Measuring Earthquakes
advertisement

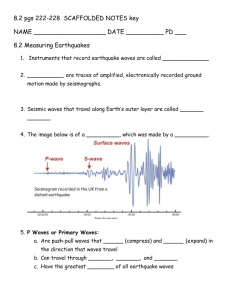
Measuring Earthquakes Objectives- Describe properties of the different kinds of earthquake waves and the scales used to measure them. When plates move against or along each other pressure builds up. Eventually the pressure gets released, often suddenly. Energy travels rapidly outwards through the earth. The location where the rocks first begin to move (inside the lithosphere) is called the focus. To a geologist (actually a seismologist), this point is important, but most people would not understand it. The epicenter (epi = top) is the location on the earth’s surface directly above the focus. The vibrations or waves generated by the earthquake are called seismic waves. They travel outwards from the focus in all directions. The types of rocks and soil determine how much the ground shakes. There are three types of seismic waves: Primary or P waves, Secondary or S waves, and Surface waves. The P waves are the fastest of the three. They travel around 6km/sec. P waves make the surface of the ground move like an accordion. P waves can travel through both solids and liquids. S Waves travel about 4 Km/sec and are the second fastest of the waves. The make the ground go up and down. S waves can only travel through solids. Surface waves are the slowest of the waves. They make the water roll like waves on water. Earthquakes are detected using a seismograph. Older mechanical seismographs looked like the one shown. The spring held the pen stationary. When the earthquake occurred, the base moved, but not the pen. In other words, the paper moves underneath the pen leaving a mark on the paper. The stronger the earthquake, the higher the marks. Newer seismographs work on the same principle, but are electronic. There have been several scales used to measure earthquake magnitude or the amount of energy released. Most people are familiar with the Richter scale. It was developed in the 1930’s. The Richter scale was limited in its effectiveness, mostly to California earthquakes and smaller earthquakes. It was based upon the height of the wave that was recorded. The Moment Magnitude Scale, the currently used scale works for all earthquakes. The scale measures the magnitude or the amount of energy released. For every whole number, ten times more energy is released. This would be like going from a 3 to 4 on the Moment Magnitude Scale. Going from a 3 to a 5 would be a 100 times increase in the amount of energy. The number is the product of how much the fault move and how much force it takes to move it. Sounds complicated. In order to determine the epicenter of an earthquake, seismologists need readings from a minimum of three seismographs. By using the differences in the time between the P and S waves arriving at a specific location, the can tell how far away they are from the focus. Remember that the speed P and S waves travel are known and the farther away the location is from the epicenter, the greater the difference between when the P and S waves arrive. If only one seismograph station is used, every location on a circle drawn at the appropriate distance away from the seismograph would be a possible location. If two seismographs are used, then there could be 2 intersections of the circles around each seismograph. Only with three could you get one location. Questions: 1. View the website Seismic Waves (sunshine.chpc.utah.edu). Read the information and answer the questions. 2. Complete the chart on seismic waves Type of Wave Speed Ground motion P S Surface 3. How much more energy does an earthquake with a magnitude of 7 release than a magnitude 3 earthquake? 4. Suggest a reason why information from California earthquakes cannot be applied to all earthquakes to determine their strength. (rest is not from website) 5. The point where a rock under stress breaks and triggers an earthquake is called the ____________. 6. The point on the surface directly above the focus is the ________________________. 7. What are seismic waves? 8. True or false- Seismic waves carry the energy of an earthquake away from the focus in all directions. 9. True or false- Surface waves move more quickly than P waves and S waves. 10. A device that records the ground movements caused by seismic waves is a(n) _________________________. 11. True or False- The closer an earthquake, the greater the time between the arrival of P waves and the arrival of S waves.