f) cellular defences
advertisement
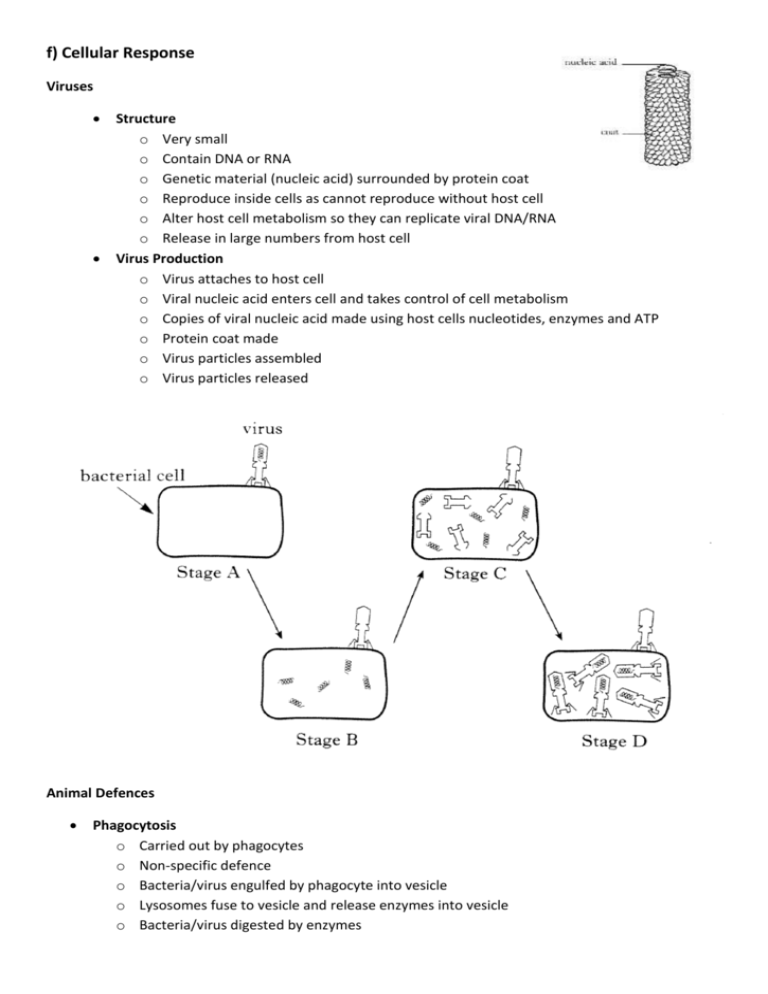
f) Cellular Response Viruses Structure o Very small o Contain DNA or RNA o Genetic material (nucleic acid) surrounded by protein coat o Reproduce inside cells as cannot reproduce without host cell o Alter host cell metabolism so they can replicate viral DNA/RNA o Release in large numbers from host cell Virus Production o Virus attaches to host cell o Viral nucleic acid enters cell and takes control of cell metabolism o Copies of viral nucleic acid made using host cells nucleotides, enzymes and ATP o Protein coat made o Virus particles assembled o Virus particles released Animal Defences Phagocytosis o Carried out by phagocytes o Non-specific defence o Bacteria/virus engulfed by phagocyte into vesicle o Lysosomes fuse to vesicle and release enzymes into vesicle o Bacteria/virus digested by enzymes Antigen Phagocytotic WBC WBC engulfs antigen trapping it in a vacuole Lysosomes containing powerful protein digesting enzymes fuse with the vacuole Enzymes released into the vacuole Antigen digested Digested parts diffuses into cytoplasm Antibody production o antibodies are made of protein o produced by lymphocytes o production stimulated by non-self antigens/proteins o antibodies are specific to the shape of antigens o antibody renders bacteria/virus harmless by combining with antigen o Antibodies are produced from first contact with bacteria/virus Production is slower and lower in volume o Second contact is faster, higher in volume and lasts longer Transplant surgery o transplanted tissues have foreign antigens and are recognised as non-self o antibodies made against transplant and tissue is rejected o risk of rejection is reduced by suppressors/drugs which suppress immune system Plant defences Toxic chemicals Give an unpleasant taste which discourages animals from eating the plant o tannins o cyanide o nicotine Barrier substances Isolate injured area to prevent spread of disease o Resins











