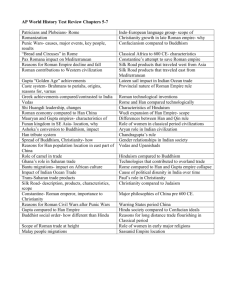
Chapter 5 Quiz Roman and Han Empires 1. The economic wealth of
advertisement

Chapter 5 Quiz Roman and Han Empires 1. The economic wealth of the early Roman State was based on [A] mining. [B] the military. [C] farming. [D] mercantilism. 2. The Roman Republic was not a true democracy; it was ruled by [A] several assemblies of wealthy male citizens. [B] quasi-democratic institutions. [C] the military. [D] an emperor. 3. Which statement is true about Roman women? [A] They were equal to Roman men. [B] They were powerless and virtually slaves in their own homes. [C] They exercised influence over husbands and sons. [D] They had no say in family matters. 4. Two protracted and bloody wars against the Carthaginians were important because [A] Rome won control of the western Mediterranean. [B] it was the first time Rome had ever lost a war. [C] they limited Rome’s southern expansion. [D] Roman slaves were freed. 5. When Rome took control of a foreign land, it [A] immediately enslaved the female population. [B] gave all of the newly conquered peoples the same privileges as the Roman elite. [C] opened libraries and universities. [D] allowed considerable autonomy to cooperative local elites. 6. On what factor do scholars agree was the reason behind why Rome and Han China flourished simultaneously? [A] Actually, no theory has won the support of most scholars. [B] availability of bronze and other precious metals. [C] the volume of trade along the Silk Road [D]climate change 7. The circumstance surrounding Jesus’ ministry and acclimation by his followers as the messiah was [A] the barbarian invasion of Rome. [B] widespread unrest caused by slave rebellions. [C] the Roman occupation of Judaea. [D] the collapse of the Roman Empire. 8. Why was becoming Christian considered an act of disloyalty in the Roman Empire? [A] One of Christianity’s tenets (beliefs) was to overthrow dictators. [B] Rome had a strong monotheistic tradition. [C] Christians could not worship the emperor as a deity. [D] Rome required all citizens to learn about all the world religions. 9. Because of the influence of Confucian ethics, Chinese values emphasized [A] rugged individualism. [B] wealth and business ownership. [C] obedience and proper conduct. [D] independence of children. 10. The Qin emperor was committed to standardization of coinage, weights and measures, the law code, and writing. This shows a commitment to [A] the creation of a unified Chinese civilization. [B] the incorporation of Confucian principles. [C] a profound respect for education. [D] the concept of a harmonious society. 11. In order to supply administrators for the empire, the Han used officials from the gentry class and adopted [A] Daoism. [B] a version of Confucianism to guide government. [C] Buddhism. [D] noble values and customs. 12. The leading export commodity of China during the Han was [A] cotton textiles. [B] tea. [C] rice. [D] silk. 13. The important Han innovations include the development of [A] the saddle, penicillin, and bronze. [B] the canal, the three field system, and concrete. [C] the wheel, the stirrup, and the pully. [D] the horse collar, watermill, and crossbow 14. The early Han emperors reformed the Legalist system by [A] making it harsher. [B] eliminating it. [C] replacing it with the Mandate of Heaven. [D] incorporating Confucianism.