HERE
advertisement

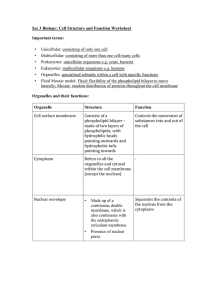
What do I need to know for Monday’s test? Prokaryotes Single cell Does NOT have a membrane bound nucleus protecting the DNA Small, simple organisms Example—bacteria Eukaryotes Multi-cellular (many cells) DNA is found in the nucleus Larger, more complex organisms Example—plants and animals Cell theory All living things are made of one or more cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things Cells come from other cells Organelles Cell membrane = surrounds cell to protect it. The cell membrane controls what can go into or out of a cell AND what is not allowed to go into or out of a cell. Nucleus = membrane -bound organelle that stores and protects the DNA. Cytoplasm = the fluid that fills the cell holding the organelles in place. It fills the space between the cell membrane and the nucleus Ribosomes = Make proteins Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)- Covered with ribosomes, the RER processes the proteins created by the ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) = makes lipids and breaks down toxins Golgi body – packages proteins into vesicles and ships them out of the cell. Mitochondria = the power house of the cell. It makes energy Centrioles = used in animals cells during cell division (animal cells only) Lysosome = vesicle containing enzymes that will break down food and waste Vacuole = in plants it is very large and stores water. In animals, it stores nutrients and waste Chloroplast = green organelle found in plants used to convert solar energy into glucose. It is responsible to photosynthesis Cell Wall = outermost layer of the plant cell. It supports the plant cells making them rigid. It lies right on top of the cell membrane Diffusion = the movement of molecules across the cell membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration Osmosis = the movement of WATER across the cell membrane from areas of high concentration to are of low concentration. STUDY, STUDY, STUDY!!!! Make flashcards!!! Writing helps you remember vocabulary