FNL – Unit 5 & 6 Study Sheet
advertisement

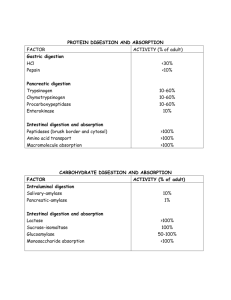
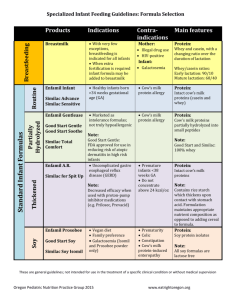
FNL – Unit 5 & 6 Study Sheet Infant Digestive System & Feeding 1. Know the parts of the digestive system and their functions – – – – – Mouth: some digestion and breakdown of food Esophagus: two principal jobs--to push food or fluid from the mouth to the stomach and to stop backflow, or reflux, of the contents of the stomach. Stomach: This is responsible for storing the swallowed food, combining and disintegrating the food, and regulating excretion of the stomach contents Small intestine: in charge of digestion and most of the absorption of nutrients. The digestive enzymes break down proteins into amino acids; carbohydrates into glucose and other monosaccharides; and fats into glycerol and fatty acids. Large intestine (colon): This curves upward, across and down to the rectum. It is mostly in charge of the absorption of water and electrolytes. Make sure you can label the digestive system 2. What are the three digestive problems infants have? Gas, Reflux and inflammation of the digestive tract 3. Oral Structures and Reflexes – – – Sucking- to rhythmically receive nourishment by mouth Swallowing- extra valve in back helps prevent choking Breathing- babies usually pause from eating to breathe Coordination of sucking, swallowing and breathing – Tongue Thrust- to prevent choking 4. Foods To Avoid – – – – – – – Honey and corn syrup: These foods may contain bacterial spores that cause food-borne illnesses, which are often fatal in infants. Salted and overly sweet foods: A baby’s immature kidney cannot handle much salt. Too much sugar in the diet displaces the calories and essential nutrients available in cereals, fruits, meats and vegetables. Too much formula: Don’t feed 6-month-olds more than about 40 ounces of formula. Too much formula displaces the calories and other nutrients from solid foods. Too much apple or pear juice: Too much may cause diarrhea. Foods that cause choking: Hot dogs, candy, nuts, grapes, coarsely cut meats, raw carrots, apples and popcorn are all foods that can get caught in a baby’s throat. Cow’s milk: Only breast milk or formula should be fed until after the first birthday. Cow’s milk has too much protein and sodium and too little iron for babies less than one year old. Citrus fruits and strawberries: These foods may cause an allergic reaction if fed before one year of age. 5. Advantages of Breastfeeding – – – – – – – Antibodies passed from a nursing mother to her baby can help lower the occurrence of many conditions such as infections and allergies. Breast milk is easily digested by a newborn's immature system. Breast milk also naturally contains many of the vitamins and minerals that a newborn requires. Free Convenient May help prevent obesity. Lowers the risk of breast cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and may also decrease the risk of uterine and ovarian cancer. 6. Disadvantages of Breastfeeding – – – – Breastfed babies need to eat more often. Requires a substantial time commitment from mothers. Women who are breastfeeding need to be careful about what they eat and drink, since things can be passed to the baby through the breast milk. Medical conditions such as HIV or AIDS or those that involve chemotherapy or treatment with certain medications may make breastfeeding unsafe. Newborn Nutrition & Feeding 1. What are the three Types of Formula? – – – Cow’s Milk Formula Most used and best tolerated Cow’s milk is altered to resemble human milk Cow’s milk protein allergies are possible – – – Soy-Based Formula Possible cow’s milk allergy alternative Vegan infants Cow’s milk allergies = soy milk allergies – – – – – Protein Hydrolysate Formulas Hypoallergenic formula Family history of milk/soy allergies Cow’s milk pre-digested Easier to digest Allergic reaction less likely 2. What are the three types of formula preparation? Powdered – Least expensive – 1 scoop powdered/2 oz. water Concentrated liquid – Most popular – 1 ounce formula/1 ounce water Ready-to-feed – Water not needed – Most convenient – Most sterile of infant formula – Most expensive 3. DHA – Docosahexaenoic Acid 4. ARA – Arachidonic Acid 5. What is the purpose of mealtimes? – – – – Communication Giving and receiving love Celebration Sensory exploration - Socialization - Sharing personal values - Physical growth and health - Relaxation, habit 6. What is the responsibility of the infant during mealtime? – – – – Gives permission for nipple to enter mouth Uses mealtime social pauses Let’s caregiver know when it’s time for burping Stops eating when full 7. How often should you breastfeed? Every 2 hours 8. What is the correct bottle feeding position? The infant should be cuddled and held in a semi-upright position during feeding. 9. What are some hazards of infant feeding? – – – Choking Overfeeding Inability to bond with caregiver 10. What are the dos and don’ts of burping? – – – – Done during and after feeding Wait until baby stops drinking Hold baby in one of two positions (shoulder or lap) Gently stroke / pat back 11. Why should you burp an infant? – – Releases stomach gas Prevents regurgitation