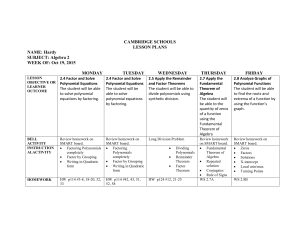
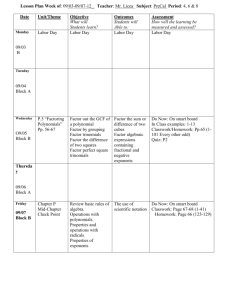
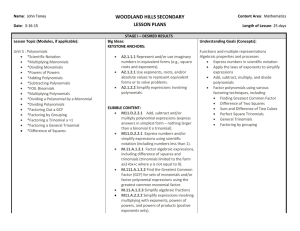
Unit Title: Polynomials Time Frame: 9 blocks Six Weeks: 4 th & 5 th
advertisement

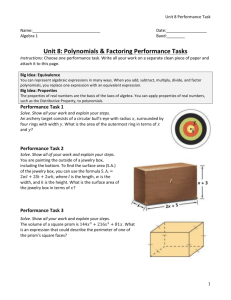
Mathematics Curriculum Document for Algebra 1 Unit Title: Polynomials Time Frame: 9 blocks Six Weeks: 4th & 5th Unit Number: 8 Curriculum Enduring Understandings (Big Ideas): The student will know: There are many ways to solve problems, but some are more efficient than others. Patterns help us to solve problems and understand data in the world. “Like terms” mean same variables with the same exponents The relationship between multiplying and factoring is analogous to multiplying and dividing The student will be able to: Identify and classify monomials, binomials and trinomials Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials Apply polynomial operations to application problems (including perimeter, area, and volume) Identify special patterns including perfect square trinomials and difference of two squares binomials Factor polynomials completely Essential Questions: How do we know which method is most efficient? How do we use patterns to solve problems? How are arithmetic and algebra related? Student Understanding (student friendly TEKS): I can simplify polynomial expressions by adding, subtracting, and multiplying. (taken from A.4A and A.4B) I can factor polynomials. (taken from A.4A) I can use polynomial expressions to solve word problems. (taken from A.4A and A.11A) Unit Title: Polynomials Unit Number 8 Revised Spring 2013 Page 1 of 3 Mathematics Curriculum Document for Algebra 1 TEKS: (A.4) Foundations for functions. The student understands the importance of the skills required to manipulate symbols in order to solve problems and uses the necessary algebraic skills required to simplify algebraic expressions and solve equations and inequalities in problem situations. The student is expected to: (A) find specific function values, simplify polynomial expressions, transform and solve equations, and factor as necessary in problem situations; (B) use the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to simplify algebraic expressions; and (A.11) Quadratic and other nonlinear functions. The student understands there are situations modeled by functions that are neither linear nor quadratic and models the situations. The student is expected to: (A) use patterns to generate the laws of exponents and apply them in problem-solving situations; Targeted College Readiness Standards: IB1, IIB1, IIIC1, IVC1, IVC2, VIIIA1, VIIIA2, VIIIA3, VIIIA4, VIIIA5, IXA1, IXA2, IXA3, IXC1, IXC2 Targeted ELPs: 1C, 2G, 2I, 3B, 3D, 3F Academic Vocabulary: Polynomial Language of Instruction: Binomial Constants Degree Exponents Leading coefficient Like-terms Monomial Perfect square trinomial Trinomial Instruction Instructional Resources: Textbook: Chapter 9 Sections 1, 2, 3, 4 (GCF only), 5 (factoring only), 6 (factoring only), 7 (factoring only), 8 (Pre AP) Unit Title: Polynomials Unit Number 8 Revised Spring 2013 Page 2 of 3 Mathematics Curriculum Document for Algebra 1 Closing the Distance Grade 9Lesson #11 Engaging Mathematics Algebra 1 (p. 66-86) Algebra 1 Assessments Instructional Suggestions/Examples for PSAT preparedness Technology: Career Connections/Real Life Application: Exemplar Lessons: Research Based Instructional Strategies: Assessment Student self-assessment & reflection: Exit Ticket Prompt: How can we use algebra to solve geometry problems? Unit Title: Polynomials Acceptable evidence or artifacts: Performance Task Unit 8 Unit 8 Test- Common Assessment Unit Number 8 Revised Spring 2013 Page 3 of 3