How does blood travel through this blood vessel?
advertisement

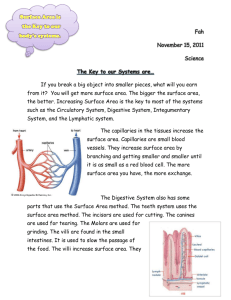
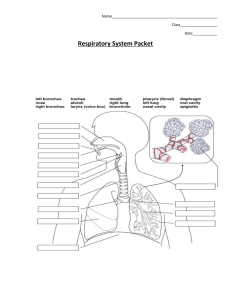
Circulatory and Respiratory Test Study Guide Answer Key 1. What is the function of the veins? How does blood travel through this blood vessel? Veins bring blood back to the heart from the body. The blood goes through these vessels with a valve so it only goes one way. It travels under less pressure than in the arteries. 2. What is the function of the arteries? How does blood travel through this blood vessel? Arteries take blood away from the heart towards cells in the body. The walls are very thick as the blood is under great pressure as it is pumped from the heart, and goes to the capillaries. 3. What is the function of the capillaries? How does blood travel through this blood vessel? The capillaries surround the cells and are very thin so that materials like nutrients and gases can pass through. For example as the capillary goes around the alveoli it exchanges oxygen for carbon dioxide. 4. Explain why your heart and breathing rate speeds up as you exercise. When you exercise your muscles are using more oxygen to function so your breathing rate and heart rate increase to get the oxygen to your cells and the carbon dioxide back to your lungs. 5. What is the main function of the respiratory system? The circulatory system? The respiratory system exchanges carbon dioxide which is waste for oxygen that the body needs. The circulatory system sends nutrients and gases throughout the body and returns wastes to the heart. 6. What are the 4 main components of blood? Explain the function of each one. Red blood cells – transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to the lungs for exchange in the alveoli. White blood cells – helps the body’s immune system to fight infections. Platelets – help to clot the blood so bleeding slows down or stops. Plasma – the liquid portion of blood, carries the cells throughout the body. 7. Describe what is happening in the alveoli during the gas exchange in your lungs. Give details. How are capillaries involved? In the alveoli the oxygen leaves the lungs and enters the blood stream and the carbon dioxide leaves the blood stream and enters the lungs. The capillaries are the blood stream where this gas exchange occurs. 8. If a person has a tracheotomy can they still speak? Explain why or why not. They cannot speak since no air crosses the larynx, the vocal cords will not vibrate so no sound is produced. The tracheotomy bypasses the larynx and the air enters below this organ. 9. Describe how the respiratory and circulatory systems work together. The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body through the lungs and gets carbon dioxide and other wastes out. The circulatory system is the vehicle and street that the gases take to get to cells in the body and back to the lungs. 10. What happens when liquid “goes down the wrong pipe”? The epiglottis, a small flap, has not covered the trachea when the person swallowed so liquid went down the trachea instead of the esophagus. 11. Explain why one model below is better than the other model. Model A: Circulatory System Model Model B: Circulatory System Model Body Lungs Model B is better because it shows that the right side of the heart sends the blood to the lungs so carbon dixoide can be changed for oxygen and then the blood goes back to the left side of the heart to be sent to the body. The body uses the oxygen, releases carbon dioxide then sends the blood back to the heart to exchange again. Model A shows mixing of the blood as there are no chambers in the heart in this model and we know the blood with O2 and the blood with CO2 does not mix. 12. Recall the pull model for the lungs. Which evidence best supports the model. Explain why. The best evidence for the pull model is evidence 1 because a person with damage to their diaphragm from the parasite, has difficulty breathing and pain. This would only happen if the diaphragm, a muscle was used during the process of inhaling and allowing the lungs to expand. Evidence 3 is also supportive. 13. Explain the components of the respiratory system in order? Nose or mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. 14. What are the components of the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood vessels 3. Blood 15. What muscles do we use to get oxygen into our bodies and carbon dioxide out? We use the diaphragm to allow the lungs to expand and we use the heart as a pump. 16 – 18. Interpret the graph below. Answer the questions. 16) Which blood vessels cover the most area of the body? The capillaries cover the most area of the body this is so gas exchange can happen frequently. 17) Which blood vessels have the most blood pressure? The arteries are have the most blood pressure because the blood leaving the heart is squeezed out with a lot of force so the blood can reach the entire body. 18) In which blood vessel does blood slow down in speed? The blood slows down substantially in the capillaries to allow time for the oxygen and carbon dioxide to exchange in the body’s cells. 19) What are the functions of the nose? Why are these functions important to lung health? The nose filters, warms, and moistens the air entering the body. This is important so so particles do not reach the alveoli in the lungs and we do not shock the alveoli with cold, dry air.