Grade 5 SFUSD Math Scope & Sequence
advertisement
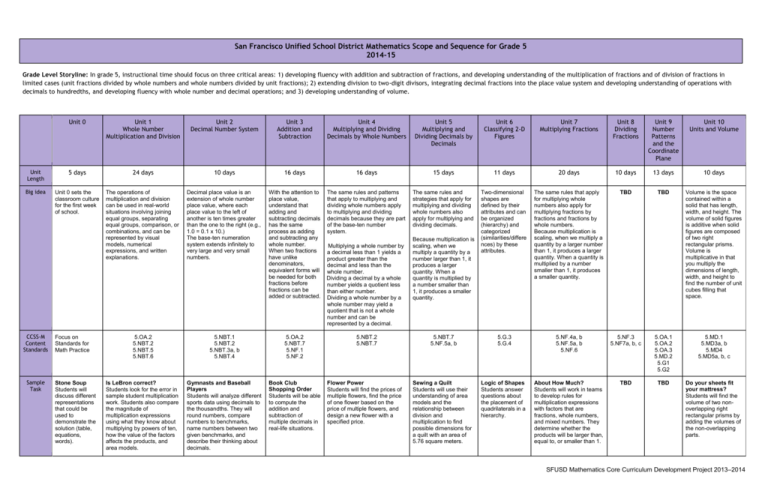
San Francisco Unified School District Mathematics Scope and Sequence for Grade 5 2014-15 Grade Level Storyline: In grade 5, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: 1) developing fluency with addition and subtraction of fractions, and developing understanding of the multiplication of fractions and of division of fractions in limited cases (unit fractions divided by whole numbers and whole numbers divided by unit fractions); 2) extending division to two-digit divisors, integrating decimal fractions into the place value system and developing understanding of operations with decimals to hundredths, and developing fluency with whole number and decimal operations; and 3) developing understanding of volume. Unit 0 Unit 1 Whole Number Multiplication and Division Unit 2 Decimal Number System Unit 3 Addition and Subtraction Unit 4 Multiplying and Dividing Decimals by Whole Numbers Unit 5 Multiplying and Dividing Decimals by Decimals Unit 6 Classifying 2-D Figures Unit 7 Multiplying Fractions Unit 8 Dividing Fractions Unit 9 Number Patterns and the Coordinate Plane Unit 10 Units and Volume Unit Length 5 days 24 days 10 days 16 days 16 days 15 days 11 days 20 days 10 days 13 days 10 days Big idea Unit 0 sets the classroom culture for the first week of school. The operations of multiplication and division can be used in real-world situations involving joining equal groups, separating equal groups, comparison, or combinations, and can be represented by visual models, numerical expressions, and written explanations. Decimal place value is an extension of whole number place value, where each place value to the left of another is ten times greater than the one to the right (e.g., 1.0 = 0.1 x 10.) The base-ten numeration system extends infinitely to very large and very small numbers. With the attention to place value, understand that adding and subtracting decimals has the same process as adding and subtracting any whole number. · When two fractions have unlike denominators, equivalent forms will be needed ·for both fractions before fractions can be added or subtracted. The same rules and patterns that apply to multiplying and dividing whole numbers apply to multiplying and dividing decimals because they are part of the base-ten number system. The same rules and strategies that apply for multiplying and dividing whole numbers also apply for multiplying and dividing decimals. Two-dimensional shapes are defined by their attributes and can be organized (hierarchy) and categorized (similarities/differe nces) by these attributes. The same rules that apply for multiplying whole numbers also apply for multiplying fractions by fractions and fractions by whole numbers. Because multiplication is scaling, when we multiply a quantity by a larger number than 1, it produces a larger quantity. When a quantity is multiplied by a number smaller than 1, it produces a smaller quantity. TBD TBD Volume is the space contained within a solid that has length, width, and height. The volume of solid figures is additive when solid figures are composed of two right rectangular prisms. Volume is multiplicative in that you multiply the dimensions of length, width, and height to find the number of unit cubes filling that space. 5.OA.2 5.NBT.2 5.NBT.5 5.NBT.6 5.NBT.1 5.NBT.2 5.NBT.3a, b 5.NBT.4 5.OA.2 5.NBT.7 5.NF.1 5.NF.2 5.NBT.7 5.NF.5a, b 5.G.3 5.G.4 5.NF.4a, b 5.NF.5a, b 5.NF.6 5.NF.3 5.NF7a, b, c 5.OA.1 5.OA.2 5.OA.3 5.MD.2 5.G1 5.G2 5.MD.1 5.MD3a, b 5.MD4 5.MD5a, b, c Is LeBron correct? Students look for the error in sample student multiplication work. Students also compare the magnitude of multiplication expressions using what they know about multiplying by powers of ten, how the value of the factors affects the products, and area models. Gymnasts and Baseball Players Students will analyze different sports data using decimals to the thousandths. They will round numbers, compare numbers to benchmarks, name numbers between two given benchmarks, and describe their thinking about decimals. Book Club Shopping Order Students will be able to compute the addition and subtraction of multiple decimals in real-life situations. Sewing a Quilt Students will use their understanding of area models and the relationship between division and multiplication to find possible dimensions for a quilt with an area of 5.76 square meters. Logic of Shapes Students answer questions about the placement of quadrilaterals in a hierarchy. About How Much? Students will work in teams to develop rules for multiplication expressions with factors that are fractions, whole numbers, and mixed numbers. They determine whether the products will be larger than, equal to, or smaller than 1. TBD TBD Do your sheets fit your mattress? Students will find the volume of two nonoverlapping right rectangular prisms by adding the volumes of the non-overlapping parts. CCSS-M Content Standards Sample Task Focus on Standards for Math Practice Stone Soup Students will discuss different representations that could be used to demonstrate the solution (table, equations, words). Multiplying a whole number by a decimal less than 1 yields a product greater than the decimal and less than the whole number. Dividing a decimal by a whole number yields a quotient less than either number. Dividing a whole number by a whole number may yield a quotient that is not a whole number and can be represented by a decimal. 5.NBT.2 5.NBT.7 Flower Power Students will find the prices of multiple flowers, find the price of one flower based on the price of multiple flowers, and design a new flower with a specified price. Because multiplication is scaling, when we multiply a quantity by a number larger than 1, it produces a larger quantity. When a quantity is multiplied by a number smaller than 1, it produces a smaller quantity. SFUSD Mathematics Core Curriculum Development Project 2013–2014