Surgery Take-Home Quiz Answers
advertisement

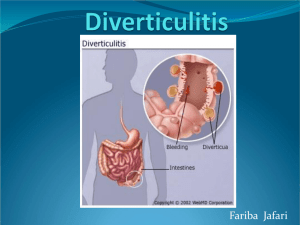
Surgery Board Review Take-Home Quiz Answers March, 2011 1. Beckwith-Wiedemann: a. Macroglossia b. Macrosomia c. Hypoglycemia (islet cell hyperplasia) d. Hemihypertrophy e. Hypospadias f. Omphalocele 2. How might a TE fistula present in the newborn period? How does presence/absence of gastric bubble on KUB clue you in about which type of TE fistula the patient has? Which type of TE fistula might present weeks to months later (outside of the immediate newborn period)? a. Resp distress, inability to tolerate initial feed, drooling, inability to pass NG. If there is no gastric bubble (may even see scaphoid abdomen) then no air is passing through the proximal GI tract... It is either pure atresia, or proximal fistula with no connection distally. H type might not present immediately. 3. In a patient with malrotation (even without volvulus) describe the classic findings of imaging done by upper GI. What if a barium enema was done, which clues would you see? Upper GI: In the normal “duodenal sweep” the distal duodenum passes back across the midline to the left (and even superiorly) to make a nice C shape. With malrotation, the duodenum does not cross the midline. “Corkscrew” will only be seen if there is volvulus, and may not be apparent even then. Something you may even see on KUB: small intestines lie primarily to the R and colon mostly on the L. Barium enema is not indicated for this diagnosis, but is sometimes done if intussusceptions is falsely suspected. It would show cecum on L. 4. In Hirschprung’s, on BE you would see small distal colon, transition zone, and dilated proximal colon. The dilated area is actually the normally innervated area. If you perform rectal exam, the child will typically evacuate the colon (defecate explosively). The characteristic findings mentioned above will not be seen if the colon is empty. 5. Peutz-Jeghers: Hamartomatous polyps: Melanotic mucocutaneous pigmentation lips, gums / GI bleeding/AD inheritance/ Premalignant-Surgical resection indicated 6. Neonatal abdominal masses a. Congenital obstructive hydronephrosis and mulitcystic kidney disease b. Maternal hormone stimulation c. <5cm - nothing the withdrawal of hormonal stimulation will lead to resolution >5cm – aspiration d. malignant sacrococcygeal teratoma 7. Imperforate hymen a. Infancy – hydrocolpos with resultant abdominal mass and possible respiratory suppression b. Puberty – cyclic abdominal pain, large pelvic or lower abdominal mass, absence of menses c. GU tract abnormalities 8. Head masses a. Hemangiomas should be treated when the patient develops Kasaback-Merrit syndrome, if there is impending airway compromise or if there is periorbital involvement b. Surgical excision should be done on a preauricular pit or sinus when there are infectious complications c. A ranula should be surgically corrected when it impairs lingual mobility, feeding, speech and/or breathing d. A patient with a lingual thyroid is at risk for hypothyroidism 9. Neck masses a. Thyroglossal duct cyst – complete excision b. Benign reactive lymphadenopathy – treat the underlying infection c. Lymphadenitis – antibiotics and I&D if necessary d. Atypical infection – complete resection e. TB – aggressive anti-TB therapy, resection is avoided 10. Abdominal wall defects a. Omphalocele – should be repaired shortly after birth but is more elective because of the protective covering. A staged repair may have to be done b. Gastroschisis – is a surgical emergency and should be repaired as soon as possible dur to the risk of dessication or injury to the exposed bowel c. Umbilical hernia – repair may be deferred until after the 5th birthday because most will resolve spontaneously. Repair should be done sooner if >2cm, proboscoid, or if there is a history or high risk of incarceration d. Inguinal Hernia – prompt repair should be done since it will not resolve spontaneously and it will have a high risk of incarceration e. Hydrocele – repair should be done at about 12-18months of age since many will undergo spontaneous resolution before that age. Those that do not resolve within that time most likely have a persistent communication that is in need of surgical repair.