Mid Term Review Sheet
advertisement
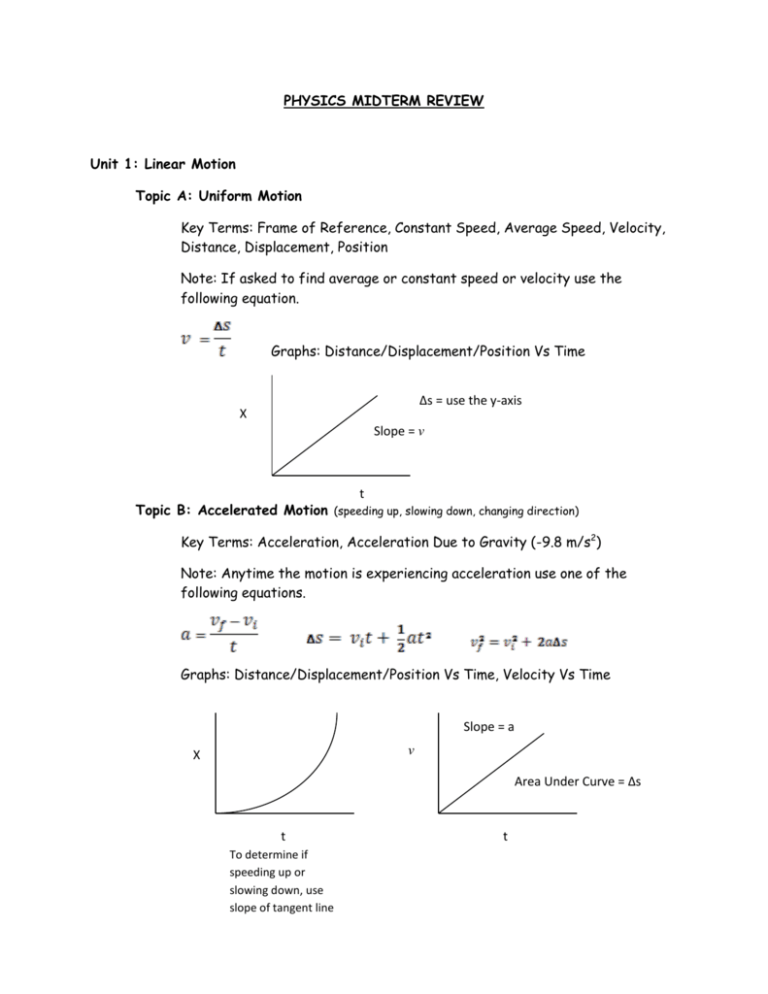
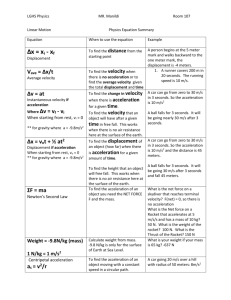
PHYSICS MIDTERM REVIEW Unit 1: Linear Motion Topic A: Uniform Motion Key Terms: Frame of Reference, Constant Speed, Average Speed, Velocity, Distance, Displacement, Position Note: If asked to find average or constant speed or velocity use the following equation. Graphs: Distance/Displacement/Position Vs Time ∆s = use the y-axis X Slope = v t Topic B: Accelerated Motion (speeding up, slowing down, changing direction) Key Terms: Acceleration, Acceleration Due to Gravity (-9.8 m/s2) Note: Anytime the motion is experiencing acceleration use one of the following equations. Graphs: Distance/Displacement/Position Vs Time, Velocity Vs Time Slope = a v X Area Under Curve = ∆s t To determine if speeding up or slowing down, use slope of tangent line t Unit 2: Vectors and 2D Motion Topic A: Vectors Key Terms: Head to Tail, Resultant, Component θ Bx C By A Cy Ay B Ax Cx Topic B: Projectiles Key Terms: Range, Displacement Note: When solving problems involving the motion of a projectile, remember to separate into horizontal “x” motion and vertical “y” motion since they are independent of each other. Then use the kinematics equations. Projectiles Launched Horizontally Notes on “x” Motion: V Vx = V (constant) a=0 Notes on “y” Motion: ∆Y Vyi = 0 ∆X (Range) a = -9.8 ∆Y = is negative “-“ Projectiles Launched at an Angle (from the ground and landing on the ground) Notes on “x” Motion: Vy = 0 @ max Vx = Vcosθ (constant) height a=0 Notes on “y” Motion: V a = -9.8 θ ∆X (Range) ∆Y = 0 Vyi = Vsinθ Unit 3: Newton’s Laws of Motion Key Terms: Force (Applied, Frictional, Gravity <weight>, Normal, Tension), Free Body Diagram 1st Law: Inertia Balanced Forces Constant Motion State of Equilibrium 2nd Law: ΣF = ma Unbalanced Force (Net Force) Accelerated Motion Acceleration is in the Direction of the Net Force Acceleration and Net Force have a Direct Relationship Acceleration and Mass have an Inverse Relationship 3rd Law: Action – Reaction Forces are Equal and Opposite Act on Different Objects Solving Problems 1. Read the Problem 2. Draw a FBD with ALL Forces 3. ΣForces in “x” and “y” set = ma 4. Solve for Unknown Unit 4: Circular Motion and Universal Gravitation Topic A: Circular Motion Key Terms: Centripetal Acceleration, Centripetal Force, Linear (Tangential) Velocity, Frequency, Period Motion v Fc ac Note: A centripetal force is not a real force. It is some other force acting as a centripetal force. Examples: friction (car turning), gravity (orbiting bodies), tension (conical pendulum), normal (carnival rides), weight (something on the Earth’s surface) Topic B: Universal Gravitation Key Terms: Gravitational Force, Kepler’s Laws Force of Gravity Depends on: 1. Mass of Objects (Direct Relationship) 2. Distance Between Centers (Inverse Square Relationship)