Relative and Absolute Ages of Rocks Quiz Study Guide
advertisement
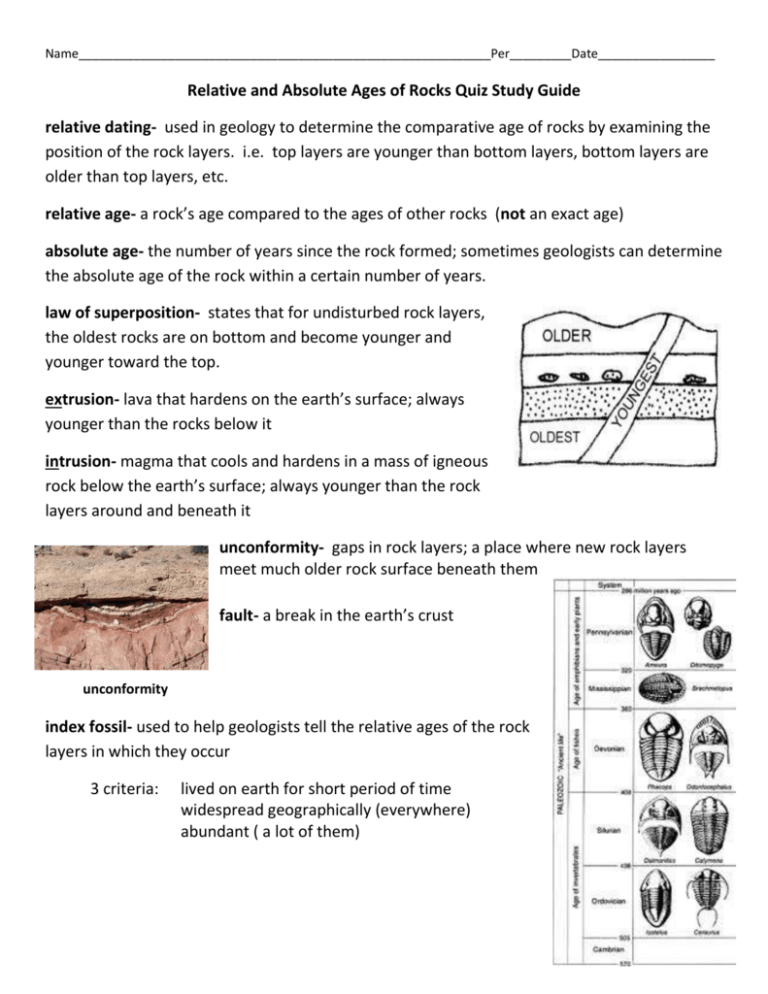
Name____________________________________________________________Per_________Date_________________ Relative and Absolute Ages of Rocks Quiz Study Guide relative dating- used in geology to determine the comparative age of rocks by examining the position of the rock layers. i.e. top layers are younger than bottom layers, bottom layers are older than top layers, etc. relative age- a rock’s age compared to the ages of other rocks (not an exact age) absolute age- the number of years since the rock formed; sometimes geologists can determine the absolute age of the rock within a certain number of years. law of superposition- states that for undisturbed rock layers, the oldest rocks are on bottom and become younger and younger toward the top. extrusion- lava that hardens on the earth’s surface; always younger than the rocks below it intrusion- magma that cools and hardens in a mass of igneous rock below the earth’s surface; always younger than the rock layers around and beneath it unconformity- gaps in rock layers; a place where new rock layers meet much older rock surface beneath them fault- a break in the earth’s crust unconformity index fossil- used to help geologists tell the relative ages of the rock layers in which they occur 3 criteria: lived on earth for short period of time widespread geographically (everywhere) abundant ( a lot of them)







