CHEM2710-121912
advertisement

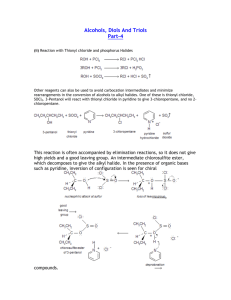
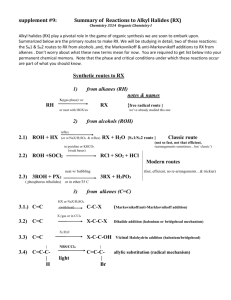
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE TITLE & NUMBER: Organic Chemistry 1: CHEM 2710 CREDITS: 5 (4 Lec/1Lab) PREREQUISITES: CHEM 1611: General Chemistry 2 CATALOG DESCRIPTION: Organic Chemistry 1 is a study of the chemistry of carbon compounds emphasizing the theories and mechanisms which account for their physical and chemical properties. Techniques of purification, separation, and synthesis are practiced in the laboratory. Organic Chemistry 1 is meant for students planning to major in biology, chemistry, chemical engineering, pharmacy, and certain medical fields. OUTLINE OF MAJOR CONTENT AREAS: I. II. III. IV. V. Review of general chemistry A. Covalent bonds B. Lewis structures C. Octet rule D. Resonance E. Quantum mechanics F. Hybrid orbitals G. VSEPR Theory Representative carbon compounds A. Carbon-carbon covalent bonds B. Introduction to hydrocarbons C. Introduction to functional groups Acids and bases in organic chemistry A. Introduction to organic reactions and mechanisms B. Review of acid/base reactions C. Relationship between equilibrium constant and Gibbs free energy Alkanes and cycloalkanes A. Shapes of alkanes B. Nomenclature C. Physical properties D. Conformations E. Chemical reactions Stereochemistry A. Constitutional and stereoisomers B. Enantiomers and chiral molecules C. Nomenclature of enantiomers CHEM 2710 1 Hibbing Community College, a technical & community college, is an equal opportunity educator& employer VI. VII. VIII. D. Optical activity E. Synthesis of enantiomers F. Separation of enantiomers Nucleophilic substitution and elimination of alkyl halides A. Physical properties of alkyl halides B. Nucleophiles C. Leaving groups D. Thermodynamics and kinetics of chemical reactions E. SN2 reactions F. SN1 reactions G. E2 reactions H. E1 reactions I. Substitution versus elimination Alkenes and alkynes A. Nomenclature B. Physical properties C. Synthesis of alkenes 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides 2. Dehydration of alcohols 3. Dehalogenation of vicinal dihalides 4. Reduction of alkynes D. Synthesis of alkynes 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl dihalides 2. Reaction of metal acetylides with primary alkyl halides E. Addition reactions/Markovnikov's Rule F. Reactions of alkenes 1. Hydrogenation 2. Halogenation 3. Hydrohalogenation 4. Hydration 5. Addition of sulfuric acid 6. Halohydrin formation 7. Syn hydroxylation 8. Oxidative cleavage 9. Ozonolysis G. Reactions of alkynes 1. Hydrogenation 2. Halogenation 3. Hydrohalogenation 4. Oxidation Radical reactions A. Homolytic bond dissociation energies B. Halogenation of alkanes C. Anti-Markovnikov addition D. Addition polymerization CHEM 2710 2 Hibbing Community College, a technical & community college, is an equal opportunity educator& employer IX. Alcohols and ethers A. Structure and nomenclature B. Physical properties C. Synthesis of alcohols 1. Hydration of alkenes 2. Oxymercuration-demercuration 3. Hydroboration-oxidation 4. Reduction of carbonyl compounds 5. Grignard synthesis D. Reactions of alcohols 1. Reaction with hydrogen halides 2. Reaction with phosphorus trihalides 3. Dehydration 4. Reaction as acids 5. Ester formation 6. Oxidation to from aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids E. Synthesis of ethers: Williamson synthesis F. Reactions of ethers: cleavage by acids G. Epoxides H. Crown ethers COURSE GOALS/OBJECTIVES/OUTCOMES: Students will 1. predict the hybridization and geometry of the atoms in an organic molecule. 2. draw three-dimentional representations of organic molecules. 3. predict general trends in the boiling points and solubilities of organic compounds based on their size, polarity, and hydrogen bonding ability. 4. use the IUPAC system to name alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, cyclic and bicyclic compounds, alkyl halides, alcohols, and ethers. 5. classify molecules as chiral or achiral and identify mirror planes of symmetry. 6. identify chiral carbon atoms and name them using the (R) and (S) nomenclature. 7. identify enantiomers, diastereomers, and meso compounds. 8. predict the stereochemistry of products of organic reactions. 9. predict the products of nucleophilic substitution reactions, elimination reactions, radical reactions and addition reactions. 10. predict and explain the rearrangement of carbocations in first-order reactions. 11. describe the physical properties of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, cyclic and bicyclic compounds, alkyl halides, alcohols, and ethers. 12. describe synthesis routes for alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, cyclic and bicyclic compounds, alkyl halides, alcohols, and ethers. 13. describe the chemical reactions of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, cyclic and bicyclic compounds, alkyl halides, alcohols, and ethers. 14. use the E-Z and cis-trans systems to name geometric isomers. 15. describe the basics of polymer chemistry. 16. descibe and perform basic organic laboratory techniques such as filtration, CHEM 2710 3 Hibbing Community College, a technical & community college, is an equal opportunity educator& employer crystallization, melting point determination, extraction, and distillation. HCC COMPETENCIES MET: Thinking Creatively & Critically STUDENT ASSESSMENT SHALL TAKE PLACE USING INSTRUMENTS SELECTED/DEVELOPED BY THE COURSE INSTRUCTOR. SPECIAL INFORMATION: (SPECIAL FEES, DIRECTIVES ON HAZARDOUS MATERIALS, ETC.) Hazardous chemicals will routinely be used in laboratory. Students will be supplied with pertinent information relating to these materials at the appropriate time. AASC APPROVAL DATE: December 19, 2012 REVIEW DATE: December 2017 CHEM2710:so 121912 CHEM 2710 4 Hibbing Community College, a technical & community college, is an equal opportunity educator& employer