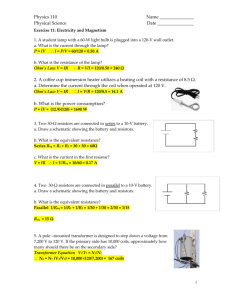
500Ω
advertisement
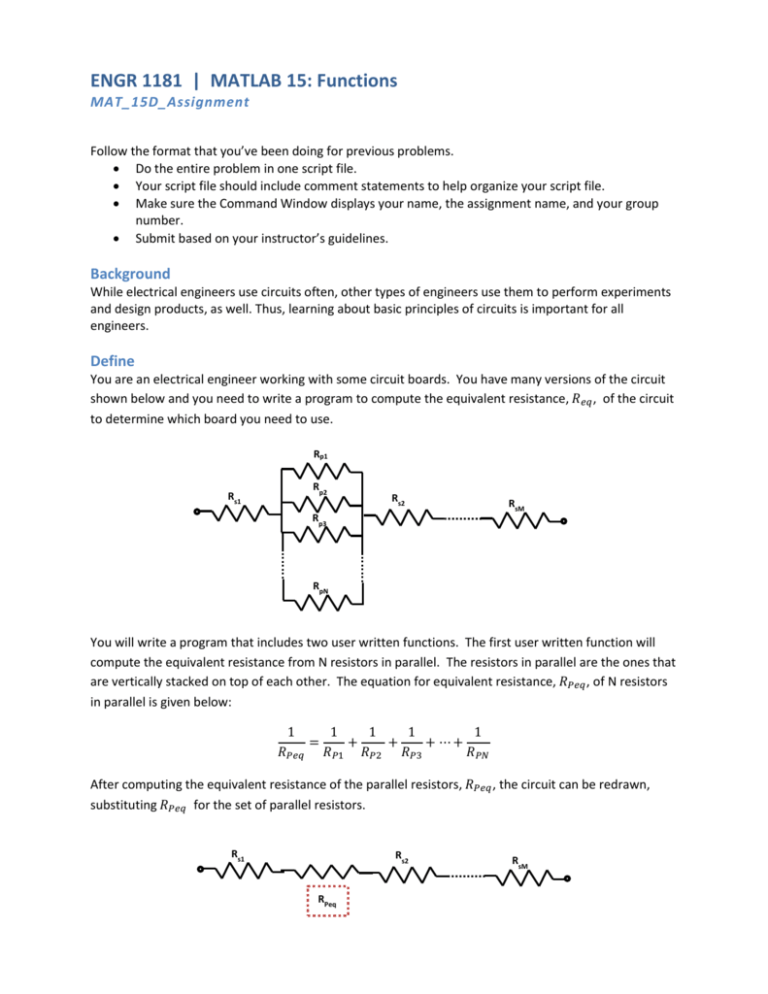
ENGR 1181 | MATLAB 15: Functions MAT_15D_Assignment Follow the format that you’ve been doing for previous problems. Do the entire problem in one script file. Your script file should include comment statements to help organize your script file. Make sure the Command Window displays your name, the assignment name, and your group number. Submit based on your instructor’s guidelines. Background While electrical engineers use circuits often, other types of engineers use them to perform experiments and design products, as well. Thus, learning about basic principles of circuits is important for all engineers. Define You are an electrical engineer working with some circuit boards. You have many versions of the circuit shown below and you need to write a program to compute the equivalent resistance, 𝑅𝑒𝑞 , of the circuit to determine which board you need to use. Rp1 Rp2 Rs1 Rs2 RsM Rp3 RpN You will write a program that includes two user written functions. The first user written function will compute the equivalent resistance from N resistors in parallel. The resistors in parallel are the ones that are vertically stacked on top of each other. The equation for equivalent resistance, 𝑅𝑃𝑒𝑞 , of N resistors in parallel is given below: 1 𝑅𝑃𝑒𝑞 = 1 1 1 1 + + + ⋯+ 𝑅𝑃1 𝑅𝑃2 𝑅𝑃3 𝑅𝑃𝑁 After computing the equivalent resistance of the parallel resistors, 𝑅𝑃𝑒𝑞 , the circuit can be redrawn, substituting 𝑅𝑃𝑒𝑞 for the set of parallel resistors. Rs1 Rs2 RPeq RsM As a result you now have a set of only resistors in series (horizontally attached to one another). The second user written function will compute the equivalent resistance from M resistors in series. Be sure to include the parallel equivalent resistance, 𝑅𝑃𝑒𝑞 , in this computation. The equation for equivalent resistance, 𝑅𝑒𝑞 , of M resistors in series is given below: 𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑅1 + 𝑅2 + 𝑅3 + ⋯ + 𝑅𝑀 A help sheet that includes a sample calculation is included at the end of this assignment. The user will input the number of resistors in parallel and the number of additional resistors in series. For example Circuit A has 4 resistors in parallel and 3 additional resistors in series. Then, the user will input the resistance in Ohms (Ω) of each resistor, in order. Set up the program to run repeatedly until the user quits the program. Instructions Represent Consider making a flowchart or algorithm to represent your solution process. Plan Create a script file Include comment statements in your program to plan out the solution. Implement Part 1: Write a function file for calculating the equivalent resistance for N resistors in parallel. The function should be sent a vector that contains all the resistances. You may send other information as needed. The function should return the equivalent resistance. Print the function file to pdf and submit to the Carmen Dropbox. Continue on to Part 2. Part 2: Write a function file for the series resistors. In the script file, perform the following tasks: Prompt the user for all inputs Compute the equivalent resistance of the resistors using the two functions described above. Display this value to the screen Prompt the user to see if he/she wants to quit. Repeat the program if necessary. You may need to clear the vectors. To clear individual variables type clear and then the variable name. Use the program to determine which circuits (A-D) on the following page give an equivalent resistance of 1300 Ω. Add an fprintf() statement to the end of your program which prints to the command window the answer. Your program must be run to show the results for all 4 circuits given. Evaluate Perform a hand calculation to verify your answer. Document Print (paper or pdf depending on instructor preference) the final version of your script file. Print (paper or pdf depending on instructor preference) the command window output. Print (paper or pdf depending on instructor preference) the calculation for the evaluate step. If paper: Staple the script file, function files, output, and verification together and turn it in. If pdf: Combine pdf files together and submit to Carmen Dropbox. 750Ω 500Ω 1000Ω 100Ω 80Ω 1000Ω A) 250Ω 100Ω 100Ω 500Ω B) 500Ω 100Ω 700Ω C) 200Ω 1000Ω 135Ω 65Ω 1000Ω 750Ω D) 500Ω 500Ω 500Ω Equivalent Resistance Sample Calculation If given the circuit shown below, the following steps outline how to compute the equivalent resistance: 5Ω 10Ω 25Ω 45Ω 65Ω 20Ω 20Ω 1) There are 4 resistors in parallel and 3 additional resistors in series. 2) Compute the equivalent resistance of the resistors in parallel (5Ω, 10 Ω, 20 Ω, 20 Ω). 1 𝑅𝑃𝑒𝑞 1 𝑅𝑃𝑒𝑞 = = 1 1 1 1 + + + ⋯+ 𝑅𝑃1 𝑅𝑃2 𝑅𝑃3 𝑅𝑃𝑁 1 1 1 1 + + + = 0.4 5Ω 10Ω 20Ω 20Ω 𝑅𝑃𝑒𝑞 = 2.5Ω 3) Redraw the circuit 25Ω 45Ω 65Ω 2.5Ω 4) Compute the equivalent resistance of the resistors in series (including the parallel equivalent resistance just computed). 𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 𝑅1 + 𝑅2 + 𝑅3 + ⋯ + 𝑅𝑀 𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 25Ω + 2.5Ω + 45Ω + 65Ω 𝑅𝑒𝑞 = 137.5Ω 5) The equivalent resistance of the circuit is 137.5Ω.