(2) SCH4U Sept 8th to Sept 12th 2014
advertisement

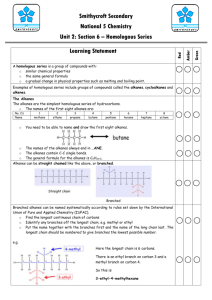
(2) SCH4U Organic Chemistry – September 8th to September 12th 2014 (FLIP WEEK) Date Mon Sept 8th Topic/Activities Check for signed SIS Homework pp. 15-16 Practice UC # 1, 2 Learning Goals I will be able to use proper scientific terminology to describe organic chemistry and alkanes I will be able to explain the structure, properties, uses of alkanes Success Criteria define: organic compound, inorganic compound, hydrocarbon, organic families, functional groups, alkane describe what IUPAC is and their function in chemistry education name alkanes using IUPAC rules draw structural diagrams for alkanes describe the properties and uses of alkanes Alkenes and Alkynes Practice pp. 18-19 UC # 3, 4, 5, 6 ClassNet PRINT: Hydrocarbons Introduction ClassNet PRINT: Hydrocarbons Practice 1) Tues Sept 9th Wed Sept 10th Alkanes a. b. c. d. General structure Nomenclature Physical and chemical properties Uses (1) Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Practice (PPT) (2) How to identify alkanes and cycloalkanes? Acyclic alkanes general formula CnH2n+2 Cyclic alkanes general formula CnH2n (3) General Properties of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes (4) Alkenes and Alkynes Nomenclature Alkenes and Cycloalkenes Practice (PPT) Alkynes Practice (PPT) Alkenes and Cycloalkenes Practice (WS) (5) Isomers of Alkyl Groups n-propyl (normal), isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, sbutyl (secondary), t-butyl (tertiary) Using Propyl and Butyl Isomers Practice (WS) (6) Structural and Geometric Isomers cis-trans geometric isomers of alkenes (7) General Properties of Alkenes and Alkynes (8) Diagnostic Testing for the Presence of Multiple Bonds adding bromine water (orange) or aqueous potassium permanganate (purple) (9) Combustion of Hydrocarbons (10) Organic Halides Properties Nomenclature (11) Aromatic Hydrocarbons Properties and Nomenclature Aromatics Practice p. 21 UC # 7, 8 General Hydrocarbons Section 1.2 Questions pp. 22-23 UC # 1, 2, 3, 4 I can use the following words correctly: organic compound, functional group, saturated hydrocarbon, unsaturated hydrocarbon, structural isomer, geometric isomer I can properly name, write formulas, and create structures for hydrocarbons and aromatic compounds I can describe the similarities and differences in physical properties (e.g. solubility in different solvents, odour, melting point, boiling point) of hydrocarbons I can explain the concept of isomerism in hydrocarbons and how variations in the properties of isomers relate to their structural and molecular formulae I can build molecular models for each class of hydrocarbons, organic halides and aromatics I can identify the reactants and products of complete and incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons memorize general formula for alkanes and cycloalkanes CnH2n+2 and CnH2n - subscript “n” represents number of carbons in a hydrocarbon hydrocarbons are non-polar, explain how intermolecular forces, specifically London dispersion forces impact physical properties of alkanes and cycloalkanes (e.g. state at room temp, m.p, b.p., solubility in water, solubility in benzene (non-polar substance) “like dissolves like” alkanes are saturated compounds, very stable, at SATP reactions are very slow alkanes only react with reactive substances like halogens – slow substitution reactions requiring light as a catalyst alkanes undergo rapid combustion reactions – require a spark or flame and oxygen alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one double bond between two carbons, double bond must be in parent chain double bond locks molecule in certain position, creating geometric isomers, called cis (same side) and trans (opposite side) alkenes general formula CnH2n alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one triple bond between two carbons, triple bond must be in parent chain alkynes general formula CnH2n-2 triple bonds prevents rotation, but also prevent cis-trans formation presence of double or triple bonds make alkenes and alkynes very reactive complete combustion of hydrocarbon always produces water and carbon dioxide incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon produces water and/or carbon, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide Date Thurs Sept 11th Topic/Activities 1. ClassNet PRINT: Hydrocarbons Reactions (pdfPPT) 2. Hydrocarbon Reactions Homework p. 27 Practice UC # 1, 2, 3 p.30 Practice UC # 4, 5, 6 p. 31 Section 1.3 UC # 2, 3, 4 Fri Sept 12th QUIZ: Hydrocarbon Nomenclature 1. 2. 3. ClassNet PRINT: Alcohols & Ethers (pdf-PPT) Alcohols Ethers p. 41 Practice UC # 1, 2, 3 p. 42 Practice UC # 4, 5 p. 44 Practice UC # 7, 8, 9 p. 46 Practice MC # 11 p. 48 Practice UC # 12, 13 p. 48 Section 1.5 UC # 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 Learning Goals I can explain and develop examples for the reactions involving hydrocarbons (e.g. combustion, addition, substitution) Success Criteria predict the products of combustion reactions of alkanes predict the products of substitution reactions of alkanes explain Markovnikov’s rule as it applies to reactions of alkenes and alkynes predict the products of addition reactions of alkenes and alkynes including: o halogenations o hydrogenation o hydrohalogenation o hydration predict the products of substitution reactions of cyclic hydrocarbons and aromatics predict the products of addition reactions of cyclic hydrocarbons and aromatics Worksheet – Reactions and Functional Groups (alkenes and alcohols) I can properly name, write formulas, and create structures for alcohols and ethers I can build molecular models for alcohols and ethers I can describe the similarities and differences in physical properties (e.g. solubility in different solvents, odour, melting point, boiling point) of alcohols and ethers I can explain reaction pathway use to produce alcohols and ethers define: alcohol, hydroxyl group, primary alcohol, secondary alcohol, tertiary alcohol, polyalcohols, cyclic alcohols name alcohols using IUPAC rules draw structural diagrams for alcohols describe the properties and uses of alcohols describe how to create alcohols using hydration reactions predict the products of combustion of alcohols predict the products of elimination reactions of alcohols define: ether, condensation reaction name ethers using IUPAC rules draw structural diagrams for ethers describe the properties and uses of ethers describe how to create ethers from alcohols