4/Dopamine/Dobutamine (MM contact)
Bronch with gram stain immediately after consent is obtained and CXR 1 hour after
(We should try to bronch peds pts when the proper equipment is available)
o Call Pharmacy after sputum gram stain result is returned to see if antibiotic
adjustments need to be made
Per Lung Management Protocol
o Hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef) No loading dose. Maintenance dose is 6
mg/kg IV every 6 hour
o Ancef (Cephazolin): Infants and Children: 50-100mg/kg/day IV divided into
3 doses given q8h. Max dose is 6gm/day. Neonates: Postnatal age less
than 7 days: 40 mg/kg/day q12h; Postnatal age greater than 7 days and
less than 2 kg: 40 mg/kg/day q12h; Postnatal age greater than 7days and
greater than 2 kg: 60 mg/kg/day q8h
o NO NARCAN FOR KIDS UNDER 15 YEARS OF AGE. Narcan at
BEGINNING of case. Children >15years give 8mg. Narcan Rationale: Used
in effort to prevent or minimize Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema
o Norcuron can be given before or after Narcan. Do Not Give Norcuron if
Narcan was not given. Dose is 0.1mg/kg/dose (no max dose). May be
repeated prn. (Half-Life is 25-40 minutes). Norcuron rationale: Helps to
decrease spinal reflexes and relaxes the diaphragm and other respiratory
muscles to help ventilate
o Albuterol 2.5 mg or 5 mg Q 4 hours. In-line nebulizer is first choice, if unavailable
use unit/dose puff. Observe for Sinus Tachycardia
o Mucomyst nebulizer, 3-5cc of 20% solution or 10cc of 10% solution Q 4 hours.
Use ONLY in conjunction with Albuterol, never alone. Use only if patient has thick
secretions
T-4 Policy 5-09
For Pediatric donors (<16 years of age)
A. Add 200 mcg Levothyroxine (T4) 500 ml of 0.9% normal saline. Administer the
following bolus over 30 to 45 minutes, then start I.V. infusion as follows:
AGE
BOLUS
INFUSION
0-6 months
>6-12 months
>1-5 years
6-12 years
>12-16 years
5 mcg/kg
4 mcg/kg
3 mcg/kg
2.5 mcg/kg
1.5 mcg/kg
1.4 mcg/kg/hr
1.3 mcg/kg/hr
1.2 mcg/kg/hr
1.0 mcg/kg/hr
0.8 mcg/kg/hr
(T4 can be concentrated as needed to decrease IV rate and volume)
B. If T4 therapy is being initiated early in donor management (prior to, or
immediately following brain death) do not give bolus and immediately start the
infusion.
C. DO NOT administer Insulin, Vasopressin or Solu-Medrol as rapid
succession boluses prior to the T4 bolus, but rather administer Insulin (per
hospital protocol) and/or Solu-Medrol or Solu-Cortef and/or Vasopressin as
clinically indicated.
D. Administer Hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef) or Methylprednisolone (Solu-medrol) in
the following manner: 6mg/kg every 6 hours maintenance.
NOTE: “clinically indicated” in C refers to treatment for Hyperglycemia, DI
or for the lung protocol as appropriate-not for initiating the T4 protocol
LABS
Type and Screen (if not already done)
Labs-Initial and every 4 hours or as needed for specific organ placement:
Lytes, CBC with Diff, Mg, Phos, BUN, Cr, Glucose, Albumin, Total Protein,
PT/PTT, Fibrinogen or FSP, Amylase, Lipase, Serum Troponin, CPK with MB
bands, ABG with ICa, AST, ALT, ALK PHOS, Total and Direct bili, LDH, UA. One
time Labs (order with initial set of labs): GGT, LDH, Cholesterol, Sputum Culture
with bronch
T/C for 2 units PRBC’s on hold in blood bank. Obtain pre-transfusion
sera if applicable (>2ml)
Electrolyte Replacement Guide
K<3.0
K 3.0-3.9
1 mEq/kg over 2 hours-recheck K after infusion and repeat prn
0.5 mEq/kg over 2 hours-recheck K after infusion and repeat prn
*Max 20 mEq/dose. Max rate 0.5 mEq/kg/h. Peripheral IV dilute 20%
solution
ICa <1.1
10ml/kg CaCl over 30 minutes-repeat prn or CaGluconate 100mg/kg over
1 hour. Recheck ICa after infusion and repeat prn
*Max dose 1 gram/dose
Mg 1.0-1.9 25mg/kg MagSulfate over 1 hour repeat prn Q4-6h
Mg <1.0
50mg/kg MagSulfate over 1hour repeat prn Q4-6h
*Max dose 2 grams/dose
Phos 2.0-2.9 K Phos 0.1 mMol/kg/dose IV over 4-6 h
Phos 1.0-1.9 KPhos 0.2 mMol/kg/dose IV over 4-6 h
Phos<1.0
KPhos 0.3mMol/Kg/dose
(3 mMol Kphos= 4.4 mEq K)
If pt is hyperkalemic use NaPhos (if pt is not hypernatremic as well)
FLUIDS
o IV maintenance solutions should contain Na (if serum Na levels are normal),
D5% (unless pt is having uncontrolled hyperglycemia) and KCl (unless there is
hyperkalemia present). Sodium concentrations are based on patient wt and
serum sodium levels. For maintenance solution consider:
<10kg
D5% / 0.2NaCl / 20Meq/L KCl
10-20kg
D5% / 0.3NaCl / 20Meq/L KCl
>20kg
D5% / 0.45NaCl / 20Meq/KCl
*NOTE: Infants less than 6 months should have 10% Dextrose for maintenance
solution.
**Infants and children have increased fluid and electrolyte requirements and losses from
those of an adult and therefore require dextrose and electrolytes included in their
maintenance fluid.
Using Patient’s kg Weight to Calculate Hourly Maintenance:
10 kg or less = 100 mL/kg/24hrs.
10-20 kg = 1000 mL + 50 mL/kg for each kg over 10 kg/24 hrs.
Over 20 kg = 1500 mL + 20 mL/kg for each kg over 20 kg/24 hrs.
(Insensible = 20-40 mL/kg/24 hrs-already figured into maintenance)
OR:
1st 10 kg = 4 ml/kg (ex: 7kg=28ml/h)
2nd 10 kg = 2 ml/kg (ex: 12kg=44ml/h)
>20 kg = wt (kg) + 40 (ex: 24kg=64ml/h)
**Insensible loss is the loss of water by diffusion through the skin and by
evaporation from the respiratory tract. It is called “insensible” because we do not know
that we are actually losing water at the time that it is leaving the body. The fluid for
maintenance therapy replaces losses from 2 processes: evaporative (ie, insensible)
losses and urinary losses. Evaporative losses consist of solute-free water losses
through the skin and lungs. Under ordinary conditions, insensible losses account for
approximately 30-35% of total maintenance volume. Ambient humidity and temperature
affect insensible losses. Patients receiving humidified air have less insensible loss than
those not receiving humidified air. Patients with hyperthermia or tachypnea have
exaggerated (greater) insensible losses. Clinically this significant if your pt is febrile,
diaphoretic and/or tachypneic he may require slightly higher maintenance fluids.
Fluid Resuscitation
10-20 ml/kg of Normal Saline. Reassess, repeat as needed
NOTE: If Serum Na is elevated, consider 0.2NS bolus of 5-10ml/kg
Transfusion Therapy
Packed red blood cells 10-15 cc’s/kg Administer over 2-3 hours. May be administered
faster if hypotension or bleeding requires more aggressive correction of anemia
Fresh frozen plasma 10-15 cc’s/kg Administer over 1-2 hours.
May be administered faster if correction of coagulopathy is associated with volume
depletion or hypotension
Cryoprecipitate 5-10 cc’s/kg Administer for hypofibrinogenemia Or 1 unit for every 10
kg of body weight
Platelets < 15 kg: 10-20 cc’s/kg Administer slowly over 2-3 hours, >15 kg: single unit of
platelets
**For Pediatric pts, blood products are ordered according to wt-example: 10kg pt with
hgb of 8.8 you would order 100ml (10ml/kg) of PRBC’s. Then recheck Hgb. If repeat
hgb is 9.5 you would order another 100ml of PRBC’s. The blood bank should keep the
original unit, allocate it to that pt and then use it again for the 2 nd transfusion, saving
your pt from being exposed to multiple units.
Ordering PRBC’s for low Hgb
Hemoglobin
8-10
6-8
<6
PRBC’s
10ml/kg
15ml/kg
20ml/kg
Gift of Life Medication List
Medications
For Pediatrics <40kg or 16 years of age
Albuterol Nebulizer
Amiodarone
0.5cc/3cc NS
Pulseless V-Fib or V-Tach: 5 mg/kg rapid IV
bolus and do not exceed 300 mg
Perfusing Tachycardia: 5 mg/kg IV over 50
min; repeat twice up to a total loading dose
of 15 mg/kg
{Additional Note-infusion rate is 515mg/kg/min}
50-100 mg/kg/day IV q8h
10 mg/kg IV
100 mg/kg IV
25-50 mg/kg/day IV q6-8h
2-4 mcg/day IV in 2 divided doses
0.25 mg/kg IV for 2 minutes then 5-15 mg/hr
3-20 mcg/kg/min IV
3-20 mcg/kg/min IV
0.05-0.3 mcg/kg/min IV
0.5-1 mg/kg IV
1-2 cc/kg IV
6 mg/kg IV Q6
0.1-0.2 mg/kg/dose IV
q4-6h up to 1.7-3.5 mg/kg/day; Initial dose
not to exceed 20 mg
0.1 unit/kg then 0.05-0.2 unit/kg/hr IV
1 mg/kg IV then
then
20-50 mcg/kg/min
0.25-0.5 g/kg IV every 4-6 hr
6 mg/kg IV Q6
8 mg IVP x1
0.5-8 mcg/kg/min IV
0.08-0.1 mg/kg IV then 0.05-0.1 mcg/kg/min
maintenance
0.05-0.3 mcg/kg/min IV
0.25-0.5 mEq/kg by central line or IV (<20
mEq/hr)
0.08-0.36 mMol/kg/dose IV
over 4-6 h; 3mMol Phos= 4.4 mEq K
1 mEq/kg/dose over 20-30 minutes
25 mg/kg IV
0.5 - 10 milliunits/kg/hr IV
{Additional Note-Vaso dosing for DI-0.5
milliunits/kg/hr for Shock-0.3-2
milliunits/kg/min
Ancef (avoid w/ PCN allergy)
Calcium Chloride
Calcium Gluconate
Clindamycin (give w/ PCN allergy)
Desmopressin (DDAVP)
Diltiazem (Cardizem)
Dobutamine (MM contact required)
Dopamine
Epinephrine (Epi)
Furosemide (Lasix)
Glucose 25%
Hydrocortisone
Hydralazine
Insulin-regular
Lidocaine
Mannitol
Methylprednisolone
Narcan (age 15 and older)
Nitroprusside (Nipride)
Norcuron (Vecuronium)
Norepinephrine (Levophed, NE)
Potassium Chloride
Potassium Phosphate
Sodium Bicarbonate
Solu-medrol
Vasopressin (aqueous pitressin)
Additional Drips and Doses
Non Formulary per GOLM Policy
Consult Medical Manager for approval or hospital physician prior to use
DRUG
DILUTION
CONCENTRATION
USUAL DOSE RANGE
Esmolol
2500 mg in 250mL 10 mg/mL
Loading: 500 mcg/kg
5000 mg in 250mL 20 mg/mL
Infusion: 50-500 mcg/kg/min
7500 mg in 250mL 30 mg/mL
Labetalol
250 mg in 50 mL
5 mg/mL
0.4-1 mg/kg/hour
MAX 3 mg/kg/hour
Milrinone
undiluted
1 mg/mL
Loading: 50 mcg/kg
Infusion: 0.375-0.75 mcg/kg/min
Phenylephrine 10 mg in 250 ml
40 mcg/ml
0.1-0.5 mcg/kg/min
Procainamide 500 mg in 250 mL 2000 mcg/mL
Loading: 3-6 mg/kg/dose (Max
1 g in 250 mL
100 mg) over 5 min May repeat
2 g in 250 mL
4000 mcg/mL
until controlled, up to a max load
8000 mcg/mL
of 15 mg/kg. MAX 500 mg in 30
minutes. Initiate infusion at 20-80
mcg/kg/min (MAX 2 gm/day)
Prostaglandin 0.25 mg in 50 mL
5 mcg/mL
0.05-0.2 mcg/kg/min
E1
0.50 mg in 50 mL
10 mcg/mL
0.50 mg in 25 mL
20 mcg/mL
Terbutaline
Undiluted
1mg/ml
Loading: 2-10 mcg/kg
Infusion: 0.1-0.4 mcg/kg/min
Cardiovascular Agents (Expected Hemodynamic Changes)
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine
Cardiac
Output
↑
↑
Dobutamine
↑
↓
↓
increased
CO)
↑ (slight)
↓
Dopamine
< 6mcg
> 6mcg
↑
↑
↑
↑↑
↑slight
↑↑
↑slight
↑↑
↑
↑
↑
↑↑
Digoxin
↑
↔
↔
↔
↔ (↓ in
↓
↔
↔
Milrinone
↑
↓
↓
preload
sensitive
pt)
↑
↓
↓
Nitroglycerin (IV)
20-40 mcg/min
50-250 mcg/min
↔
↑
↓
↓
↔
↓
Nitroprusside
PCWP
SVR
↑
↑
↑
↑
Mean
BP
↑
↑
↑ (with
↔
↓
Heart
Rate
↔
↑
↔
↑
↑
↓
↓
↓
↑
↑ = increase ↓ = decrease ↔ = no change
CVP
PVR
↑
↑
↑
↑
↓
↓
↓
↓
↔
↑
↔
↓
↓
Additional Medications
Non-formulary per GOLM Policy
Consult Medical Manager or hospital physician prior to use
Medications
Dosages
Comments
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
10-15 mg/kg/dose PO/PR q4h
Acetazolamide (Diamox)
diuretic dose: 5 mg/kg/dose IV daily
Acyclovir (Zovirax)
30 mg/kg/day IV q8h
HSV meningitis dose: 20mg/kg/dose
for pts <12years
Adenosine
1st dose 0.05 mg/kg/dose Max 6mg Rapid IV push
2nd dose 0.1 mg/kg
Subsequent doses 0.2 mg/kg
Max 12 mg
Altepase (Activase)
0.1-0.6 mg/kg bolus or 0.3-0.5
Dose is frozen and will
mg/kg/hr
need time to thaw. May
PICC line: 1 mg/mL 0.5 mL at a
repeat doses
time
Aminophylline
No previous hx 6 mg/kg IV over 30
Check levels 30 min after
min.
infusion
Previous hx 3 mg/kg IV over 30 min
low levels 0.5 mg/kg for every 1
mg/L-increase needed in level
goal12 mg/L
Amphotericin B
test dose: 0.1 mg/kg/dose
Max of 1 mg
0.25 mg/kg/day over 4-6h
Increase daily as
tolerated
Amphotericin
B
Lipid 2.5-5 mg/kg/day daily
(Abelcet)
Ampicillin
100-200 mg/kg/day IV q4-6h
200-400 mg/kg/day IV q4-6h
(meningitis dose)
Ampicillin/Sulbactam
100-200 mg/kg/day IV q4-6h
Ampicillin component
(Unasyn)
Bumetanide (Bumex)
>6 mths: 0.015-0.1 mg/kg/dose
Max 0.1 mg/kg/day or 10
PO/IV/IM q6-24h
mg
Cefepime
50 mg/kg/dose q12h
q8h for febrile neutropenia
Cefotaxime
100-200 mg/kg/day q6h
Neonate use only
Ceftazidime
150 mg/kg/day q8h
Needs ID approval
Ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
50-75 mg/kg/day q12-24h
Meningitis 100 mg/kg/day q12-24h
Charcoal (Actidose)
Infant <1yr: 1 gm/kg/dose NG/PO
Children and adults q2-6h
q4-6h
NG/PO/PR single dose
Children 1-12 yrs: 1-2 gm/kg/dose with sorbitol
or 15-30 gm
Adults: 25-50 gms or 1-2 gm/kg
Chlorothiazide (Diuril)
IV: 2-8 mg/kg/day q8-24h
Give with lasix per CVS
PO: 20-80 mg/kg/day q12h
Cisatracurium
Co-trimoxazole (Bactrim)
IV: 0.1mg/kg q1h
>2 months: 8 mg TMP/kg/day IV
May increase up to 20 mg
TMP/kg/day
Dexamethasone (Decadron) cerebral edema: 1-1.5 mg/kg/day
airway edema/extubation:
2 mg/kg/day
Diphenhydramine(Benadryl) 5 mg/kg/day PO/IV q6-8h
Epinephrine Lavage
0.1 mg in 19 mL NS
Erythromycin
20-40 mg/kg/day IV q6h
Fibrin Glue
Mix Equal parts of Thrombin and
Ca Gluconate to make 10 mL
Draw up 10 mL of cryoprecipitate
and squirt both solutions
simultaneously onto site to be
glued
Fluconazole (Diflucan)
3-6 mg/kg/day PO/IV daily
Flumazenil (Romazicon)
Initial: 0.01 mg/kg (Max 0.2 mg)
May repeat for total of 1 mg
Gentamicin
5-7.5 mg/kg/day q8h
Ibuprofen (Motrin)
5-10 mg/kg/dose PO q6-8h
Magnesium Sulfate
25-50 mg/kg/dose IV
Metolazone (Zaroxolyn)
0.2-0.4 mg/kg/day PO q12-24h
Metronidazole
IV: 30 mg/kg/day q6h
PO: 15-35 mg/kg/day q8h
Milrinone
Loading: 50 mcg/kg
gtt: 0.375-0.75 mcg/kg/min
Oxacillin
100-200 mg/kg/day IV q4-6h
Pancuronium Bromide
0.1 mg/kg/dose IV q1hslowly
(Pavulon)
Phytonadione (Vitamin K)
Children:1-2 mg/dose
Procainamide (Pronestyl)
Loading: 3-6 mg/kg/dose over 5 min
gtt: 20-80 mcg/kg/min
3% Sodium Chloride
5 mL/kg IV to raise Na by 4 mEq/L
Spironolactone
Tromethamine (THAM)
Tobramycin
1.5-3.3 mg/kg/day q6-24h
1 mEq/kg
5-7.5 mg/kg/day IV/IM q8h
Vancomycin
10-40 mg/kg/day IV q6h
60 mg/kg/day for neurosurgical pts
0.2-0.4 mg/kg/day divided q12-24h
Zarolxolyn (Metolazone)
>1 mg/mL must be filtered
for serious gram neg.
infections
Max 10 mg/dose x 6
doses
Max 4 gm/day
Reverses
Benzodiazepines
Check levels
dilute to 20% solution
Max dose 4 g/day
Infuse over 1 hour
Max 12 g/day
Not to exceed 100
mg/dose
May repeat q5-10 min to
max 17 mg/kg/load
Max 2g/24h
Check Na before
repeating
Severe acidosis
Max 300 mg/day
Check levels
Max 2 gm/day
Infuse over 1 hr
Max adult dose 2.5-5
mg/day
CODE DRUGS
Commonly Used Emergency Drugs
Drug
Route
Adenosine
IV
Amiodarone
IV
Bumetanide
Calcium chloride 10%
CalciumGluconate 10%
Corticosteroids, stress
dose; Hydrocortisone
IV
IV
IV
IV
0.05-0.25 mg/kg IV rapid push,
followed by rapid 0.9 NS flush
5 mg/kg over 30 min followed
by continuous infusion 5-15
mcg/kg/min
0.015-0.1 mg/kg/dose
10-30 mg/kg MAX 1 gm
100 mg/kg MAX 1 gm
Bolus 1-2 mg/kg (MAX 100 mg)
Maint 1mg/kg/dose (MAX 100
mg/dose)
2-4 ml/kg
25% Dextrose
Enalaprilat
Epinephrine (1:10,000)
Epinephrine(1:1000)
Etomidate
Flumazenil
IV
IV
ET
IV
IV
Hydralazine
Insulin/glucose infusion
for hyperkalemia
IV
IV
Ketamine
Lidocaine
Lorazepam
Magnesium Sulfate
IV
IV
IV
IV
Mannitol
Naloxone
Nifedipine
Pancuronium
Sodium Bicarbonate
IV
IV
SL/NG
IV
IV
Sodium chloride, 3%
IV
THAM(buffer,
0.3mEq/mL)
Vecuronium
IV
IV
Dose
5-10 mcg/kg/dose
0.1 mL/kg
0.1 mL/kg
0.1-0.4 mg/kg/dose
Initial dose 0.01 mg/kg MAX 0.2
mg, then 0.005-0.01 mg/kg
MAX 3 mg in 1h
0.15 mg/kg
5 units regular insulin in 100 mL
of 25% dextrose, infuse at 0.1
unit insulin/kg/hr
0.5-3 mg/kg
1 mg/kg
0.03-0.1 mg/kg MAX 4 mg
25-50mg/kg
MAX 2 gm
0.25-1 g/kg
0.1 mg/kg
0.25-0.5 mg/kg
0.1 mg/kg
1 mEq/kg/dose-dilute 1:1 with
NS
5 mL/kg (to ↑serum Na+ by 4
mEq/L)
according to base deficit: 0.3 x
body wt in kg x base deficit
0.1 mg/kg
Defibrillation
Cardioversion
Defibrillating
0.5 joules/kg
2 joules/kg
Frequency
↑ by 0.05 mg/kg q 2
min up to 0.25 mg/kg
q 6-24 hrs
q 15-30 min
q 15-30 min
Once
q 6-8h
Dilute 50% 1:1 with
sterile water
q 8-24h
q 5-15 min
q 1 min initial
q20min subsequent
q 4-6 h
check serum K+, d/c
when K+ < 6 mEq/L
single dose
q 5-10 min
q 15 min
May be given over 1020 minutes. Check with
MD first
q 2-8 h
q 15-30 min
q 6-8 h
q1h
Infuse over 20 minutes
x 1, check serum Na+
x 1, check ABG
q 30-60 min