Mathematics - Measurement: Mass
advertisement

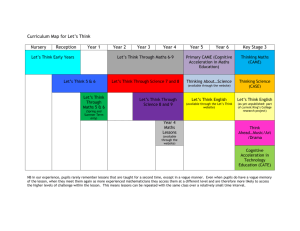
Mathematics – 3D Space Strand: Space & Geometry Stage: 3 Term: 4 Stage 3 Term 4 Week 4 Substrand: 3D Space Week: 4 Language: face, edge, vertex, vertices, triangular prism, square prism, cube, rectangular prism, pentagonal prism, triangular pyramid, square pyramid, rectangular pyramid, cross-section, perspective, surface, net, curved, view points, polyhedron. Outcome SGS3.1 – Recognises 3D objects, including particular prisms and pyramids, on the basis of their properties, and visualises, sketches and constructs them given drawings of different views. Maintenance Times Tables Mentals Gp 3- tables practise /using your tables Key Ideas: 1. Identify 3D objects, including particular prisms and pyramids, on the basis of their properties. 2. Construct 3D models given drawings of different views. Working Mathematically Questioning: Applying Strategies: Communicating: Reasoning: Reflecting: WMS3.1 - Asks questions that could be explored using mathematics in relation to Stage 3 content. WMS3.2 - Selects and applies appropriate problem-solving strategies, including technological applications, in undertaking investigations. WMS3.3 - Describes and represents a Mathematical situation in a variety of ways using mathematical terminology and some conventions. WMS3.4 - Gives a valid reason for supporting one possible solution over another. WMS3.5 - Links mathematical ideas and makes connections with, and generalisations about, existing knowledge and understanding in relation to Stage 3 content. Activities Activities: 1. Review properties of some 3D shapes using mathematical language to describe them eg. I have a square base, 5 vertices and 4 triangular faces. What am I?( smartkiddies interactive black 3D space What am I?) Ask students to draw both the 3D shape and its net. Students write their own descriptions of some pictured solids. (BLM 4 Targeting Maths) 2. Review terms faces, edges, vertices (corners) curved and flat surfaces- fill in table for 3D objects with this information. Top Group: Test Euler’s Theorem: Edges= faces + vertices – 2 to see if it works for all solid shapes. (only works for Assessment 3D shapes with flat surfaces.) p82. 3rd Group: label some common 3D shapes, count their faces, edges, corners and sketch their nets. 3. Display examples of top view, side view and front view of a 3D shape and ask students to identify it. Students then draw given views for selected 3D shapes. Construct 3D models with centicubes given a drawing of its top view. Students then sketch models of from other views. (Sample Units of Work p146) 4. On isometric dot paper demonstrate constructing a 3D shape. Students select some examples to draw and label. Resources Targeting Maths BLM 4 NSW Signpost Maths 6 p73 NSW Signpost Maths Teachers Resource Book p LIII, 194 Advanced Primary Maths 6 p82 Jigsaw Maths Checkbook 4 p43 Maths Plus 6 p46 Centicubes Isometric dot paper 5. With 24 interlocking cubes students build a rectangular prism. Describe the prism in terms of its length, width and height? Ask students to draw a simple perspective drawing on grid paper noting length, width and height. Ask students if they can build other models using the same number of cubes. Repeat drawing each model and recording the length, width and height. Ask students if they noticed anything. (Each cube will have the same volume.) Centicubes Sample Units of Work p146 Evaluation Maths Plus 6 p62 Top Group: Using the volume formula calculate the volume of 3D shapes and rank them in ascending order. 6. Cube Puzzle: A wooden cube 3cmx3cmx3cm is painted red. The painted cube is then broken up into 1cm cubes. Get students to estimate: * how many cubes are there altogether? * how many cubes do not have any paint on them? Will there be some? Why/why not? * how many will have paint on one face? * how many will have paint on two faces? * how many will have paint on four or more faces? Computer: Interactive Smartkiddies – Black – What am I? – identifying objects based on properties. Computers: Students access Targeting Maths 5/6, Smart kiddies and Copacabana: Get Smart activities based on 3D Space. Students work at their own level to enhance differentiation.www.copacabana-p.schools.nsw.edu.au/Get_Smart.htm Computers Internet Mathematics – 2D Space Strand: Space & Geometry Stage: 3 Term: 4 Stage 3 Term 4 Key Ideas: Substrand: 2D Space Week: 5 Language: Week 5 scalene, isosceles, equilateral, regular shape, irregular shape, rotational symmetry, protractor, acute angle, obtuse angle, straight angle, reflex angle, revolution, circle, circumference, diameter, radius, quadrant, tessellating Outcomes SGS3.2a: Manipulates, classifies and draws 2D shapes and describes side and angle properties. Maintenance * Tables with missing units. * Balancing equations. * Reading a protractor correctly. * Correctly using a compass using language of radius/diameter. Assessment Observation of students correctly using a protractor and the compass. SGS3.2b : Measures, constructs and classifies angles. Identify right-angled, isosceles, equilateral and scalene triangles. The sum of angles of a triangle is 180º and the sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360º. Correctly identify parts of a circle. Measure angles using a protractor. Construct angles using a protractor. Working Mathematically Questioning: Applying Strategies: Communicating: Reasoning: Reflecting: WMS3.1 - Asks questions that could be explored using mathematics in relation to Stage 3 content. WMS3.2 - Selects and applies appropriate problem-solving strategies, including technological applications, in undertaking investigations. WMS3.3 - Describes and represents a Mathematical situation in a variety of ways using mathematical terminology and some conventions. WMS3.4 - Gives a valid reason for supporting one possible solution over another. WMS3.5 - Links mathematical ideas and makes connections with, and generalisations about, existing knowledge and understanding in relation to Stage 3 content. Activities 1. Students identify, record and classify angles in the environment using the correct terms. Divide page into 6 rectangles with headings Right, Acute, Obtuse, Straight, Reflex and Revolution. Extend activity by asking students to estimate each angle and then, if possible, check. Correctly label angles and draw shapes that have specific properties. eg. 3 sides and 3 acute angles. Look at a picture and identify angles and answer a series of true or false questions. 2. Review the 4 types of triangles and their properties. Label triangles-ask students why they chose that name for the triangle. On those same triangles ask students to label which are acute, right and obtuse. Watch smartkiddies interactive (Black 417) to review using a protractor to measure angles. On worksheet (MP 6 p54) use a protractor to measure each angle and fill in the missing angles. 3. Construct triangles using the protractor- demonstrate on the whiteboard how to construct an angle at one end of a line and another angle at the other end. Explain where the two lines intersect forms the vertex of a triangle. Ask: What will be the size of that angle? How did you get that answer? Allow students to construct their own triangles and measure and label the types of angles formed. 4. Constructing Circles: review how we set the compass to get an exact radius/diameter. Let students practise on scrap paper until they can accurately construct a compass (put pressure on compass point and not pencil point, move paper if it is hard to turn compass, etc). Allow students to make designs on paper. Construct circles with specific properties eg. radius 3cm. Resources Sample Units of Work p153 NSW Targeting Maths 6 p32 Maths Plus 5 p42 Maths Plus 6 p54 Reference: Maths Plus 6 p80. NSW Signpost Maths 6 p86 Maths Plus 6 p134 Targeting Maths 6 p154-156 Advanced Primary Maths 6 p144 Evaluation 5. Angles at intersecting lines : explain intersecting lines to the student and point out an example in the classroom. eg.doorframes. Students try and identify others. Create intersecting lines and label types of angles created. Extension Resources Top Group Look at parallel lines and an intersecting line. Which angles will be equal. Given a measurement of an angle, calculate the size of other angles. Excel Year 7 6. Tessellations: look at woodlandsjuniorschool or amblesideprimary for interactive activities/computer time activities for examples. Students design their own tessellating patterns in their workbook. Computer sites. Computer: Students have access to computers to develop and explore 2D Space activities. Specifically Targeting Maths, Smart kiddies, Cococabana-GetSmart, Woodlands Junior School , Amblesideprimary Evaluation Computers: Students access Targeting Maths 5/6, Smart kiddies and Copacabana: Get Smart activities based on addition & subtraction, Chance & Data. Students work at their own level to enhance differentiation.www.copacabanap.schools.nsw.edu.au/Get_Smart.htm Computers Internet