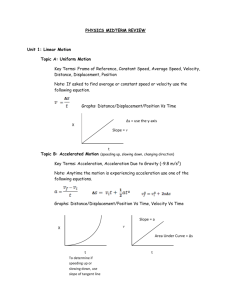
Physics Equation Summary 2014
advertisement
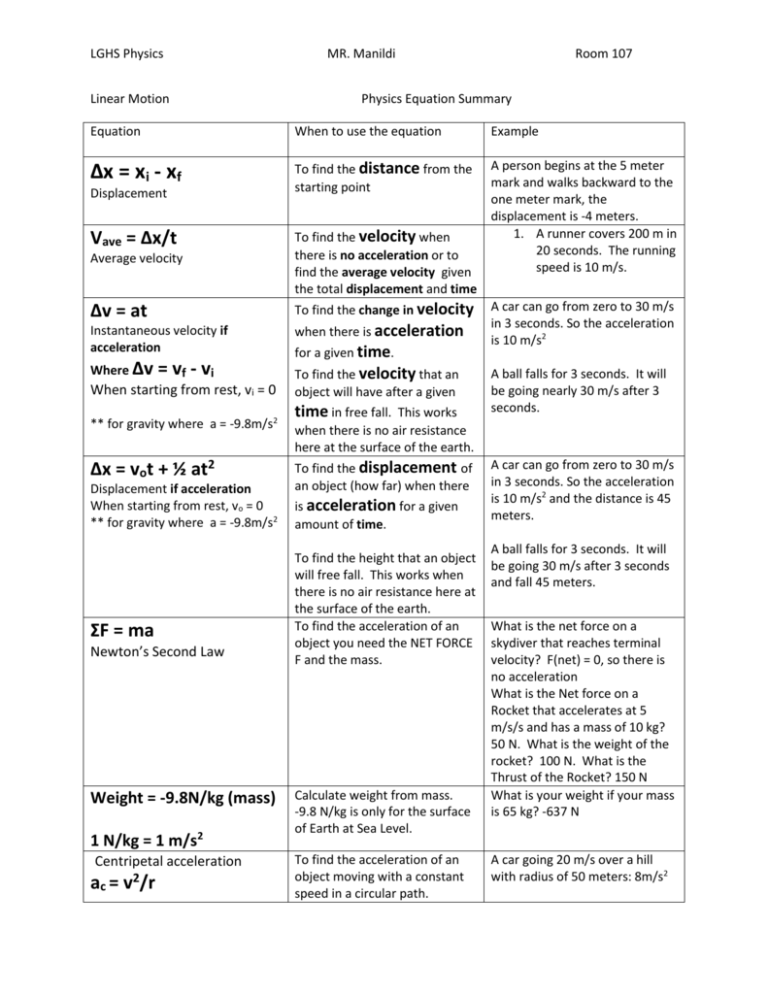
LGHS Physics Linear Motion MR. Manildi Room 107 Physics Equation Summary Equation When to use the equation Example ∆x = xi - xf To find the distance from the starting point A person begins at the 5 meter mark and walks backward to the one meter mark, the displacement is -4 meters. 1. A runner covers 200 m in 20 seconds. The running speed is 10 m/s. Displacement Average velocity To find the velocity when there is no acceleration or to find the average velocity given the total displacement and time ∆v = at To find the change in velocity Instantaneous velocity if acceleration when there is acceleration Where ∆v To find the velocity that an object will have after a given time in free fall. This works when there is no air resistance here at the surface of the earth. A ball falls for 3 seconds. It will be going nearly 30 m/s after 3 seconds. To find the displacement of an object (how far) when there is acceleration for a given amount of time. A car can go from zero to 30 m/s in 3 seconds. So the acceleration is 10 m/s2 and the distance is 45 meters. Vave = ∆x/t = vf - vi When starting from rest, vi = 0 ** for gravity where a = -9.8m/s2 ∆x = vot + ½ at2 Displacement if acceleration When starting from rest, vo = 0 ** for gravity where a = -9.8m/s2 ΣF = ma Newton’s Second Law Weight = -9.8N/kg (mass) 1 N/kg = 1 m/s2 Centripetal acceleration ac = v2/r for a given time. To find the height that an object will free fall. This works when there is no air resistance here at the surface of the earth. To find the acceleration of an object you need the NET FORCE F and the mass. Calculate weight from mass. -9.8 N/kg is only for the surface of Earth at Sea Level. To find the acceleration of an object moving with a constant speed in a circular path. A car can go from zero to 30 m/s in 3 seconds. So the acceleration is 10 m/s2 A ball falls for 3 seconds. It will be going 30 m/s after 3 seconds and fall 45 meters. What is the net force on a skydiver that reaches terminal velocity? F(net) = 0, so there is no acceleration What is the Net force on a Rocket that accelerates at 5 m/s/s and has a mass of 10 kg? 50 N. What is the weight of the rocket? 100 N. What is the Thrust of the Rocket? 150 N What is your weight if your mass is 65 kg? -637 N A car going 20 m/s over a hill with radius of 50 meters: 8m/s2 LGHS Physics MR. Manildi Room 107 To find the centripetal force of an object moving with a constant speed in a circular path. To find the gravitational force of attraction between any two objects at a distance “r” A car 1000 kg car going 20 m/s over a hill with radius of 50 meters: 8000 Newtons G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 Universal Gravitation Constant Measured by Cavendish Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth We usually round this to 10 m/s/s for Earth. This depends on the Mass of Earth and the distance from the earth but is accepted as constant on the surface of earth. ΣFc = m v2/r FG = G 𝒎𝟏 𝒎𝟐 𝒓𝟐 Law of Universal Gravitation The distance between them is ‘r’ If the force between the two objects is F, and you double both masses and ½ the distance, what is the new force? 16 F CONSTANTS g = -9.8 m/s2