Algebra I 3rd Quarter - South Henry School Corporation / Overview
advertisement

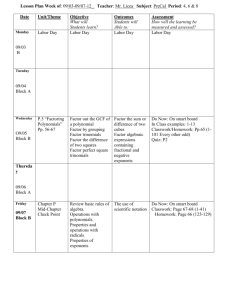
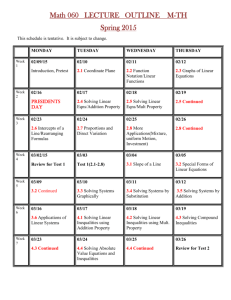
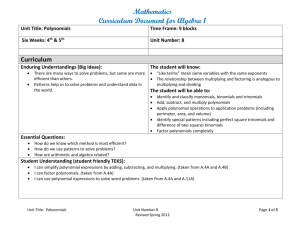
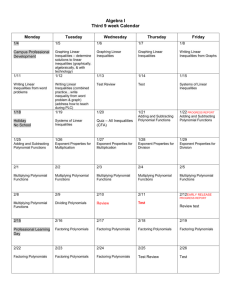
South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter Quarter: Three Standards Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content Skills Assessment Resources: Textbook: Prentice Hall Mathematics Algebra I Prentice Hall Mathematics Algebra I Practice Workbook Solutions Manual Big Ideas: In order to solve systems of inequalities, the coordinate plane will be shaded and the solution set id the overlap of the shaded regions rather than the intersection of two lines. There is more than one way to factor a polynomial depending on whether it has a leading coefficient of 1, a leading coefficient other than 1, a perfect square, or a difference of two squares. Essential Questions: When graphing inequalities on a coordinate plane, what is the difference between a dashed boundary line and a solid boundary line? What is the difference in the solution set of a system of equations and a solution set of a system of inequalities? How is it useful to simplify expressions by combining like terms? Why is it useful to write a number in scientific notation? Why is it helpful to factor a polynomial? Unit/Chapter Standards Content Skills Assessment Chapter 7 Part 2 Solving Systems of Inequalities Common Core Standards Linear Inequalities Graph linear inequalities on a coordinate plane Daily Assessments Represent and solve equations and inequalities graphically Dashed/Solid Boundary Lines 7-5: Linear Inequalities 7-6: Systems of Linear Inequalities A-REI. Represent and solve equations and inequalities graphically D.12. Graph the solutions to a linear inequality in two Systems of Linear Inequalities Graph systems of inequalities to find the solution set Write a system of inequalities based on a graph of the solutions Checked by students and graded by teacher Or Graded by teacher Textbook Assignments South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Quarter: Three Academic Year: 2013-2014 Unit/Chapter Standards Content Skills Assessment Chapter 8 Exponents and Exponential Functions variables as a half-plane (excluding the boundary in the case of a strict inequality), and graph the solution set to a system of linear inequalities in two variables as the intersection of the corresponding halfplanes. Zero and Negative Exponents Simplify and evaluate expressions that involve negative exponents or zero as the exponent Worksheet Assignments 8-1: Zero and Negative Exponents Exponents 8-2: Scientific Notation 8-3, 8-4: Multiplication Properties of Exponents 8-5: Division Properties of Seeing Structure in Exponents Expressions Scientific Notation Multiplication Properties of Exponents Division Properties of Exponents Common ratio 8-7: Exponential Functions 8-8: Exponential Growth and Decay A-SSE. Write expressions in equivalent forms to solve problems B.3. Choose and produce an equivalent form of an expression to reveal and explain properties of the quantity represented by the expression. B.3.a Factor a quadratic expression to reveal the zeros of the function it defines. B.3.b. Complete the square in a quadratic expression to reveal the maximum or minimum value of the In- Class Oral Responses Weekly/Bi-Weekly Multiply Powers to simplify algebraic expressions Notes Check Quizzes Geometric Sequences 8-6: Geometric Sequences Write a number in scientific or Standard notation Observations Arithmetic Sequences Exponential Functions Exponential Growth and Decay Growth Factor Simplify algebraic expressions using properties of exponents Find the next terms in a sequence Determine whether a sequence is arithmetic or geometric Evaluate an exponential function for a specified value Make a table and use it to graph an exponential function Tests South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter Quarter: Three Standards Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content Skills function it defines. Use an exponential function to model compound interest Arithmetic with Polynomials & Rational Expressions Chapter 9 Polynomials and Factoring 9-1: Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 9-2: Multiplying and Factoring 9-3: Multiplying Binomials 9-4: Multiplying Special Cases 9-5: Factoring Trinomials of the Type 𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 9-6: Factoring Trinomials of the Type 𝑎𝑥 2 + 𝑏𝑥 + 𝑐 9-7: Factoring Special Cases 9-8: Factoring by Grouping A-APR. Perform arithmetic operations on polynomials. A.1. Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to the integers, namely, they are closed under the operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication; add, subtract, and multiply polynomials. A-APR. Understand the relationship between zeros and factors of polynomials. B.3. Identify zeros of polynomials when suitable factorizations are available, and use the zeros to construct a rough graph of the function defined by the polynomial. Degree of monomials and polynomials Adding/Subtracting Polynomials Factoring Multiplying Binomials Real World Application that involves multiplying binomials Square of a Binomial Classify a polynomial based on the degree and the number of terms Add/subtract polynomials by vertically lining up like terms Simplify an expression by multiplying a polynomial by a common term Use the Greatest Common Factor to factor out a monomial Difference of Squares Factoring trinomials with a coefficient of 1 and a coefficient other than 1 Factor by Grouping Perfect-Square Trinomials Use FOIL to multiply binomials Use FOIL to multiply binomials to solve real word problems (Finding an area) Assessment South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter Quarter: Three Standards Function, Building Functions B-BF. Build a function that that models a relationship between two quantities. A.2. Write arithmetic and geometric sequences both recursively and with an explicit formula, use them to model situations, and translate between the two forms. Standards for Mathematical Practice MP1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. MP2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively. MP3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. MP4: Model with mathematics. MP5: Use appropriate tools strategically. MP6: Attend to precision. Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content Skills Difference of two squares Square a binomial and multiply to find the difference of squares Factoring by finding two factors that multiply to c and add to b. Factor trinomials by grouping Factor perfect square trinomials and difference of squares Assessment South Henry School Corporation • Tri Junior-Senior High School • Straughn, IN Curriculum Map Course Title: Algebra I Unit/Chapter Quarter: Three Standards MP7: Look for and make use of structure. MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Academic Year: 2013-2014 Content Skills Assessment