HAZID Field Review Document
advertisement
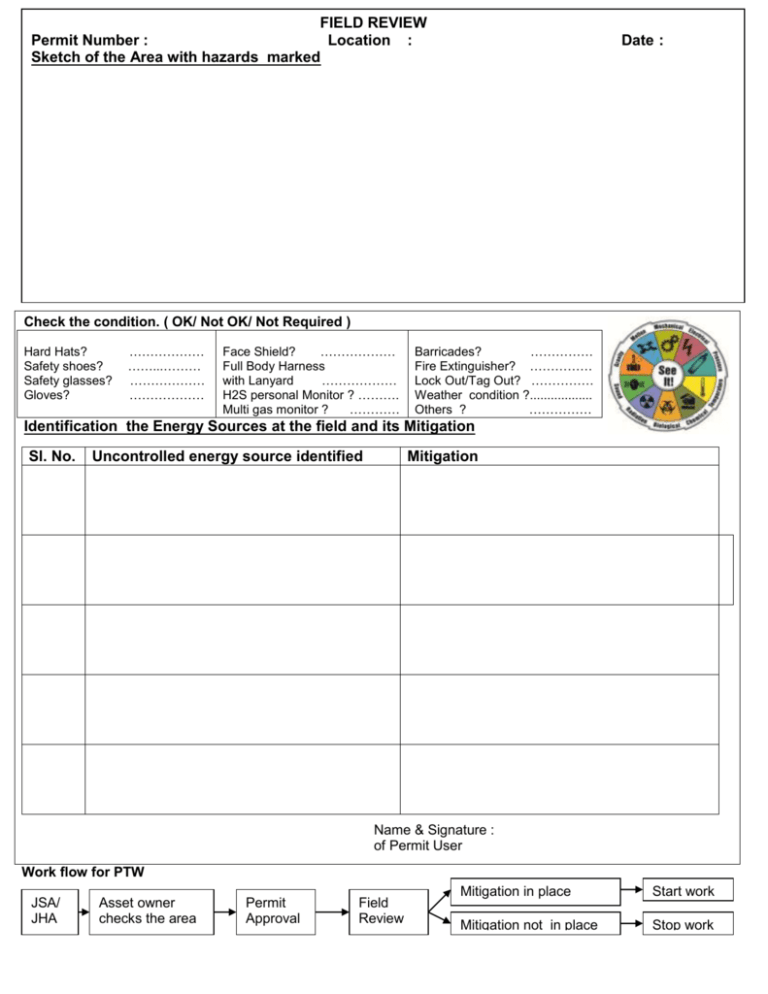
FIELD REVIEW Permit Number : Location : Sketch of the Area with hazards marked Date : Check the condition. ( OK/ Not OK/ Not Required ) Hard Hats? Safety shoes? Safety glasses? Gloves? ……………… ……...……… ……………… ……………… Face Shield? ……………… Full Body Harness with Lanyard ……………… H2S personal Monitor ? ………. Multi gas monitor ? ………… Barricades? …………… Fire Extinguisher? …………… Lock Out/Tag Out? …………… Weather condition ?.................. Others ? …………… Identification the Energy Sources at the field and its Mitigation Sl. No. Uncontrolled energy source identified Mitigation Name & Signature : of Permit User Work flow for PTW JSA/ JHA Asset owner checks the area Permit Approval Field Review Mitigation in place Start work Mitigation not in place Stop work Hazard Identification Tool Chemical Gravity The energy present in chemicals that inherently, or through reaction, has the potential to create a physical or health hazards to people, environment or equipment. Examples: flammable vapors, reactive hazards, toxic compounds, corrosives, combustibles, oxygendeficient atmospheres, welding fumes, and dusts The force caused by the attraction of all other masses to the mass of the earth. Examples: falling object, collapsing roof, and a body tripping or falling Motion The change in position of objects or substances. Examples: vehicle, vessel or equipment movement; flowing water; wind; and body positioning: lifting, straining, or bending Electrical Mechanical The energy of the components of a mechanical system, i.e. rotation, vibration, motion, etc. within otherwise stationary piece of equipment/machinery. Examples: rotating equipment, compressed springs, drive belts, conveyors, and motors Temperature The measurement of differences in the thermal energy of objects or the environment, which the human body senses as either heat or cold. Examples: open flame; ignition sources; hot or cold surfaces, liquids or gases; steam; friction; and general environmental and weather conditions Pressure Energy applied by a liquid or gas which has been compressed or is under a vacuum. Examples: pressure piping, compressed cylinders, control lines, vessels, tanks, hoses, and pneumatic and hydraulic equipment Radiation The energy emitted from radioactive elements or sources and naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM). Examples: lighting issues, welding arcs, solar rays, microwaves, lasers, X-Rays, and NORM scale The presence and flow of an electric charge. Examples: power lines, batteries transformers, static charges, lightning, energized equipment. Biological Living organisms that can present a hazard. Examples: animals, bacteria, viruses, insects, blood-borne pathogens, improperly handled food, and contaminated water Sound Sound is produced when a force causes an object or substance to vibrate––the energy is transferred thru the substance in waves. Examples: equipment noise, vibration, high-pressure release. Planning Training 1. Do I understand the task and how to perform it ? 2. Have I identified the hazards associated with the task ? 3. How will I eliminate the hazards associated with the task ? 4. Have I planned all job task ? 1. Have I been trained to do this work ? 2. Have I been trained to use the tools or equipment required ? 3. Have I been trained on the procedures of this work ? Proper tools & Equipment State of mind 1. Will I give full attention to this task ? 2. Will I stop and redo my plan if something unforeseen happens ? 3. Am I meeting or exceeding the safety requirements for this task ? 1. Do I have the PPE, I need ? 2. Do I have the right tools and equipment ? 3. Have I checked if the tools and equipment are in good working condition ? In case of Emergency, Call Land line: 23984444, Mobile: 66471717